Abstract
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS, endotoxin) is a ubiquitous component of dust and air pollution and is suspected to contribute after inhalation to an activation of eosinophils in bronchial tissues of asthmatic patients, provoking inflammatory and allergic processes. We were therefore interested in the interaction of eosinophil granulocytes with LPS and have examined the activation of and uptake to human peripheral blood eosinophils by LPS. Eosinophils were stimulated by LPS and the endotoxic component lipid A and the release of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and of the eosinophil-specific granule protein eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) was estimated. The results show induction of TNF-α and ECP-release by LPS and lipid A in a dose-dependent manner. Anti-CD14 monoclonal antibody (moAb) (clone MEM-18) and the synthetic lipid A partial structure 406 blocked the release of TNF-α and ECP by LPS-stimulated eosinophils. Studies with radioactively labeled LPS showed dose-dependent uptake of3H-LPS to eosinophils. The 3H-LPS uptake was found to be specific because preincubation with unlabeled LPS, compound 406 and also anti-CD14 antibodies inhibited uptake of3H-LPS to eosinophil granulocytes. By flow cytometry using anti-CD14 moAb and by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technique, CD14 expression was detectable. Furthermore, messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of Toll-like receptors (TLR) 2 and TLR 4 was detected, indicating the presence of these CD14 coreceptors. The results indicate that eosinophils can take up LPS and can be stimulated by LPS in a CD14-dependent manner. Hence, in addition to allergens, eosinophils interact with endotoxin, a process that possibly exacerbates ongoing inflammatory and allergic processes.
Introduction
Human eosinophils, like other granulocytes, are terminally differentiated effector cells that are recruited from the bloodstream into tissue sites during inflammatory, particularly allergic, reactions.1 In asthmatic patients, the airways contain an increased number of eosinophils and the severity of their asthmatic symptoms correlates with the number of eosinophils in the bronchial tissue.1-3 Eosinophils synthesize and release a number of substances, including leukotrienes, and a variety of granule-associated proteins such as eosinophil cationic protein (ECP). If released inappropriately, these substances contribute to tissue damage and to the pathogenesis of allergic diseases.1-4 In addition to their capacity to release lipid mediators and cytotoxic granule proteins, eosinophils may contribute to the inflammatory process through expression and synthesis of cytokines including tumor necrosis factor alpha/beta (TGF-α/β), macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha (MIP-1α), interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-5, IL-8, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α. Furthermore, cytokines increase expression of β2 integrins on eosinophils, which are involved in the adhesion, transendothelial migration of eosinophils, and also in a variety of adherence-dependent functions.5-7
Although stimuli such as calcium ionophore and ionomycin have been found capable of eliciting cytokine expression in eosinophils in vitro,8,9 physiologic stimuli and the mechanisms that are involved in the regulation of eosinophil cytokine responses remain largely unknown. A potent candidate stimulus is lipopolysaccharide (LPS, endotoxin), the major constituent of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria.10 LPS is present in the upper respiratory tract,11 and its levels increase in the infected and inflamed state locally and systemically. Furthermore, LPS is a continuous ingredient of the environment, including air pollution.12,13 In this context, LPS has been detected in a variety of dust extracts, and it has been suggested that chronically inhaled airborne endotoxin could contribute to the development or the enhancement of several chronic obstructive bronchial diseases, including asthma.12,14-19 Inhalation of low doses of endotoxins has been reported to contribute to bronchial constriction in asthmatic patients.16-18 Hence, in addition to allergens, LPS inhalation could further activate myeloic cells, including eosinophils, thus exacerbating the ongoing inflammatory process.
To our knowledge, the only evidence for stimulation of human eosinophils by LPS has been provided by the work of Takanaski et al,20 showing release of GM-CSF, TNF-α, and IL-8 in LPS-stimulated human peripheral blood eosinophils. However, the mechanism underlying interaction of LPS with eosinophils was not investigated. In monocytes/macrophages as well as in neutrophils, it is accepted that LPS binds to a specific membrane receptor, the 55-kd, glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored, membrane-bound CD14 molecule21-26 that is also present as a soluble protein (sCD14) in serum.27 CD14 binds lipid A, the endotoxic principle of LPS, and mediates cell activation10,21,24-26 28 that results in the production of proinflammatory cytokines like IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, and TNF-α.
In this report, we demonstrate that the inflammatory agent LPS and its endotoxic principle lipid A are activators of secretion of both the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and the eosinophil-specific granule protein ECP. Moreover, for the first time we demonstrate that eosinophils do take up LPS in a specific way. Our data show that CD14 indeed appears to be involved in eosinophil activation and LPS uptake, thus providing potential novel mechanisms for activation and regulation of functions of human eosinophils. Moreover, expression of the recently discovered LPS coreceptors Toll-like receptors (TLR) 2 and TLR4, which may be responsible for transmembrane signaling induced by LPS,29 30 were detected in human peripheral blood eosinophils.
Materials and methods
Lipopolysaccharide, lipid A, and lipid A partial structure
LPS was prepared from Salmonella friedenau and purified by the phenol-chloroform-petroleum ether method.31,32 This preparation contains less than 0.2% protein and nucleic acid as determined by chemical analysis. Lipid A was obtained from the Escherichia coli Re-mutant strain F515 by treating phenol-chloroform-petroleum ether-extracted LPS with acetate buffer.32 LPS as well as lipid A was kindly provided by H. Brade (Research Center Borstel, Borstel, Germany). Synthetic compound 406 (precursor Ia), which represents a tetraacyl partial structure of E coli-lipid A lacking dodecanoic and tetradecanoic acids, was synthesized as described previously.33 Compound 406 was a kind gift of S. Kusumoto (Osaka University, Osaka, Japan).
3H-LPS was biosynthetic radiolabeled and isolated from theE coli K-12 strain LCD25.34 This preparation was obtained from LIST Biological Laboratories, Campbell.
Reagents and antibodies
Unless otherwise indicated, all fine chemicals were purchased from Sigma (Deisenhofen, Germany), Serva (Heidelberg, Germany), or Pharmingen (San Diego, CA). The CD14-specific moAb used was MEM-18 (Immunoglobulin IgG1)2 and was a kind gift from V. Horejsi (Institute of Molecular Genetics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague, Czech Republic); purified mouse IgG1 (Sigma) was used as the isotype control. Normal human sera were obtained from healthy volunteers.
Eosinophil isolation
Blood was drawn from healthy nonatopic volunteers and separated by density gradient centrifugation with Ficoll-Isopaque (Pharmacia, Freiburg, Germany). The bottom layer containing neutrophils, eosinophils, and erythrocytes was harvested. Erythrocytes were eliminated by hypotonic lysis. Granulocytes were resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline–bovine serum albumin (PBS-BSA) 0.4%, washed, and incubated for 40 minutes at 4°C with anti-CD16–conjugated micromagnetic beads (Miltenyi Biotec GmbH, Bergisch-Gladbach, Germany). On passing through the magnetic column (MACS, Miltenyi Biotec GmbH), neutrophils bound to the beads were retained within the column, whereas eosinophils were passed through and collected. In each preparation, an eosin stain of the cells, which is specific for eosinophils, was performed on a cytospin smear containing a count of at least 500 cells to ensure pure eosinophil preparation. The purification procedure resulted in a highly purified preparation of eosinophils (more than 98%).
Isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and monocytes
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy donors were obtained from the top layer after density gradient centrifugation on Ficoll-Isopaque (Pharmacia). After repeated washing in HBSS (Biochrom, Berlin, Germany), monocytes were isolated by counterflow elutriation using the JE-6B elutriator system (Beckmann Instruments, Palo Alto, CA) as described previously.35
TNF-α and eosinophil cationic protein release in human eosinophils
Cell cultures were performed in RPMI 1640 medium (Biochrom) supplemented with 10% human serum, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin.
For the stimulation experiments, eosinophils (2 × 106/mL) were treated with LPS or lipid A for 16 hours at 37°C (under 5% CO2) in 200-μL cultures (triplicate wells) in U-form microtiter plates (Greiner, Nürtingen, Germany). For inhibition studies, anti-CD14 moAb (MEM-18) or the antagonistic compound 406 was added at 4°C to the cells for 20 minutes before stimulation with LPS or lipid A. After incubation, supernatants were harvested and analyzed for cytokine activity or ECP content. The concentration of TNF-α in supernatants was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). ECP content in supernatants was measured with the RIA kit (Pharmacia) as described by the manufacturer.
Uptake of 3H-LPS
For determination of 3H-LPS uptake, eosinophils, PBMCs, or monocytes were seeded in 24-well plates (2 × 106 cells/mL). Incubation with 3H-LPS was performed in the presence of 10% human serum for 1 hour at 37°C, cells were washed 3 times with PBS and lysed in PBS containing 2% SDS. Tritium counting of the lysates was performed in a liquid scintillation counter (Packard). In blocking experiments, eosinophils were pretreated with anti-CD14 moAb (MEM-18), the isotype control IgG1 (Sigma), the antagonistic compound 406, or unlabeled LPS for 30 minutes.
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometric analysis were performed using a FACS-Calibur (Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany). For immunofluorescent staining, anti-CD14–FITC moAb (My4-FITC; IgG2b) from Coulter were used. The cells (105/mL) were washed, resupended in 100 μL of azide-PBS and incubated with the FITC-labeled anti-CD14 antibodies for 30 minutes at 4°C. Incubation was stopped by adding 1.5 mL ice-cold azide-PBS. After washing, the cells were resuspended in 400 μL azide-PBS. Unlabeled cells and cells incubated with the isotype (IgG2b-FITC, Sigma) were used as controls.
Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
Eosinophil and monocyte messenger RNA (mRNA) was isolated from 2 × 106 cells using oligo-dT magnetic beads (Dynal, Hamburg, Germany), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Synthesis of complementary DNA (cDNA) was performed with Oligo-dT17 as the primer for reverse transcriptase (Superscript, Gibco-BRL, Eggenstein, Germany) in the presence of 650 U/mL RNase-inhibitor. Thirty cycles of amplification of cDNA was conducted in an automatic DNA thermal cycler (Perkin-Elmer Cetus, Norwalk, CT) using an annealing temperature of 52°C (hCD14) or 58°C (hTLR2 and hTLR4). For the amplification of 2 μL cDNA, 200 μM deoxynucleotide triphosphate (Pharmacia), 1.25 units Taq polymerase (Gibco-BRL), and gene-specific sense and antisense primers (1 μM for hCD14, hTLR2, and hTLR4, or 0.1 μM for β-actin) were used at a final volume of 50 μL. PCR primer used were for hCD14 (ACTTATCGACCATGGAGC and AGGCATGGTGCCGGTTA), β-actin (AGCGGGAAATCGTGCGTG and CAGGGTACATGGTGGTGCC), hTLR2 (CACCGTTTCCATGGCCTG and GGACTTTATCGCAGCTCT), and hTLR4 (CTGGCTGCATAAAGTATGGT and ATAGATGTTGCTTCCTGCCA). All PCR products and the molecular weight marker VI (pBR328 DNA × BglI + pBR328 DNA ×HinfI, Boehringer, Mannheim, Germany) were resolved by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, and DNA bands were visualized by staining the gel with 0.01 μg/mL ethidium bromide.
Statistics
Each experiment was performed at least 3 times with cells from different donors. From these experiments, a typical one is shown demonstrating representative results. The results represent the mean ± SD of triplicate cultures. P values, if demonstrated, are estimated by the Student t test.
Results
LPS and lipid A–induced cytokine production in eosinophils
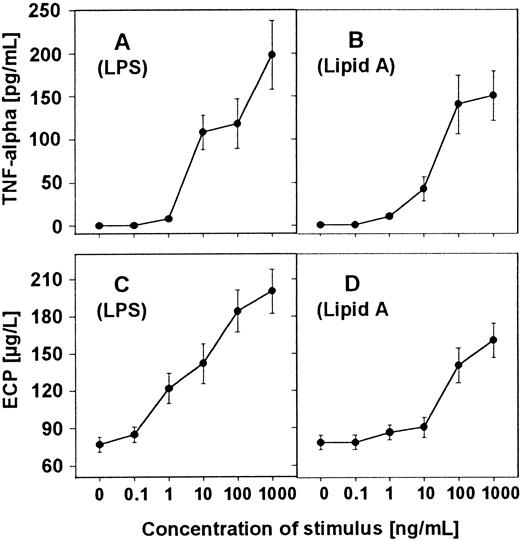
First, we investigated the ability of LPS and lipid A to induce the cytokine TNF-α. Eosinophils (2 × 106/mL) were stimulated with increasing concentrations of LPS or lipid A for 16 hours, supernatants were harvested, and TNF-α content was determined by ELISA. The results show that LPS and lipid A are able to induce TNF-α production in a dose-dependent manner (Figure1A,B). The optimal biologic activity of LPS and lipid A in inducing TNF-α is expressed at a concentration of 10 ng of LPS or 10 000 ng of lipid A per milliliter.
Induction of TNF-α and ECP release in human eosinophils by LPS and lipid A.
Eosinophils (2 × 106/mL) were stimulated with increasing concentrations of LPS (A and C) or lipid A (B and D) as indicated for 16 hours. TNF-α content in the culture supernatant was measured by ELISA (A and B). ECP concentration was determined in radioimmunoassay (C and D).
Induction of TNF-α and ECP release in human eosinophils by LPS and lipid A.
Eosinophils (2 × 106/mL) were stimulated with increasing concentrations of LPS (A and C) or lipid A (B and D) as indicated for 16 hours. TNF-α content in the culture supernatant was measured by ELISA (A and B). ECP concentration was determined in radioimmunoassay (C and D).
LPS- and lipid A–induced eosinophil cationic protein production in human eosinophils
To ensure the activation of human eosinophils by LPS and lipid A, the release of an eosinophil-specific protein was determined. Eosinophils were stimulated for 16 hours, supernatants were harvested, and ECP was measured by RIA. The results demonstrate that eosinophils were able to release ECP after stimulation with LPS and lipid A in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1C,D).
Effect of anti-CD14 moAb and lipid A partial structures on LPS-induced cytokine release by eosinophils
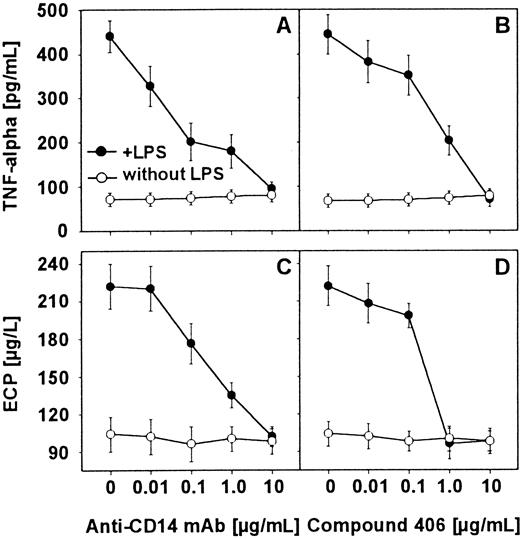
To find out whether the LPS-induced TNF-α release by human eosinophils was CD14 dependent, eosinophils (2 × 106/mL) were preincubated in the presence of various concentrations of anti-CD14 moAb (MEM-18) for 20 minutes at 4°C. In addition, the use of compound 406, a synthetic antagonistic lipid A partial structure, showed that interaction of LPS with eosinophils is similar to that found in monocytes and neutrophils. After 16 hours of stimulation with LPS (100 ng/mL), supernatants were harvested and the TNF-α content was determined by ELISA. Whereas the anti-CD14 moAb or compound 406 alone was not able to induce TNF-α production in eosinophils, both reagents inhibited LPS-induced release of TNF-α (Figure2A,B). Mouse IgG1, which was used as an isotype control, could not reduce the LPS-induced monokine production.
Inhibition of LPS-induced TNF-α and ECP release by anti-CD14 moAb and compound 406.
Eosinophils were preincubated with increasing concentrations of anti-CD14 moAb MEM-18 (A and C) and the antagonistic compound 406 (B and D) for 20 minutes at 4°C. After 16 hours of stimulation with LPS (100 ng/mL), supernatants were harvested. TNF-α content in the culture supernatant was measured by ELISA (A and B). ECP concentration was determined in radioimmunoassay (C and D).
Inhibition of LPS-induced TNF-α and ECP release by anti-CD14 moAb and compound 406.
Eosinophils were preincubated with increasing concentrations of anti-CD14 moAb MEM-18 (A and C) and the antagonistic compound 406 (B and D) for 20 minutes at 4°C. After 16 hours of stimulation with LPS (100 ng/mL), supernatants were harvested. TNF-α content in the culture supernatant was measured by ELISA (A and B). ECP concentration was determined in radioimmunoassay (C and D).
Effect of anti-CD14 moAb and lipid A partial structures on LPS-induced release of ECP in eosinophils
This experiment was performed to prove whether the LPS-induced ECP release was also CD14 dependent. To answer this question, eosinophils (2 × 106/mL) were preincubated in the presence of various concentrations of the anti-CD14 moAb (MEM-18) or the lipid A partial structure compound 406 for 20 minutes at 4°C. After 16 hours of stimulation with LPS (100 ng/mL), supernatants were harvested, and ECP content was determined by RIA. The anti-CD14 moAb or compound 406 alone was not able to induce ECP production in eosinophils. The results show that anti-CD14 moAb and compound 406 both blocked the LPS-induced release of ECP (Figure 2A,B). Mouse IgG1, which was used as an isotype control, could not reduce the LPS-induced ECP production.
Specific 3H-LPS uptake by human eosinophils
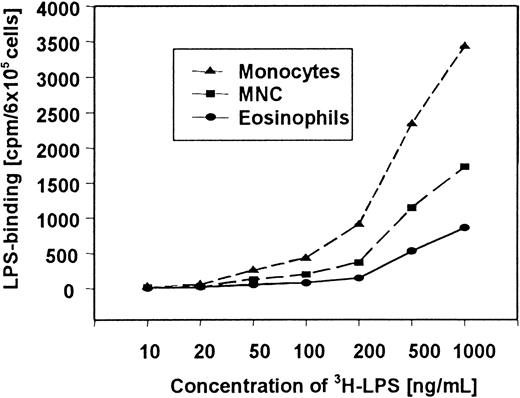
In further studies, we compared the uptake of 3H-LPS by eosinophils, mononuclear cells, and monocytes. It was found that all cells showed dose-dependent uptake of 3H-LPS. However, the3H-LPS uptake of monocytes and mononuclear cells was considerably higher than the 3H-LPS uptake of eosinophils (Figure 3). A statistical significant (P < .05) uptake of 3H-LPS by eosinophils was observed with 100 ng/mL or more.
Dose-dependent uptake of 3H-LPS to human eosinophils, PBMCs, and monocytes.
Cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of3H-LPS as indicated for 60 minutes at 37°C, washed 3 times, and lysed with PBS containing 2% SDS. 3H-LPS counting of the lysates was performed with a liquid scintillation counter.
Dose-dependent uptake of 3H-LPS to human eosinophils, PBMCs, and monocytes.
Cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of3H-LPS as indicated for 60 minutes at 37°C, washed 3 times, and lysed with PBS containing 2% SDS. 3H-LPS counting of the lysates was performed with a liquid scintillation counter.
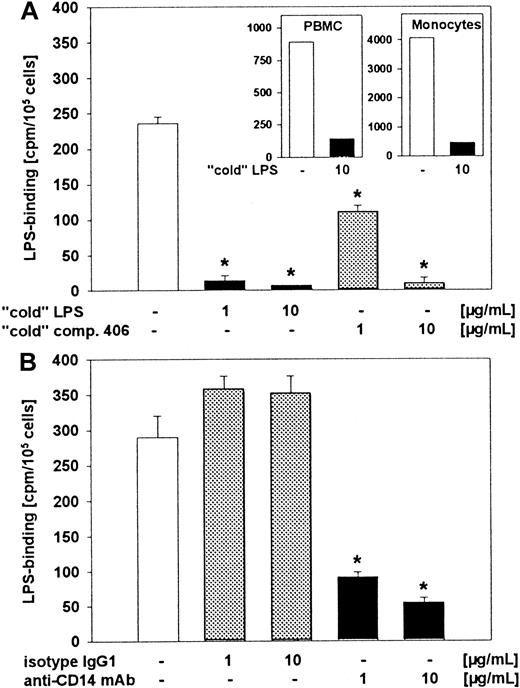
Next, we analyzed the specificity of 3H-LPS uptake by human eosinophils by using unlabeled LPS. For further characterization of the structural requirement of 3H-LPS uptake of eosinophils, we also investigated the inhibiting activity of anti-CD14 moAb and compound 406 in this system. Cells were pretreated with unlabeled LPS, compound 406 (Figure 4A), or with anti-CD14 moAb (MEM-18) (Figure 4B) for 30 minutes, followed by an incubation with 3H-LPS. The specificity of the uptake of3H-LPS could be confirmed by the addition of unlabeled LPS in eosinophils as well as in PBMCs and monocytes (Figure 4A). In addition, compound 406 and anti-CD14 moAb also led to a drastic decrease of 3H-LPS uptake in eosinophils (Figure 4A,B). No effect on 3H-LPS uptake of eosinophils was observed after preincubation with an isotype moAb, IgG1 (Figure 4B).
Inhibition of 3H-LPS uptake in eosinophils by unlabeled LPS, compound 406, and anti-CD14 moAb.
Eosinophils were preincubated with different concentrations of unlabeled (“cold”) LPS, compound 406 (A), or anti-CD14 moAb (B) for 30 minutes at 4°C before 3H-LPS (500 ng/mL) was added. In the figure inserts, inhibition of uptake of 3H-LPS in PBMCs and monocytes by unlabeled LPS is shown. After 1 hour of incubation, cells were washed with PBS 3 times and lysis in PBS containing 2% SDS.3H-LPS counting of the lysates was performed with a liquid scintillation counter. Statistical significance versus : *P < .001.
Inhibition of 3H-LPS uptake in eosinophils by unlabeled LPS, compound 406, and anti-CD14 moAb.
Eosinophils were preincubated with different concentrations of unlabeled (“cold”) LPS, compound 406 (A), or anti-CD14 moAb (B) for 30 minutes at 4°C before 3H-LPS (500 ng/mL) was added. In the figure inserts, inhibition of uptake of 3H-LPS in PBMCs and monocytes by unlabeled LPS is shown. After 1 hour of incubation, cells were washed with PBS 3 times and lysis in PBS containing 2% SDS.3H-LPS counting of the lysates was performed with a liquid scintillation counter. Statistical significance versus : *P < .001.
Expression of CD14 on human eosinophils
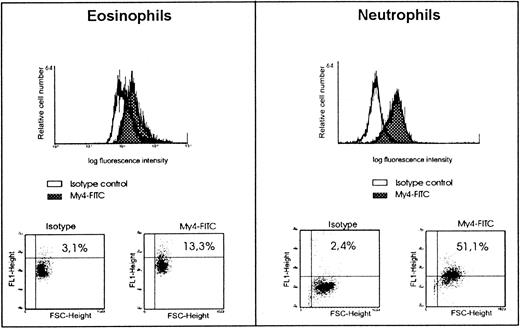
Inhibition of LPS-stimulation and 3H-LPS uptake in human eosinophils by anti-CD14 moAb indicated the presence of CD14 on the surface of these cells. Proof for the expression of this membrane molecule was obtained by anti-CD14 moAb and flow cytometric analysis. The results of these experiments showed an expression of CD14 on eosinophils to a degree less than that found on neutrophils (Figure5). However, it should be mentioned that, in 2 of the 10 experiments, a similar degree of CD14 expression on eosinophils and neutrophils was found (data not given).
Expression of CD14 on eosinophils and neutrophils as determined by FACS analysis.
For immunofluorescent staining of eosinophils and neutrophils, anti-CD14 moAb (My4-FITC, IgG2b) and the isotype control IgG2b-FITC were used. Representative data on CD14 expression on eosinophils compared with neutrophils are shown.
Expression of CD14 on eosinophils and neutrophils as determined by FACS analysis.
For immunofluorescent staining of eosinophils and neutrophils, anti-CD14 moAb (My4-FITC, IgG2b) and the isotype control IgG2b-FITC were used. Representative data on CD14 expression on eosinophils compared with neutrophils are shown.
We also used RT-PCR and detected CD14-mRNA expression on human eosinophils (Figure 6A). Because the eosinophil preparations that we used were highly purified (more than 98%), the possibility that mRNA expression was due to other cells types such as monocytes seems very unlikely. To completely rule out this option, a preparation containing the maximum number of potentially contaminating monocytes (1:20) was investigated for CD14 mRNA expression. Although CD14 mRNA was also detectable by RT-PCR with this low number of monocytes, much smaller amounts of RT-PCR products were detected from these cells, indicating that the contribution of monocytes to the CD14 mRNA expression in eosinophils was indeed negligible (Figure 6A).
CD14, TLR2, and TLR4 mRNA expression of eosinophils and monocytes.
RT-PCR was performed to analyze the mRNA expression of CD14 (A), TLR2, and TLR4 (B) on human eosinophils and monocytes. Eos: Eosinophils (2 × 106 cells); Mo: monocytes (2 × 106cells); Monocytes 1:20: monocytes (0.1 × 106cells); N: negative control without mRNA; M: molecular weight markers.
CD14, TLR2, and TLR4 mRNA expression of eosinophils and monocytes.
RT-PCR was performed to analyze the mRNA expression of CD14 (A), TLR2, and TLR4 (B) on human eosinophils and monocytes. Eos: Eosinophils (2 × 106 cells); Mo: monocytes (2 × 106cells); Monocytes 1:20: monocytes (0.1 × 106cells); N: negative control without mRNA; M: molecular weight markers.
Expression of TLR2 and TLR4 on human eosinophils
TLR2 and TLR4 are transmembrane molecules recently described to be CD14 coreceptors during LPS stimulation. Here we used RT-PCR to investigate the expression of these molecules in human eosinophils. The data show the presence of TLR2 and TLR4 mRNA in human peripheral blood eosinophils (Figure 6B).
Discussion
LPS is known to trigger release of cytokines in monocytes and neutrophils,10,22,24,26 37 and endotoxin-induced leukocyte infiltration has been widely studied. However, the interaction between eosinophils and microbial components such as LPS so far has not been defined in detail. In an attempt to better understand the relationship between LPS and eosinophils, it was of interest therefore to determine whether eosinophils directly interact with or respond to LPS.
Our data show that LPS induces the release of TNF-α of human eosinophils (Figure 1A). This is consistent with the findings of Takanaski et al.20 These authors have stimulated isolated eosinophils in the presence of LPS and found expression of TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-8. Expression of ECP induced by LPS stimulation has not been investigated so far but is evident from the results presented in Figure 1C,D. Cellular content of ECP in normal eosinophils has been measured to be about 10 μg/106 cells.4Therefore, from our results, we calculate that LPS-stimulated eosinophils release up to 10% of the total available pool of ECP.
Our special interest focused on the question whether this activation is CD14 dependent, and whether it can be inhibited by antagonistic lipid A partial structures. Our data show that CD14 indeed appears to be involved in eosinophil activation by LPS (Figure 2A,C). Furthermore, the current study demonstrates a CD14-dependent uptake of LPS to human eosinophils (Figure 3). The involvement of CD14 is evident in FACS analyses (Figure 5) as well as in experiments showing the blocking of activation and 3H-LPS uptake of the cells by anti-CD14 moAb (Figure 4B).
The 3H-LPS uptake was found to be dose dependent and specific, as the addition of a 10-fold excess of unlabeled LPS resulted in a nearly complete inhibition of the 3H-LPS uptake (Figure 4A). From our results, we have calculated uptake of 60 pg3H-LPS/106 cells or 9000 molecules per cell after incubation of the eosinophils with 20 ng 3H-LPS/mL. This rate is at the low range of the amount of LPS-uptake found in neutrophils.37 Concerning the role of CD14 as a site of LPS recognition, our experiments show that this protein is involved. First, anti-CD14 moAb (clone MEM-18), which blocks the biologic activity of LPS, as well as the uptake to human monocytes and neutrophils, also inhibits the specific uptake of LPS to human eosinophils (Figure 2A,C). Second, the same inhibition was also observed by the use of compound 406, a lipid A partial structure (Figure 2B,C). Compound 406 has been said to represent an LPS antagonist that inhibits LPS bioactivity28,38,39,40 and, in higher doses, effectively blocks the uptake of LPS in a competitive way.41 At low doses, a noncompetitive inhibition by compound 406 has been shown in THP-1 cells.42
The presence of CD14 on eosinophils has been demonstrated by flow cytometric analysis (surface CD14) as well as by RT-PCR (CD14 mRNA) (Figures 5 and 6A). It has been previously mentioned, however, that eosinophils isolated from nonatopic healthy donors did not express CD14 molecules on their surfaces.20 The eosinophils used in those experiments were of the same sources and were isolated by a method similar to that used in our experiments. In contrast to our examinations, however, the expression of CD14 was investigated by an immunocytochemical method, which was not described in detail. Thereby, the immunocytochemical method and the type of antibody used in those experiments was not described by the authors.20 The reasons for these conflicting data are therefore not obvious. However, the amount of CD14 expressed by eosinophils is rather low, and therefore we like to speculate that the lower sensitivity of the immunocytochemical method or of the anti-CD14 moAb used may account for the failure of detection of CD14.
Most recently, members of the human TLR2 and TLR4 have been implicated in the responses of cells to LPS. Toll is a type I transmembrane receptor that was first identified in Drosophila melanogaster for its role in larval development.43 At least 6 mammalian TLRs have recently been described.44,45TLRs were proposed as candidates for the CD14-associated transmembrane signal transduction. Thus, transfection of human TLR2 into HEK 293 cells rendered these otherwise LPS nonresponsive cells responsive to LPS.29,30 TLR4 was proposed as a candidate for CD14-associated signal transducer.46 In this context, it is an interesting observation that we could detect TLR2 and TLR4 expression at least as mRNA in human eosinophils (Figure 6B). However, to date, there are no functional data demonstrating how TLR might function in these cells.
In addition, other proteins may act as accessory LPS receptors. Recently, we provided evidence for a functional role of CD55 during LPS signaling.25,47 Also, the members of the β-integrin family are known to bind LPS and serve as mediators of LPS-induced activation of cells.48,49 Expression of CD55 as well as CD11b/CD186 50 on eosinophils suggests the presence of further potential LPS-binding sites on these cells. The interaction of human eosinophils with these further potential LPS-binding sites remains to be elucidated.
In summary, our data provide evidence that the inflammatory agent LPS and its endotoxic principle lipid A are activators of secretion of both the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and the granule protein ECP in human eosinophils. Moreover, we demonstrate that eosinophils do take up LPS in a specific way and that anti-CD14 moAbs and compound 406 are also potent inhibitors of uptake and activation induced by LPS. Our data thus provide potential novel mechanisms for activation and regulation of functions of human eosinophils that may lead to a better understanding of inflammatory response, eg, in chronic obstructive bronchial diseases, including asthma.
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our gratitude to Carola Schneider, Ina Goroncy, Katrin Klopfenstein, and Johanna Grosch for excellent technical support. Vaclav Horejsi (Institute of Molecular Genetics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Prague, Czech Republic) was so kind to provide us with anti-CD14 moAb, clone MEM-18. Compound 406 was a kind gift of Shoichi Kusumoto (Osaka University, Osaka, Japan). LPS and lipid A were kindly provided by H. Brade (Research Center Borstel, Borstel, Germany).
This paper is dedicated to our dear friend and estimated colleague Prof Dr Shoichi Kusumoto, University of Osaka, Japan, on the occasion of his 60th birthday.
Supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 367, project C5), the Fonds der Chemie (EthR), and HSPIII (TUM).
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Artur J. Ulmer, Research Center Borstel, Pakallee 22, 23845 Borstel, Germany; email: ajulmer@fz-borstel.de.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal