In the blast crisis phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), Bcr-Abl+ myeloblasts fail to undergo terminal maturation. The extracellular signal–regulated kinase (Erk) mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase has been shown to mediate terminal differentiation of myeloid cells. Interestingly, Bcr-Abl+ CML cell lines established from blast crisis were found to have low Erk MAP kinase activity. In this study, we analyzed the role of the Gab2 docking protein in regulation of the Erk MAP kinase in Bcr-Abl+K562 human CML cells. Overexpression of Gab2 in K562 cells resulted in transcriptional activation of the c-fos serum response element (SRE) promoter, whereas overexpression of SHP2, Grb2, and CrkL had no effect. Activation of the c-fos SRE transcriptional activity by Gab2 required tyrosine 604, which is a SHP2 docking site on Gab2, and the SHP2 tyrosine phosphatase activity. Elk1, c-Jun, and CHOPtrans-reporting assays indicated that overexpression of Gab2 selectively activated the Erk2-Elk1 signaling pathway. To determine cellular consequences of elevating the Gab2 level in K562 cells, stable cell lines for doxycycline-inducible expression of the wild-type Gab2 (Gab2WT) and an SHP2-binding defective Gab2 (Gab2Tyr604Phe) were established. Analysis of these cell lines indicated that induction of Gab2WT expression, but not Gab2Tyr604Phe expression, led to Erk activation, growth arrest, cell spreading, and enlargement; expression of megakaryocyte/platelet lineage–specific integrins αIIb/β3 (CD41/CD61); and upregulation of RNA for megakaryocyte/platelet proteins. All of these changes are characteristics of megakaryocytic differentiation. Together, these results reveal Gab2 as a limiting signaling component for Erk MAP kinase activation and terminal differentiation of K562 CML cells.
Introduction
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) arises mostly from the reciprocal t(9;22)(q34;q11) chromosomal translocation in pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells.1-3 TheBcr-Abl oncogene generated from the t(9;22) chromosomal translocation encodes a p210Bcr-Abl protein that has deregulated high tyrosine kinase activity and abnormal cytoplasmic localization.1-6 The p210Bcr-Ablactivates the signaling pathways for signal transducer and activator of transcription 5, phosphoinositide 3–kinase (PI3K), and Ras, thereby conferring growth factor–independent proliferation and survival of myeloid progenitor cells.7-11 Eventually, CML progresses from the chronic phase to the blast crisis phase, in which terminal differentiation of myeloid cells ceases.1,2 12 This leads to abnormal accumulation of immature leukemic blast cells in blood and bone marrow.
Although the precise mechanism by which CML progresses from the chronic phase to the blast crisis phase is largely unknown, Bcr-Abl+ CML cell lines established from patients in blast crisis were found to have low or no detectable Erk MAP kinase activity.13 Erk MAP kinase is known to mediate terminal differentiation in several lineages of hematopoietic cells.14-18 In particular, activation of the Erk MAP kinase is required for maturation of erythromegakaryocytic progenitor cells to megakaryocytes.17,18 In fact, activation of the Erk MAP kinase by phorbol ester or by constitutively active MAP kinase-Erk kinase-1 (MEK1) or MEK2 is sufficient to induce megakaryocytic differentiation of the K562 human CML cells.19-21 These observations point to the possibility that the low Erk MAP kinase activity in blast crisis CML cells may be a mechanism responsible for their incomplete differentiation.
It is unclear why Bcr-Abl+ CML cell lines from blast crisis have low Erk MAP kinase activity. Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase is able to activate the Ras-Raf-MEK-Erk signaling pathway in hematopoietic cells in an experimental model system.10 The elevated platelet counts of CML patients during the chronic phase also indicated that megakaryocyte progenitor cells can mature to functional megakaryocytes in this stage of the leukemia,1 12 suggesting that Erk MAP kinase is activated in these Bcr-Abl+ leukemic cells. Therefore, the loss of Erk MAP kinase activity in CML blast crisis cells is likely to be due to one or more secondary changes besides the expression of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase.
Gab1 and Gab2 are pleckstrin homology domain–containing multisite docking proteins.22-27 Gab1 was originally isolated as a Grb2-binding protein from human glioma cells22 and as a c-Met substrate in a yeast 2-hybrid screen.23 Gab2 was originally observed as a 97-kd tyrosine-phosphorylated protein associated with the SHP2 protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) in interleukin 3 (IL-3)–stimulated or Bcr-Abl–transformed BaF3 and 32D cells.28 It was subsequently purified and cloned from Bcr-Abl–transformed BaF3 cells on the basis of its ability to bind SHP2.26 However, the role of Gab2 in Bcr-Abl signaling has not been characterized.
Gab1 and Gab2 are constitutively associated with Grb2 through the interaction between proline-rich sequences and the Grb2 carboxyl-terminal–SH3 domain.29 When Gab1 and Gab2 become tyrosine phosphorylated in cells stimulated with several growth factors and cytokines, they bind SHP2, PI3K, CrkL, and Shc.26-34Gab1-SHP2 interaction is required for Erk MAP kinase activation by epidermal growth factor (EGF) and hepatocyte growth factor,24,33 whereas Gab2-SHP2 interaction is involved in IL-3–stimulated c-fos promoter activity.26 We previously found that Bcr-Abl constitutively phosphorylates Gab2 in K562 human CML cells.35 In the present study, we show evidence that Gab2 is a critical signaling component controlling the Erk MAP kinase activation and terminal differentiation of K562 cells.
Materials and methods
Plasmids
A complementary DNA (cDNA) encoding the full-length Gab2 was isolated from mouse brain cDNA (Clontech Laboratories, Palo Alto, CA) by polymerase chain reaction with the use of Pfu DNA polymerase (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) and oligo primers based on published Gab2 sequences.26 The Gab2 cDNA was cloned into pcDNA3.1 to generate a C-terminal FLAG-tagged expression plasmid (wild-type Gab2 [pGab2WT]). DNA sequence analysis indicated that the Gab2 cDNA we isolated is identical to the Gab2 cDNA isolated from the p210Bcr-Abl–transformed BaF3 cells.26
A Gab2 containing Tyr604Phe mutation (pGab2Tyr604Phe) and a Gab2 containing triple Tyr-to-Phe mutations (Tyr441Phe, Tyr465Phe, Tyr574Phe; pGab2ΔPI3K) were made using the GeneEditor in vitro site-directed mutagenesis system (Promega, Madison, WI). All mutations were confirmed by DNA sequencing. The human CrkL expression plasmid36 was kindly provided by Dr John Groffen (Childrens Hospital of Los Angeles, CA). A mouse Grb2 expression vector was constructed by inserting a 2.36-kilobase EcoRI/Xho I fragment from pKLS12 into pcDNA3.1.37 A full-length human Rap1A cDNA was obtained from ATCC (Manassas, VA), confirmed by DNA sequencing, and cloned into pcDNA3.1. An expression vector (pDsRed1-C1) for red fluorescent protein (RFP) was obtained from Clontech. Expression vectors for Gab1, SHP2, and SHP2CS have been reported.33 38
Transient transfection assays
K562 is a leukemic cell line established from the pleural effusion of a patient in the blast crisis of CML. K562 cells contain p210Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase. For the c-fosserum-response element (SRE) luciferase reporter assay, 2 × 106 K562 cells were transfected with 4.7 μg DNA consisting of 0.5 μg c-fos SRE luciferase reporter (pSRE-luc), 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal internal control vector, and various amounts of testing constructs as indicated in the figure legends. Transfection was performed by means of the DMRIE-C transfection reagent (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY) according to the supplier's instructions. At 48 hours after transfection, cells were pelleted by centrifugation, washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and lysed in 60 μL cell culture lysis reagent (Promega). Luciferase activity was then determined from the soluble cell lysates by means of the Luciferase Assay System (Promega) according to the manufacturer's protocol and a Barthold luminometer. The β-galactosidase activity was determined by a colorimetric assay as described previously.39 The luciferase activity was then normalized to β-galactosidase activity as an internal control for transient transfection efficiency.
The PathDetect (Stratagene) trans-reporting assays40 were performed by means of plasmids from PathDetect in vivo Signal Transduction Pathwaytrans-Reporting Systems according to the manufacturer's instructions. For these experiments, K562 cells (2 × 106) were transfected with 3 μg testing construct (pGab2WT, pGab2Tyr604Phe, or pcDNA3.1), along with 0.1 μg reporting construct (pFA2-Elk1, pFA2-c-Jun, or pFA-CHOP), 1 μg pFR-luc reporter, and 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal. At 48 hours after transfection, cells were processed for determination of the luciferase and β-galactosidase activities as above.
Establishment of stable K562 cell lines
pSTAR,41 a single-vector doxycycline (dox)–inducible expression system, was kindly provided by Dr Wanjin Hong. DNA fragments containing the FLAG-tagged Gab2WT, Gab2Tyr604Phe, and Gab2ΔPI3K were excised from the pcDNA3.1 constructs and subcloned into the pSTAR vector to generate pSTAR-Gab2, pSTAR-Gab2Tyr604Phe, and pSTAR-Gab2ΔPI3K. The pSTAR (empty vector control) and the pSTAR Gab2 constructs were linearized by Pvu I digestion. The linearized DNA (5 μg for each experiment) was used to transfect 1 × 106 K562 cells. At 24 hours after transfection, cells were resuspended in fresh medium (RPMI 1640 with 10% tetracycline-free fetal bovine serum) containing 800 μg/mL G418 (Mediatech, Herndon, VA). Live cells were isolated from ficoll gradient (Histopaque-1077) (Sigma, St Louis, MO) and cloned by limiting dilution at a density of 0.5 cell per well in 96-well plates in medium containing 800 μg/mL G418. G418-resistant clones were expanded and screened for dox-inducible expression of the FLAG-tagged Gab2 by immunoblotting analysis of cell lysates.
Flow cytometry analysis of CD41/CD61 expression
The stable K562 cell lines (1 × 106 cells for each experiment) were induced with dox (4 μg/mL, 7 days) or left untreated. Cells were washed twice with PBS and blocked for 20 minutes in PBS containing 2% bovine serum albumin (BSA). Cells were then incubated with a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)–conjugated antibody that reacts with the CD41/CD61 complex (mouse immunoglobulin (Ig)–G1,κ isotype, CD41a) (PharMingen, Franklin Lakes, NJ) or a FITC-conjugated anti-CD61 antibody (mouse IgG1,κ isotype) in 50 μL wash buffer (PBS plus 1% BSA) for 30 minutes in the dark. After incubation, cells were washed twice with the wash buffer and then resuspended in 0.5 mL wash buffer before analyzing with a flow cytometer. Fluorescent signal from 10 000 cells in each sample was analyzed. Mouse IgG1,κ isotype control antibody was used in each condition.
For analysis of transiently transfected K562 cells, 2.5 × 106 cells for each experiment were transfected with 0.5 μg pDsRed1-C1 and 1.5 μg of each tested pSTAR construct. After transfection, cells were incubated with or without dox for 5 days. Cells were then processed for staining with the FITC-CD41a antibody and 7-amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD, PharMingen) and analyzed by flow cytometry. The 7-AAD-staining–positive (death) cells were excluded, and 1 × 104 RFP+ cells were gated for analysis of CD41+/CD61+cells.
Erk kinase assay
K562 cells were incubated with or without 1 μg/mL dox for 18 hours. Cells (2 × 107) were lysed in buffer A (50 mM Tris [pH7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM ethyleneglycotetraacetic acid, 5 mM Na4PPi, 25 mM NaF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 2 μg/mL aprotinin, 2 μg/mL leupeptin, 100 μg/mL phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 20 mM P-nitrophenyl phosphate, and 1% Triton X-100). Cleared cell lysate supernatants were incubated with an anti-Erk2 MAP kinase antibody and protein-A agarose for 3 hours at 4°C. The immunoprecipitates were washed 4 times with buffer A. Erk MAP kinase activity in the immunoprecipitates was then determined by incubation of the immune complex with 40 μL reaction mixture (20 mM Hepes [pH 7.5], 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 10 mMP-nitrophenyl phosphate, 40 μM adenosine triphosphate [ATP], 0.375mg/mL myelin basic protein, and 10 μCi [0.37 MBq] [γ-32P]ATP) for 10 minutes at 30°C. The reaction was terminated with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)–containing gel-loading buffer and heat denaturation. The samples were resolved on 11% SDS–polyacrylamide gels. Phosphorylation of myelin basic protein was quantified by PhosphoImage (Molecular Dynamics, Sunnyville, CA) analysis of the gel.
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting
Cells were lysed in buffer B (25 mM Tris [pH7.2], 150 mM NaCl, 25 mM NaF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 2 μg/mL aprotinin, 2 μg/mL leupeptin, 100 μg/mL phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 20 mM P-nitrophenyl phosphate, and 1% Triton X-100). Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were performed essentially as described previously33,35 with the antibodies indicated in the figure legends. Anti-Gab2 antibody and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)–conjugated anti-Gab2 antibody were prepared as described.35 The sources of other antibodies were as provided previously.38
Affymetrix microarray analysis
Total RNA was isolated by means of the RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from 20 μg total RNA by means of the Superscript Choice System (Life Technologies) with oligo (dT)24 primer containing T7 RNA polymerase promoter (Genset, La Jolla, CA). In vitro transcription was carried out by means of Bioarray High Yield RNA Transcript Labeling Kit (Enzo Diagnostics, Farmingdale, NY) with biotinylated cytidine triphosphate and uridine triphosphate. The biotin-labeled complementary RNA (cRNA) was purified with an RNeasy column and fragmented at 94°C for 35 minutes in fragmentation buffer (40 mM Tris-acetate [pH 8.1], 100 mM potassium acetate, 30 mM magnesium acetate). Integrity of total RNA, cDNA, cRNA, and fragmented cRNA was assessed by electrophoresis of the samples on 1% agarose gels.
Microarray RNA analysis was performed according to the manufacturer's protocol by means of the HuGeneFL GeneChip (Affymetrix), which represents about 5600 known full-length human sequences. Scanned output files were visually inspected for hybridization artifacts and then analyzed with the Affymetrix Microarray 4.0 software. Arrays were scaled to an average intensity of 150 and analyzed independently. Genes were considered upregulated or downregulated if the expression was changed 2-fold from the control in both cell lines.
Results
Ectopic expression of Gab2 in K562 cells upregulates the c-fos SRE promoter activity
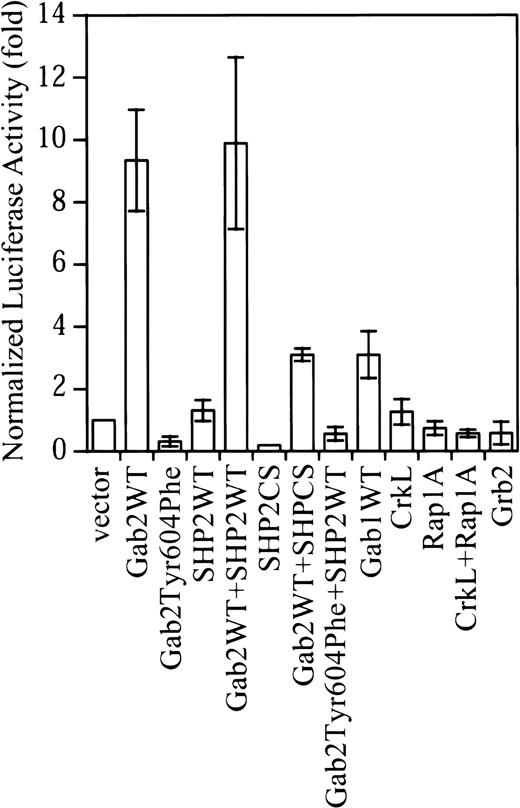
Gab2 is a substrate of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase and is constitutively tyrosine-phosphorylated in K562.35Surprisingly, although K562 cells contain endogenous Gab2, expression of exogenous Gab2 resulted in about a 10-fold increase in the SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells (Figure1). This is in contrast to the effect of Gab2 in IL-3 signaling in BaF3 cells, in which overexpression of Gab2 did not further increase the IL-3–stimulated c-fos SRE transcriptional activity.26 Similarly, expression of exogenous Gab1 in COS-7 and HEK293 cells had only a small effect on Erk activation.33 As shown in Figure 1, expression of exogenous Gab1 in K562 cells also had a much smaller effect (3-fold activation) on the c-fos SRE transcriptional activity compared with that of Gab2 in parallel experiments.
Overexpression of Gab2 activates the c-fos SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells.
K562 cells (2 × 106) cells were transfected with a total of 4.7 μg DNA consisting of 0.5 μg c-fos SRE luciferase reporter (pSRE-luc), 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal internal control vector, and 2 μg of each test construct. Where a single test construct was used, pcDNA3.1 was added to keep the amount of total DNA constant. At 48 hours after transfection, luciferase activity was measured and normalized to β-galactosidase activity. Data shown are the means and SDs of 3 or more independent experiments performed in duplicate.
Overexpression of Gab2 activates the c-fos SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells.
K562 cells (2 × 106) cells were transfected with a total of 4.7 μg DNA consisting of 0.5 μg c-fos SRE luciferase reporter (pSRE-luc), 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal internal control vector, and 2 μg of each test construct. Where a single test construct was used, pcDNA3.1 was added to keep the amount of total DNA constant. At 48 hours after transfection, luciferase activity was measured and normalized to β-galactosidase activity. Data shown are the means and SDs of 3 or more independent experiments performed in duplicate.
We previously found that Tyr-627 of Gab1 was required for Gab1-SHP2 interaction in EGF-stimulated cells.33 38 The corresponding residue in Gab2 is Tyr604. As shown in Figure2, Tyr604 is required for Gab2-SHP2 interaction in K562 cells. Expression of Gab2Tyr604Phe reduced the basal c-fos SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells (Figure 1). Expression of a catalytically inactive SHP2 mutant (SHP2CS) also decreased the basal c-fos SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells. Thus, activation of the c-fos SRE transcriptional activity by Gab2 required both Tyr604 of Gab2 and the SHP2 PTPase activity.
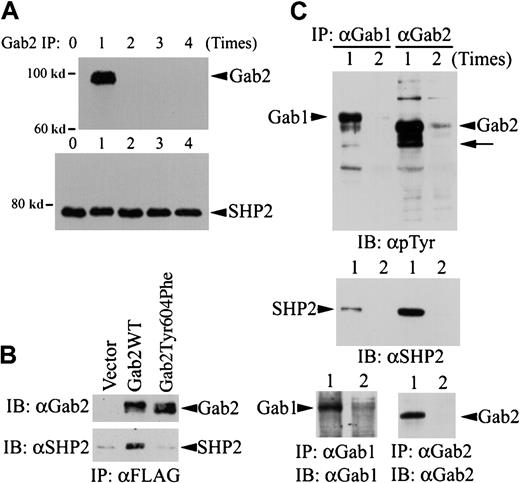
Comparison of Gab1, Gab2, and SHP2 proteins in K562 cells.
(A) Five aliquots of K562 cell lysates (from 8 × 106 cells for each experiment) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with a polyclonal anti-Gab2 antibody and protein A agarose. The immunoprecipitation was repeated up to 4 times as indicated, with fresh anti-Gab2 antibody/protein A agarose used each time to completely remove Gab2 protein from the cell lysates. After the Gab2 immunoprecipitation procedure, the cleared cell lysates were incubated with a polyclonal anti-SHP2 antibody and protein A agarose to immunoprecipitate SHP2 left in the cell lysates. Immunoprecipitates from the last Gab2 immunoprecipitation of each sample were analyzed by immunoblotting with an HRP-conjugated anti-Gab2 antibody (upper panel). The SHP2 immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with a monoclonal anti-SHP2 antibody (lower panel). (B) K562 cells (3 × 106) were transfected with pcDNA3.1 (vector), pGab2 (Gab2WT), or pGab2Tyr604Phe. At 48 hours after transfection, Gab2 and Gab2Tyr604Phe were immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody. One half of each immunoprecipitate was analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-Gab2 antibody (upper panel); the rest of the immunoprecipitates were probed with an anti-SHP2 antibody (lower panel). (C) K562 cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-Gab1 or an anti-Gab2 antibody for 1 (lane 1) or 2 (lane 2) times. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with an antiphosphotyrosine antibody (upper panel), an anti-SHP2 antibody (middle panel), or antibodies against Gab1 (lower left) or Gab2 (lower right). Arrow indicates the position corresponding to SHP2; IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting; α, anti-.
Comparison of Gab1, Gab2, and SHP2 proteins in K562 cells.
(A) Five aliquots of K562 cell lysates (from 8 × 106 cells for each experiment) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with a polyclonal anti-Gab2 antibody and protein A agarose. The immunoprecipitation was repeated up to 4 times as indicated, with fresh anti-Gab2 antibody/protein A agarose used each time to completely remove Gab2 protein from the cell lysates. After the Gab2 immunoprecipitation procedure, the cleared cell lysates were incubated with a polyclonal anti-SHP2 antibody and protein A agarose to immunoprecipitate SHP2 left in the cell lysates. Immunoprecipitates from the last Gab2 immunoprecipitation of each sample were analyzed by immunoblotting with an HRP-conjugated anti-Gab2 antibody (upper panel). The SHP2 immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with a monoclonal anti-SHP2 antibody (lower panel). (B) K562 cells (3 × 106) were transfected with pcDNA3.1 (vector), pGab2 (Gab2WT), or pGab2Tyr604Phe. At 48 hours after transfection, Gab2 and Gab2Tyr604Phe were immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody. One half of each immunoprecipitate was analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-Gab2 antibody (upper panel); the rest of the immunoprecipitates were probed with an anti-SHP2 antibody (lower panel). (C) K562 cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-Gab1 or an anti-Gab2 antibody for 1 (lane 1) or 2 (lane 2) times. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with an antiphosphotyrosine antibody (upper panel), an anti-SHP2 antibody (middle panel), or antibodies against Gab1 (lower left) or Gab2 (lower right). Arrow indicates the position corresponding to SHP2; IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting; α, anti-.
In contrast to Gab2, overexpression of SHP2 had little effect on the c-fos SRE transcriptional activity (Figure 1). Coexpression of SHP2 with Gab2 also did not further increase the c-fosSRE transcriptional activity by Gab2. Grb2 and CrkL are 2 adapter proteins that interact with both Bcr-Abl and the Gab proteins.11,29,34,36 42 Figure 1 shows that overexpression of Grb2, CrkL, and the CrkL effector protein Rap1A did not increase the c-fos SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells. Together, these observations suggest that activation of the c-fos SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells is Gab2 specific.
Gab2 is the limiting component of the Gab2-SHP2 complex
To test whether Gab2 is the limiting component of the Gab2-SHP2 complex, we depleted Gab2 from K562 cell lysates by immunoprecipitation and then examined the SHP2 protein left in these cell lysates. K562 cell lysates were subjected to a repeated immunoprecipitation procedure with an anti-Gab2 antibody for 0 to 4 times. After immunodepletion of Gab2, the cleared cell lysates were used for secondary immunoprecipitation with an anti-SHP2 antibody. The amount of Gab2 or SHP2 protein in the immunoprecipitates was then analyzed by immunoblotting. Figure 2A (upper panel) shows that no Gab2 protein was detectable after the first Gab2 immunoprecipitation, indicating that all Gab2 protein had been removed from the cell lysates. The amounts of SHP2 protein immunoprecipitable from the K562 cell lysates were essentially the same regardless of whether or not Gab2 had been immunodepleted from these cell lysates (Figure 2A, lower panel). These data illustrate that SHP2 protein is present in large excess in the Gab2 protein in K562 cells; this is consistent with the notion that Gab2 is the limiting component of the Gab2-SHP2 complex necessary for Erk MAP kinase activation.
To verify Tyr604 is required for Gab2-SHP2 interaction, we expressed FLAG-tagged Gab2WT and Gab2Tyr604Phe in K562 and analyzed coimmunoprecipitation of SHP2 with these 2 constructs. As shown in Figure 2B, SHP2 was coimmunoprecipitated with Gab2WT, but not with Gab2Tyr604Phe. This result indicates that Tyr604 is essential for Gab2-SHP2 interaction.
Figure 2C shows that Gab1 is also expressed in K562 cells. Because no antibody could cross-react with both Gab1 and Gab2, we could not compare endogenous Gab1 and Gab2 proteins in K562 cells directly. To circumvent this problem, we performed repeated immunoprecipitation to immunoprecipitate all Gab1 and Gab2 proteins in K562 cells and then compared their tyrosine phosphorylation and SHP2 association. Figure 2C (lower panel) shows that essentially all Gab1 and Gab2 proteins were immunoprecipitated from K562 cell lysates after the first immunoprecipitation. Although Gab1 was tyrosine phosphorylated in K562 cells, Gab2 appeared to associate with several tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins that were not detected in the Gab1 immunoprecipitates (Figure2C, upper panel). Furthermore, much less SHP2 was present in Gab1 immunoprecipitates than in Gab2 immunoprecipitates (Figure 2C, middle panel), suggesting that Gab1 might not be fully phosphorylated by Bcr-Abl in the SHP2 binding sites. These differences may account for the smaller effect of Gab1 on SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells (Figure 1).
Expression of Gab2 activates the Erk2-Elk1 signaling pathway in K562 cells
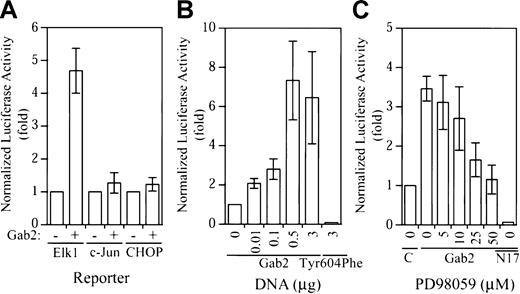
The c-fos SRE binds a ternary complex consisting of serum response factor (SRF) and Elk1/TCF.40Phosphorylation of Elk1 by the Erk MAP kinase in the C-terminal activation domain activates its transcriptional activity.40 To determine whether overexpression of Gab2 in K562 cells activates the Erk-Elk1 signaling pathway, we performed the Gal4-Elk1 trans-reporting assay.26,40,43Parallel experiments were performed with the Gal4-c-Juntrans-reporting and the Gal4-CHOP trans-reporting assays to assess activation of the JNK MAP kinase and the p38 MAP kinase pathways in K562 cells.44 45
As shown in Figure 3A, expression of Gab2 resulted in about 5-fold activation of the Gal4-Elk1trans-reporter, whereas the Gal4-c-Juntrans-reporter and the Gal4-CHOP trans-reporter were not activated by Gab2 overexpression. The effect of Gab2 on Gal4-Elk1 trans-reporter activation was dependent on the amount of cDNA used for transfection (Figure 3B). Similar to what was observed in the c-fos promoter assay, expression of Gab2Tyr604Phe reduced the Gal4-Elk1 trans-reporter activity to below the basal level (Figure 3B). To evaluate whether activation of the Gal4-Elk1 trans-reporter activity is mediated by the Erk MAP kinase, we treated transfected K562 cells with various concentrations of an inhibitor (PD98059) for MEK1, the activator of Erk2 MAP kinase (Erk1 is not expressed in K562 cells). As illustrated in Figure 3C, PD98059 inhibited the Gab2-dependent Gal4-Elk1trans-reporter activity at the lowest concentration tested (5 μM) and completely blocked the Gab2-dependent Gal4-Elk1trans-reporter activity at 50 μM. Furthermore, coexpression of a dominant-negative Ras mutant (RasN17) with Gab2 completely blocked the Gal4-Elk1 trans-reporter activity (Figure 3C). These data suggest that overexpression of Gab2 in K562 cells resulted in selective activation of the Erk2-Elk1 signaling pathway through a Ras-dependent mechanism.
Selective activation of the Elk1
trans-reporter activity by Gab2. (A) K562 cells (2 × 106) were transiently transfected with a total of 4.3 μg DNA consisting of 1 μg pFR-luc, 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal, 0.1 μg pFA2-Elk1 (or pFA2-c-Jun, pFA-CHOP as indicated), and 3 μg pcDNA3.1− or pGab2WT+. (B) Cells (2 × 106) were transiently transfected with a total of 4.3 μg DNA consisting of 1 μg pFR-luc, 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal, 0.1 μg pFA2-Elk1, and increasing concentrations of pGab2WT as indicated (total DNA was equalized to 3 μg with pcDNA3.1), or 3 μg Gab2Tyr604Phe. (C) Cells (2 × 106) were transiently transfected with a total of 4.3 μg DNA consisting of 1 μg pFR-luc, 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal, 0.1 μg pFA2-Elk1, and 3 μg pcDNA3.1, 3 μg pGab2WT (Gab2), or 0.5 μg pGab2WT and 2.5 μg pRasN17 (N17). At 18 hours prior to the luciferase assay, the transfected cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of PD98059 or mock treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (0). At 48 hours after transfection, luciferase activity was determined and normalized to the β-galactosidase activity. Data shown are means and SDs of at least 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate.
Selective activation of the Elk1
trans-reporter activity by Gab2. (A) K562 cells (2 × 106) were transiently transfected with a total of 4.3 μg DNA consisting of 1 μg pFR-luc, 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal, 0.1 μg pFA2-Elk1 (or pFA2-c-Jun, pFA-CHOP as indicated), and 3 μg pcDNA3.1− or pGab2WT+. (B) Cells (2 × 106) were transiently transfected with a total of 4.3 μg DNA consisting of 1 μg pFR-luc, 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal, 0.1 μg pFA2-Elk1, and increasing concentrations of pGab2WT as indicated (total DNA was equalized to 3 μg with pcDNA3.1), or 3 μg Gab2Tyr604Phe. (C) Cells (2 × 106) were transiently transfected with a total of 4.3 μg DNA consisting of 1 μg pFR-luc, 0.2 μg pCMV-βgal, 0.1 μg pFA2-Elk1, and 3 μg pcDNA3.1, 3 μg pGab2WT (Gab2), or 0.5 μg pGab2WT and 2.5 μg pRasN17 (N17). At 18 hours prior to the luciferase assay, the transfected cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of PD98059 or mock treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (0). At 48 hours after transfection, luciferase activity was determined and normalized to the β-galactosidase activity. Data shown are means and SDs of at least 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate.
Establishment of stable K562 cell lines for inducible expression of Gab2 and Gab2Tyr604Phe
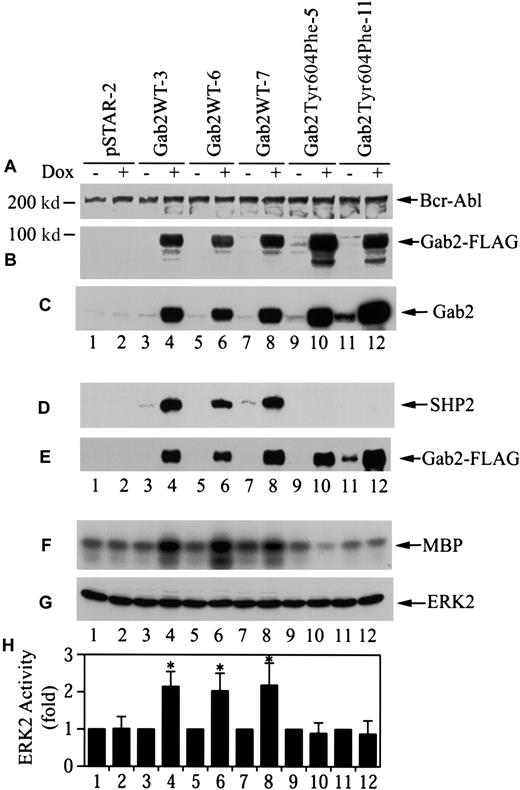
To assess the cellular consequence of Gab2 overexpression, we proceeded to establish stable K562 cell lines for dox-inducible expression of Gab2 constructs using the pSTAR vector.40Linearized pSTAR-Gab2WT, pSTAR-Gab2Tyr604Phe, and the empty vector were transfected into K562 cells. G418-resistant cell lines were obtained by limiting dilution cloning in medium containing G418 without dox. G418-resistant cell lines were then further screened for dox-inducible expression of the Gab2 constructs. As shown in Figure4B, we obtained 3 K562/pSTAR-Gab2 cell lines (Gab2WT-3, Gab2WT-6, and Gab2WT-7) and 2 K562/pSTAR-Gab2Tyr604Phe cell lines (Gab2Tyr604Phe-5 and Gab2Tyr604Phe-11) that showed dox-inducible expression of FLAG-tagged Gab2WT or Gab2Tyr604Phe. As predicted, FLAG-tagged Gab2 was not detected in a randomly selected G418-resistant cell line harboring the empty vector pSTAR (pSTAR-2) (Figure 4B). There was no apparent difference among these cell lines in p210Bcr-Abl protein (Figure 4A). Quantification of the relative amounts of endogenous and exogenous Gab2WT and Gab2Tyr604Phe proteins in these cell lines with a densitometer indicated that the exogenous Gab2WT and Gab2Tyr604Phe were overexpressed about 25-fold (Figure 4C). Figure 4D-E shows that Gab2WT in the 3 cell lines bound to the endogenous SHP2 when these cells were induced with dox. In contrast, although Gab2Tyr604Phe protein was expressed in dox-induced Gab2Tyr604Phe-5 and Gab2Tyr604Phe-11 cells, it did not bind SHP2.
Stable K562 cell lines for dox-inducible expression of wild-type and SHP2-binding defective Gab2.
(A) (B) (C) G418-resistant K562 cell lines (1 × 106cells for each experiment) were incubated with or without dox (1 μg/mL, 18 hours). Cell lysates (25 μg for each experiment) were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to Bcr-Abl (panel A), FLAG-tag (panel B), or Gab2 (panel C). (D) (E) Cells (4 × 106) were incubated with or without dox; Gab2WT or Gab2Tyr604Phe was immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody. One half of each immunoprecipitate was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-SHP2 antibody (panel D). The other half of each immunoprecipitate was probed with anti-Gab2 antibody (panel E). (F) (G) (H) Cells (5 × 106) were induced with dox as above. Endogenous Erk2 was immunoprecipitated. One half of each immunoprecipitate was used to determine Erk2 activity by phosphorylation of myelin basic protein (MBP). The rest of each immunoprecipitate was analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-Erk antibody. Panel F shows a representative autoradiograph; panel G, a representative immunoblot; and panel H, the means and SEs of Erk2 activity from 5 independent experiments. *The difference in mean Erk2 activity between dox-induced and dox-uninduced cells is statistically significant (P < .05, Wilcoxon rank sum test).
Stable K562 cell lines for dox-inducible expression of wild-type and SHP2-binding defective Gab2.
(A) (B) (C) G418-resistant K562 cell lines (1 × 106cells for each experiment) were incubated with or without dox (1 μg/mL, 18 hours). Cell lysates (25 μg for each experiment) were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to Bcr-Abl (panel A), FLAG-tag (panel B), or Gab2 (panel C). (D) (E) Cells (4 × 106) were incubated with or without dox; Gab2WT or Gab2Tyr604Phe was immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody. One half of each immunoprecipitate was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-SHP2 antibody (panel D). The other half of each immunoprecipitate was probed with anti-Gab2 antibody (panel E). (F) (G) (H) Cells (5 × 106) were induced with dox as above. Endogenous Erk2 was immunoprecipitated. One half of each immunoprecipitate was used to determine Erk2 activity by phosphorylation of myelin basic protein (MBP). The rest of each immunoprecipitate was analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-Erk antibody. Panel F shows a representative autoradiograph; panel G, a representative immunoblot; and panel H, the means and SEs of Erk2 activity from 5 independent experiments. *The difference in mean Erk2 activity between dox-induced and dox-uninduced cells is statistically significant (P < .05, Wilcoxon rank sum test).
To determine if induction of Gab2 expression in these lines affected Erk2 activity, these stable K562 cell lines were grown in the presence or absence of dox, and the endogenous Erk2 kinase activity was determined after immunoprecipition with an anti-Erk2 antibody. As shown in Figure 4F-H, dox treatment increased the constitutive Erk2 activity approximately 2-fold in the 3 K562 cell lines containing Gab2WT, but had no effect on Erk2 activity in the pSTAR-2 cells and the 2 cell lines containing Gab2Tyr604Phe.
Overexpression of Gab2 in K562 leads to growth arrest and megakaryocytic differentiation
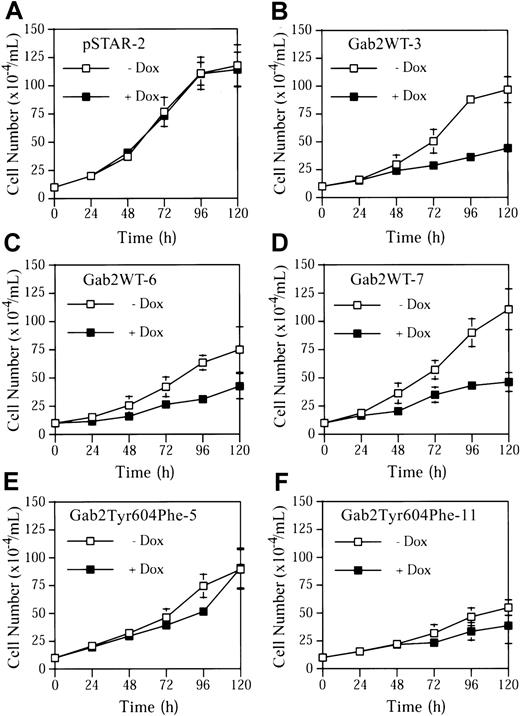
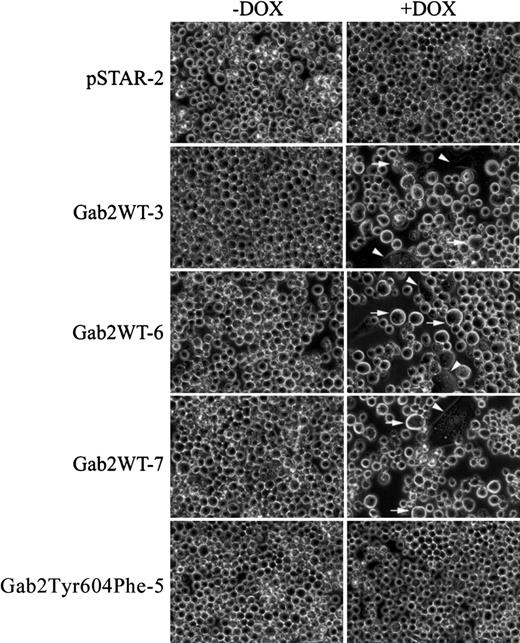
Incubation of pSTAR-2 cells with dox had no apparent effect on cell proliferation (Figure 5A). In contrast, dox consistently induced growth arrest in the 3 K562 cell lines expressing Gab2WT (Figure 5B-D). Dox had a much smaller effect on proliferation of Gab2Tyr604Phe-5 and Gab2Tyr604Phe-11 cells expressing the SHP2-binding defective Gab2Tyr604Phe (Figure 5E-F). Gab2WT-expressing K562 cells appeared to become larger when they were grown in the presence of dox, and a fraction of the cells flattened and adhered to the plates (Figure 6). These morphological changes are similar to those of K562 cells treated with phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate or transfected with constitutively active MEK1, which induces megakaryocyte lineage–specific differentiation of K562 cells by an Erk-dependent mechanism.19 46 The observed morphological changes were specific for K562 cells expressing the wild-type Gab2, because neither pSTAR-2 cells nor Gab2Tyr604Phe-5 cells (Figure 6) and Gab2Tyr604Phe-11 (not shown) underwent morphological changes when incubated with dox.
Growth arrest of K562 cell lines induced by expression of wild-type Gab2, but not by SHP2-binding defective Gab2.
K562-derived cell lines pSTAR-2, Gab2WT-3, Gab2WT-6, Gab2WT-7, Gab2Tyr604Phe-5, or Gab2Tyr604Phe-11 were plated at a cell density of 1 × 105/mL and treated with or without dox (1 μg/mL). Total cell numbers of each sample were determined every 24 hours for 120 hours. The data represent means and SDs of 2 duplicate experiments.
Growth arrest of K562 cell lines induced by expression of wild-type Gab2, but not by SHP2-binding defective Gab2.
K562-derived cell lines pSTAR-2, Gab2WT-3, Gab2WT-6, Gab2WT-7, Gab2Tyr604Phe-5, or Gab2Tyr604Phe-11 were plated at a cell density of 1 × 105/mL and treated with or without dox (1 μg/mL). Total cell numbers of each sample were determined every 24 hours for 120 hours. The data represent means and SDs of 2 duplicate experiments.
Morphological changes in K562 cell lines induced to overexpress Gab2.
K562-derived cell lines pSTAR-2, Gab2WT-3, Gab2WT-6, Gab2WT-7, or Gab2Tyr604Phe-5 were plated (5 × 104 cells/mL) in 6-well plates and treated with or without dox for 6 days. Cell were digitally photographed at × 400 magnification with a Nikon TE300 microscope equipped with a CCD camera (Diagnostic Instruments, Sterling Heights, MI). Arrowhead indicates cells that are flattened and adherent to the plates; arrow, enlarged cells.
Morphological changes in K562 cell lines induced to overexpress Gab2.
K562-derived cell lines pSTAR-2, Gab2WT-3, Gab2WT-6, Gab2WT-7, or Gab2Tyr604Phe-5 were plated (5 × 104 cells/mL) in 6-well plates and treated with or without dox for 6 days. Cell were digitally photographed at × 400 magnification with a Nikon TE300 microscope equipped with a CCD camera (Diagnostic Instruments, Sterling Heights, MI). Arrowhead indicates cells that are flattened and adherent to the plates; arrow, enlarged cells.
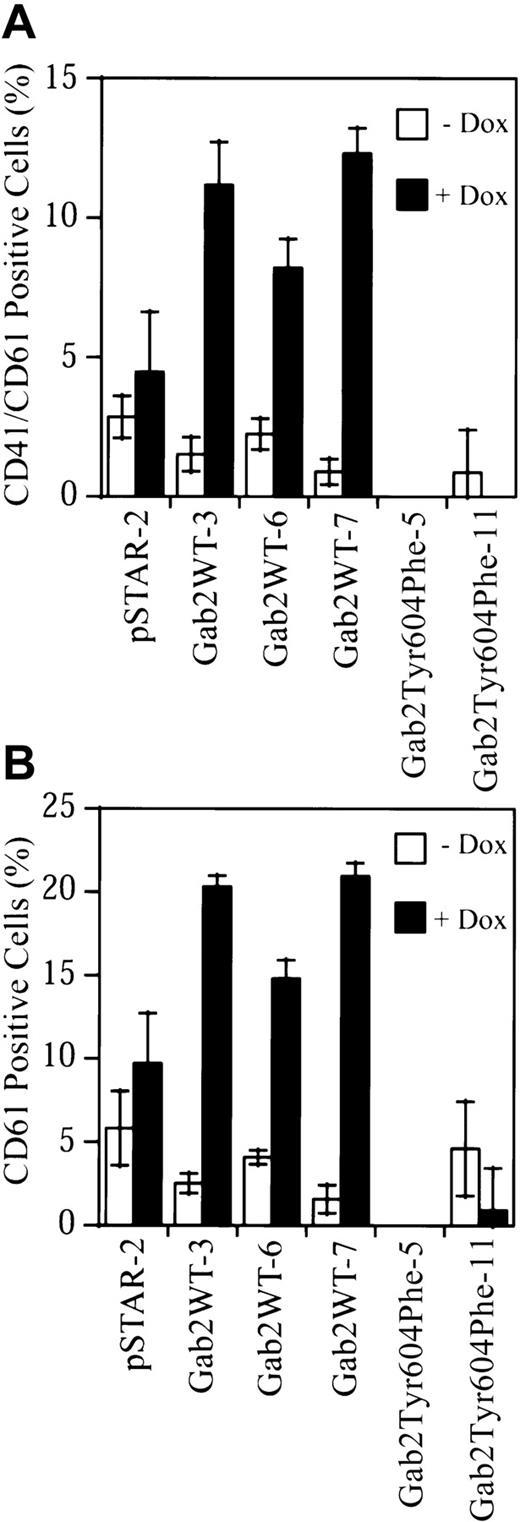
To determine if overexpression of Gab2 in K562 cells induced megakaryocytic differentiation of these cells, we analyzed cell surface expression of the megakaryocyte/platelet lineage–specific integrins αIIb/β3 (CD41/CD61).17-21 The stable K562 cell lines were treated with or without dox for 7 days. Cells were then incubated with FITC-conjugated monoclonal antibodies against the CD41/CD61 complex, CD61, or an isotype-control antibody, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Small nonspecific increases in CD41/CD61 complex (1.78-fold) and CD61 (1.83-fold) staining were observed in dox-treated pSTAR-2 control cells (Figure 7). CD41/CD61 complex staining was increased 7.4-, 3.7-, and 13.7-fold in dox-treated Gab2WT-3, Gab2WT-6, and Gab2WT-7 cells, respectively (Figure 7A). Consistently, an anti-CD61 antibody detected similar increases (8.1-, 3.6-, 13.3-fold, respectively) in CD61 staining in these 3 Gab2WT cell lines when they were induced with dox (Figure 7B). In contrast, dox reduced the cell surface CD41/CD61 complex and CD61 staining on Gab2Tyr604Phe-11 cells, while the CD41/CD61 complex and CD61 staining on Gab2Tyr604Phe-5 cells were slightly below those of the isotype control (Figure 7).
Upregulation of megakaryocyte/platelet–specific cell markers by Gab2.
K562-derived cell lines were treated with or without dox for 7 days. Cells (1 × 106) were processed for flow cytometry analyses of surface expression of CD41/CD61 complex (panel A) or CD61 (panel B). The fluorescent signal from the isotype control antibody has been subtracted from that of each sample. The results represent the means and SDs of 2 independent experiments performed in duplicate.
Upregulation of megakaryocyte/platelet–specific cell markers by Gab2.
K562-derived cell lines were treated with or without dox for 7 days. Cells (1 × 106) were processed for flow cytometry analyses of surface expression of CD41/CD61 complex (panel A) or CD61 (panel B). The fluorescent signal from the isotype control antibody has been subtracted from that of each sample. The results represent the means and SDs of 2 independent experiments performed in duplicate.
To further assess the effect of Gab2 overexpression on K562 cell differentiation, we performed Affymetrix microarray analysis of the RNA expression profile. To minimize clonal variations and experimental errors, the same analysis was performed in 2 K562 cell lines, Gab2WT-6 and Gab2WT-7, that contain dox-inducible Gab2WT, and in pSTAR-2 cells that contain vector control. Gab2WT-6, Gab2WT-7, and pSTAR-2 cells were grown in medium with or without dox for 4 days. RNA expression profiles of each cell line were analyzed with the HuGeneFL array. Table1 lists 38 messenger RNA (mRNA) species that were upregulated at least 2-fold in Gab2WT-6 and Gab2WT-7 cells by dox induction. Two of these mRNA (CD44 and glycerol kinase) were also upregulated at least 2-fold in the control pSTAR-2 cells and should be considered nonspecific to Gab2 overexpression. Consistent with increased surface expression of the megakaryocyte/platelet–specific surface marker CD41/CD61, the CD41 and CD61 mRNAs were both upregulated (Table 1).
Genes upregulated by doxycycline in K562-derived Gab2WT-6 and Gab2WT-7 cells
| Accession no. . | Name . | pSTAR-2 . | Gab2WT-6 . | Gab2WT-7 . | Average . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U25997 | Stanniocalcin precursor | ∼ 34.9 | ∼ 28.8 | ∼ 31.85 | |
| L27624 | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 | 14.9 | 9.9 | 12.4 | |
| U70981 | IL-13 receptor | ∼ 10.4 | ∼ 13.8 | ∼ 12.1 | |
| M22612 | Pancreatic trypsin 1 | 2.7 | 16.1 | 9.4 | |
| X52022 | Type VI collagen alpha 3 chain | 4.2 | 13.5 | 8.85 | |
| M35999 | Platelet glycoprotein IIIa (CD61) | ∼ 8.7 | ∼ 8.5 | ∼ 8.6 | |
| X14787 | Thrombospondin | ∼ − 2.4 | 7.5 | ∼ 7.8 | ∼ 7.65 |
| D29992 | Placental protein 5 | 8.3 | 3.9 | 6.1 | |
| U07807 | Metallothionein IV | 6.1 | 3.8 | 4.95 | |
| M26901 | Renin | 4.3 | 5.4 | 4.85 | |
| L05424 | CD44 | ∼ 2.2 | 5.3 | 4 | 4.65* |
| U15932 | Dual-specificity protein phosphatase-5 | 5.7 | 3.4 | 4.55 | |
| X71345 | Trypsinogen IV, b-form | 2.7 | 6.3 | 4.5 | |
| J03040 | SPARC/osteonectin | 6.2 | 2.1 | 4.15 | |
| U81607 | Gravin (AKAP250) | 3.6 | 4.4 | 4 | |
| U03397 | Receptor protein 4-1BB (CD137) | 3.3 | 4.7 | 4 | |
| HG2981-HT3125† | Epican, alt splice 1 | 3.4 | 4.3 | 3.85 | |
| U16799 | Na, K ATPase beta-1 subunit | 3.5 | 4.1 | 3.8 | |
| AF014958 | Chemokine receptor X | 3.9 | 3.6 | 3.75 | |
| HG4069-HT4339† | Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 3.7 | |
| HG721-HT4827† | Placental protein 14, alt splice 2 | 4.1 | 3.1 | 3.6 | |
| HG2981-HT3127† | Epican, alt splice 11 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 3.45 | |
| M55998 | α1 collagen type I gene | 4.2 | 2.3 | 3.25 | |
| X04412 | Gelsolin | 3.3 | 3.1 | 3.2 | |
| U31384 | G protein γ-11 subunit | 3.6 | 2.5 | 3.05 | |
| L19058 | Glutamate receptor (GLUR5) | 3.1 | 2.8 | 2.95 | |
| D29642 | KIAA0053 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 2.75 | |
| M34344 | Platelet glycoprotein IIb (CD41) | 2.2 | 3.2 | 2.7 | |
| U34879 | 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | − 2.4 | 2.9 | 2.4 | 2.65 |
| Z30426 | CD69 | 3.3 | 2 | 2.65 | |
| S45630 | Alpha B-crystallin | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.6 | |
| HG721-HT4828† | Placental protein 14, alt splice 3 | 3 | 2.2 | 2.6 | |
| L13943 | Glycerol kinase | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 2.55* |
| AF001294 | IPL (Tssc3) | 2 | 3.1 | 2.55 | |
| Z22534 | ALK-2 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.3 | |
| J03764 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.3 | |
| AF010193 | SMAD7 | ∼ − 54.5 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| HG2788-HT2896† | Calcyclin | 2 | 2.1 | 2.05 |
| Accession no. . | Name . | pSTAR-2 . | Gab2WT-6 . | Gab2WT-7 . | Average . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U25997 | Stanniocalcin precursor | ∼ 34.9 | ∼ 28.8 | ∼ 31.85 | |
| L27624 | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 | 14.9 | 9.9 | 12.4 | |
| U70981 | IL-13 receptor | ∼ 10.4 | ∼ 13.8 | ∼ 12.1 | |
| M22612 | Pancreatic trypsin 1 | 2.7 | 16.1 | 9.4 | |
| X52022 | Type VI collagen alpha 3 chain | 4.2 | 13.5 | 8.85 | |
| M35999 | Platelet glycoprotein IIIa (CD61) | ∼ 8.7 | ∼ 8.5 | ∼ 8.6 | |
| X14787 | Thrombospondin | ∼ − 2.4 | 7.5 | ∼ 7.8 | ∼ 7.65 |
| D29992 | Placental protein 5 | 8.3 | 3.9 | 6.1 | |
| U07807 | Metallothionein IV | 6.1 | 3.8 | 4.95 | |
| M26901 | Renin | 4.3 | 5.4 | 4.85 | |
| L05424 | CD44 | ∼ 2.2 | 5.3 | 4 | 4.65* |
| U15932 | Dual-specificity protein phosphatase-5 | 5.7 | 3.4 | 4.55 | |
| X71345 | Trypsinogen IV, b-form | 2.7 | 6.3 | 4.5 | |
| J03040 | SPARC/osteonectin | 6.2 | 2.1 | 4.15 | |
| U81607 | Gravin (AKAP250) | 3.6 | 4.4 | 4 | |
| U03397 | Receptor protein 4-1BB (CD137) | 3.3 | 4.7 | 4 | |
| HG2981-HT3125† | Epican, alt splice 1 | 3.4 | 4.3 | 3.85 | |
| U16799 | Na, K ATPase beta-1 subunit | 3.5 | 4.1 | 3.8 | |
| AF014958 | Chemokine receptor X | 3.9 | 3.6 | 3.75 | |
| HG4069-HT4339† | Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 3.7 | |
| HG721-HT4827† | Placental protein 14, alt splice 2 | 4.1 | 3.1 | 3.6 | |
| HG2981-HT3127† | Epican, alt splice 11 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 3.45 | |
| M55998 | α1 collagen type I gene | 4.2 | 2.3 | 3.25 | |
| X04412 | Gelsolin | 3.3 | 3.1 | 3.2 | |
| U31384 | G protein γ-11 subunit | 3.6 | 2.5 | 3.05 | |
| L19058 | Glutamate receptor (GLUR5) | 3.1 | 2.8 | 2.95 | |
| D29642 | KIAA0053 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 2.75 | |
| M34344 | Platelet glycoprotein IIb (CD41) | 2.2 | 3.2 | 2.7 | |
| U34879 | 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | − 2.4 | 2.9 | 2.4 | 2.65 |
| Z30426 | CD69 | 3.3 | 2 | 2.65 | |
| S45630 | Alpha B-crystallin | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.6 | |
| HG721-HT4828† | Placental protein 14, alt splice 3 | 3 | 2.2 | 2.6 | |
| L13943 | Glycerol kinase | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 2.55* |
| AF001294 | IPL (Tssc3) | 2 | 3.1 | 2.55 | |
| Z22534 | ALK-2 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.3 | |
| J03764 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.3 | |
| AF010193 | SMAD7 | ∼ − 54.5 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| HG2788-HT2896† | Calcyclin | 2 | 2.1 | 2.05 |
Data show the -fold increase. Listed here are genes that showed at least 2-fold changes in average signal intensity in both K562/Gab2WT-6 and K562/Gab2WT-7 cells, and changes of the corresponding genes in K562/pSTAR-2 cells. No gene was found to be downregulated greater than 2-fold in both K562/Gab2WT-6 and K562/Gab2WT-7 cells by dox induction. Inspection of raw intensity data was used to confirm signal intensity changes.
WT indicates wildtype; ∼, approximation; IL, interleukin.
Greater than 2-fold increase was detected in the control K562/pSTAR-2 cells.
Human Genome sequence number.
Although the relevance of some of the mRNAs that were upregulated by dox in Gab2WT-6 and Gab2WT-7 to K562 cell differentiation is unclear, among mRNAs that were upregulated are those that encode known platelet proteins: thrombospondin, plasminogen activator inhibitor–1, gelsolin, CD69, SPARC/osteonectin, and placental protein 14 (Table 1). Thrombospondin and plasminogen activator inhibitor–1 are known to be synthesized in megakaryocytes and stored in the α-granules of platelets.47-49 Gelsolin is an abundant actin filament–severing protein in platelets, which mediates platelet shape change.50,51 CD69 mediates platelet activation and aggregation.52 SPARC/osteonectin is an adhesion molecule found primarily in platelets and the matrix of bone.53Placental protein 14 is an immunosuppressive protein found in endometrial epithelium and platelets.54
In addition, the levels of mRNA for IL-13 receptor, Smad7, and the dual-specificity protein phosphatase 5 were also increased by Gab2 overexpression (Table 1). IL-13 has been found to promote megakaryocyte colony formation.55 Smad7 was reported to inhibit erythroid leukemia cell differentiation.56Dual-specificity protein phosphatase 5 (also called hVH-3) is an inducible Erk phosphatase.57 58 Therefore, the data from the microarray analysis appear to be consistent with the notion that Gab2 overexpression induced megakaryocytic differentiation of K562 cells.
Removal of PI3K-binding sites in Gab2 does not affect the ability of Gab2 overexpression to induce CD41/CD61 expression in K562 cells
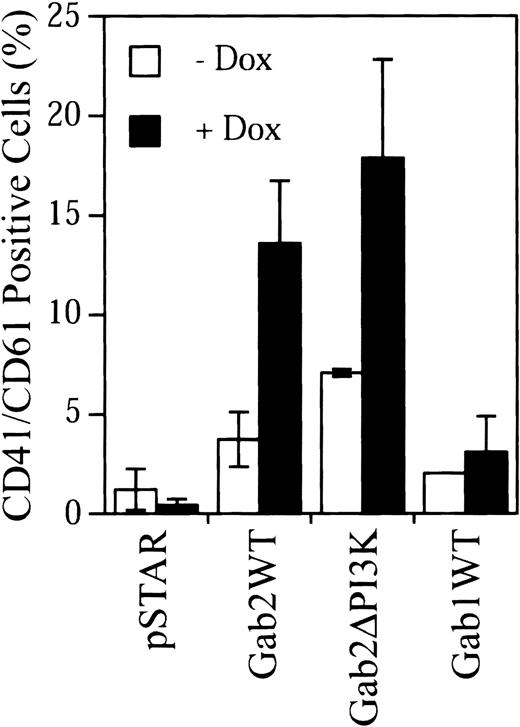
Gab2 contains 3 potential PI3K-binding sites (Tyr441, Tyr465, and Tyr574).26 27 We constructed a Gab2 mutant (Gab2ΔPI3K) in which these 3 Tyr residues were mutated to Phe. Transient expression experiments indicated that removal of these PI3K-binding sites did not affect the ability of Gab2 to activate the c-fos SRE promoter activity and Erk MAP kinase in K562 cells (data not shown). However, attempts to establish stable K562 cell lines for dox-inducible expression of Gab2ΔPI3K were not successful. As an alternative way to compare the effects of Gab2WT and Gab2ΔPI3K on K562 cell differentiation, K562 cells were cotransfected with pSTAR constructs and a plasmid for RFP, which served as a marker of transfected cells. Transfected cells were cultured with or without dox and then stained with an FITC-conjugated anti-CD41/CD61 antibody and 7-AAD. CD41/CD61+ cells were analyzed in 7-AAD−(live), RFP+ (transfected) cell population by flow cytometry. As shown in Figure 8, using this approach, we were able to detect induction of CD41/CD61 expression in K562 cells by Gab2WT, but not by the pSTAR vector control. These results were consistent with the data obtained using the stable K562 cell lines and validated the methodology. Expression of Gab2ΔPI3K caused a similar induction of CD41/CD61 expression in K562 cells as expression of Gab2WT. Therefore, elimination of PI3K-binding sites in Gab2 did not appear to affect its activity to induce CD41/CD61 expression in K562 cells. In addition, parallel experiments showed that overexpression of Gab1 did not induce CD41/CD61 expression in K562 cells (Figure 8).
Induction CD41/CD61 expression by Gab2, Gab2ΔPI3K, and Gab1.
K562 cells (2.5 × 106) were transfected with 1:4 DNA ratio of pDsRed1-C1 and the indicated pSTAR constructs. Transfected cells were incubated with or without dox (4 μg/mL) for 5 days. After staining with an FITC-conjugated anti-CD41/CD61 complex antibody and 7-AAD, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The 7-AAD+cells were excluded, and 1 × 104 RFP+ cells were analyzed for CD41/CD61 expression. The fluorescent signal from the isotype control antibody has been subtracted from that of each sample. The data are from 3 separate experiments.
Induction CD41/CD61 expression by Gab2, Gab2ΔPI3K, and Gab1.
K562 cells (2.5 × 106) were transfected with 1:4 DNA ratio of pDsRed1-C1 and the indicated pSTAR constructs. Transfected cells were incubated with or without dox (4 μg/mL) for 5 days. After staining with an FITC-conjugated anti-CD41/CD61 complex antibody and 7-AAD, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The 7-AAD+cells were excluded, and 1 × 104 RFP+ cells were analyzed for CD41/CD61 expression. The fluorescent signal from the isotype control antibody has been subtracted from that of each sample. The data are from 3 separate experiments.
Discussion
Although Gab2 was originally isolated and cloned from Bcr-Abl–transformed hematopoietic cells,26 the role of Gab2 in cell signaling and its function in Bcr-Abl+hematopoietic cells has not been characterized previously. Gab2 is readily phosphorylated by Abl tyrosine kinase in vitro (data not shown) and is constitutively phosphorylated by Bcr-Abl in K562 cells. Therefore, we used K562 cells as a model to investigate the role of Gab2 in Bcr-Abl+ CML cells.
Similar to what was observed in IL-3–stimulated pre-B cells,26 both the SHP2 docking site on Gab2 and the SHP2 PTPase activity were found to be required for the basal c-fos SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells. Tyr604 of Gab2 was found to mediate SHP2 binding to Gab2 in K562 cells. However, we have not completely ruled out the possibility that Tyr604 may also serve as a docking site for another uncharacterized SH2 domain–containing protein. Interestingly, while overexpression of Gab2 in BaF3 cells did not increase the IL-3–stimulated c-fosSRE transcriptional activity, overexpression of Gab2 in K562 cells markedly increased c-fos SRE transcriptional activity. Because overexpression of other Gab2-binding partners (Grb2, SHP2, and CrkL) that have been implicated in Bcr-Abl signaling or the Ras-MAP kinase pathway had little effect on c-fos promoter activity, our observation suggests that Gab2 is a signaling-threshold protein that limits c-fos SRE transcriptional activity in K562 cells. Indeed, our Gab2 immunodepletion experiment demonstrates that SHP2 protein exceeds Gab2 protein in K562 cells, confirming that Gab2 is the limiting factor for the Gab2-SHP2 complex in K562 cells.
Interestingly, while Gab1 is expressed in K562 cells and in normal megakaryocytes and erythroid progenitors,32,59 60 it did not appear to have the same effect as Gab2 in mediating c-fos promoter activation and CD41/CD61 expression in K562 cells. Comparison of endogenous Gab1 and Gab2 proteins in K562 cells suggests that Gab1 does not appear to be more abundant in K562 cells. Rather, Gab1 binds a lower amount of SHP2 than Gab2 does in K562 cells. Gab2 also interacts with several tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins that were not detected in Gab1 immunoprecipitates.
The PathDetect trans-reporting assays showed that overexpression of Gab2 selectively activated the Erk2-Elk1 pathway in K562 cells. The involvement of the Ras-Raf-MEK-Erk pathway in Elk1 activation in our assay was confirmed with the use of the well-characterized MEK1 inhibitor PD98059 and the dominant-negative RasN17 mutant. Furthermore, the effect of Gab2 overexpression on Erk2 activation was directly demonstrated in the 3 stable K562 cell lines expressing Gab2WT. Analysis of the dox-inducible stable K562 cell lines showed that overexpression of wild-type Gab2 in K562 cells induced growth arrest, cell flattening, expression of megakaryocytic-specific cell surface markers CD41/CD61, and upregulation of RNA for megakaryocyte/platelet proteins. These results provide additional evidence to support the notion that overexpression of Gab2 in K562 cells activates the Erk MAP kinase pathway in these cells.
Overexpression of Gab2 induces K562 cell growth arrest and differentiation, which require Tyr604 of Gab2. However, expression of Gab2Tyr604Phe did not result in stimulation of K562 cell proliferation. One possibility is that, although constitutive Erk activation caused by Gab2 overexpression inhibits K562 cell proliferation, basal or transient Erk activity is involved in K562 cell proliferation. Indeed, incubation of parental K562 cells with the MEK1 inhibitor PD98059 partially reduced the growth rate of K562 cells (data not shown). Different cellular consequences mediated by sustained versus transient Erk activation have been documented previously in PC12 cells.61 While the low basal Erk2 activity in K562 cells precluded detection of inhibition of Erk2 by Gab2Tyr604Phe, the Elk1trans-reporter and c-fos-promoter luciferase assays showed that Gab2Tyr604Phe had a inhibitory effect on the basal activities of these reporters in K562 cells. Therefore, inhibition of the basal Erk2 activity by Gab2Tyr604Phe does not necessarily give rise to a higher proliferation rate. In short, constitutive Erk activation mediates inhibition of K562 cell proliferation, but inhibition of Erk activity will not stimulate K562 cell proliferation.
We have recently shown that Gab1-SHP2 interaction activates the SHP2 PTPase, which is required for Erk MAP kinase activation by EGF-receptor tyrosine kinases.38 Because of the similar bisphosphoryl tyrosine–based activation motifs found in the C-terminal regions of Gab1 and Gab2, it is conceivable that Gab2-SHP2 interaction also activates the SHP2 PTPase. However, it remains unknown which tyrosine-phosphorylated protein must be dephosphorylated by SHP2 to permit Erk activation. A potential SHP2 substrate is Gab2 itself. Gab2 contains several optimal Abl tyrosine kinase phosphorylation sites26,62 and is highly phosphorylated by Bcr-Abl in K562 cells. Furthermore, SHP2 can dephosphorylate Gab2.27However, other possible targets, such as a Gab2-associated protein or a protein localized in the proximity of the Gab2-SHP2 complex, cannot be excluded.
Although the mechanism by which Gab2 mediates Erk MAP kinase activation requires further investigation, our experiments demonstrate that Gab2 has a critical role in the Erk MAP kinase pathway in Bcr-Abl+ K562 CML cells. Because of secondary changes, therapeutic approaches besides the inhibition of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase activity are necessary for the majority of CML patients in blast crisis.63 Interestingly, many leukemic cells, like K562 cells, retain the potential for some degree of terminal differentiation and can be reprogrammed to differentiate and stop proliferating.17,19,20 64-66 Our study identifies Gab2 as a key signaling-threshold factor that controls the terminal differentiation of K562 cells and as a potential molecular target for attenuating leukemic cell proliferation. It will be interesting to see, through further studies, what fractions of primary CML cells share the same deficit in Gab2 expression as the human K562 CML cells and can be reprogrammed to differentiation by Gab2 expression.
We thank Drs John Groffen, Wanjin Hong, and Richard Jove for reagents, and Dr Kapil Bhalla for critical reading of the manuscript. We also acknowledge Moffitt Cancer Center Core Facilities for assistance in DNA sequence, microarray, flow cytometry, and statistical analyses, especially Judi Kroeger for flow cytometry analysis.
Supported by American Cancer Society Grant RPG0028901TBE and by National Institutes of Health grant CA77467.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Jie Wu, Molecular Oncology Program, MRC 3-East, H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute, 12902 Magnolia Dr, Tampa, FL 33612; e-mail: wu@moffitt.usf.edu.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal