Key Points
Midostaurin as adjunct to chemotherapy significantly improves outcome in younger and older patients with AML and FLT3-ITD.
The data provide evidence for the use of midostaurin as the standard of care also for older patients with FLT3-mutated AML.
Abstract
We conducted a single-arm, phase 2 trial (German-Austrian Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group [AMLSG] 16-10) to evaluate midostaurin with intensive chemotherapy followed by allogeneic hematopoietic-cell transplantation (HCT) and a 1-year midosta urin maintenance therapy in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) internal tandem duplication (ITD). Patients 18 to 70 years of age with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD-positive AML were eligible. Primary and key secondary endpoints were event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS). Results were compared with a historical cohort of 415 patients treated on 5 prior AMLSG trials; statistical analysis was performed using a double-robust adjustment with propensity score weighting and covariate adjustment. Results were also compared with patients (18-59 years) treated on the placebo arm of the Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) 10603/RATIFY trial. The trial accrued 440 patients (18-60 years, n = 312; 61-70 years, n = 128). In multivariate analysis, EFS was significantly in favor of patients treated within the AMLSG 16-10 trial compared with the AMLSG control (hazard ratio [HR], 0.55; P < .001); both in younger (HR, 0.59; P < .001) and older patients (HR, 0.42; P < .001). Multivariate analysis also showed a significant beneficial effect on OS compared with the AMLSG control (HR, 0.57; P < .001) as well as to the CALGB 10603/RATIFY trial (HR, 0.71; P = .005). The treatment effect of midostaurin remained significant in sensitivity analysis including allogeneic HCT as a time-dependent covariate. Addition of midostaurin to chemotherapy was safe in younger and older patients. In comparison with historical controls, the addition of midostaurin to intensive therapy led to a significant improvement in outcome in younger and older patients with AML and FLT3-ITD. This trial is registered at clinicaltrialsregistry.eu as Eudra-CT number 2011-003168-63 and at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT01477606.
Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a he terogeneous disease with regard to morphology, immunophenotype, cytogenetic and molecular genetic abnormalities, as well as responses to treatment and patient outcomes.1-4 Mutations of the fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 gene (FLT3) are common mutations in adults with newly diagnosed AML and are present in 15% to 30% with a decreasing prevalence with older age.5 Approximately three-quarters of mutations are internal tandem duplications (ITDs) that result in duplication of nucleotide sequence varying in length and insertion site.2 The remaining mutations are point mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain (TKD). Compared with FLT3 wild-type AML, AML with FLT3-ITDs are associated with an inferior outcome.4,6-8 Outcomes are in particular poor in patients with a high mutant-to-wild-type ITD allelic ratio (AR) (≥0.5),6,8,9 and in patients without concomitant presence of a nucleophosmin-1 (NPM1) mutation.8-12
Midostaurin is a first-generation, type I multitargeted kinase inhibitor with inhibitory activity against FLT3-ITD and FLT3-TKD mutations. In the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) 10603/RATIFY study evaluating midostaurin in patients aged 18 to 59 years with newly diagnosed FLT3-mutated AML in combination with intensive chemotherapy followed by a 1-year oral maintenance therapy, midostaurin significantly improved overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS).13 Midostaurin is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and by European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed AML with FLT3 mutation in combination with standard cytarabine and daunorubicin induction and cytarabine consolidation; EMA approval includes a 1-year single-agent maintenance treatment with midostaurin following conventional consolidation therapy. Next-generation FLT3 inhibitors, such as gilteritinib, quizartinib, and crenolanib, are in clinical development.14 Gilteritinib is approved by Food and Drug Administration and EMA as a monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory AML with a FLT3 mutation.
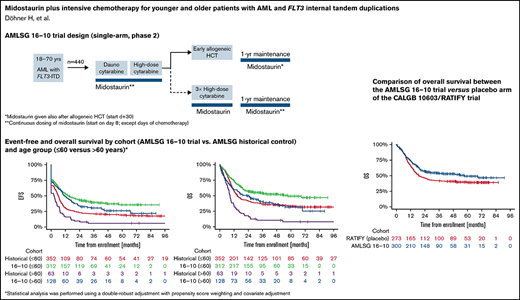
The German-Austrian Acute Myeloid Leukemia Study Group (AMLSG) 16-10 study is a large, single-arm phase 2 study that evaluated midostaurin in adult patients with newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD positive AML, not only in younger adults, but also in older patients up to the age of 70 years. We previously reported a significant improvement of EFS in the first 284 patients from the trial in comparison with a historical control population.15 We here report the final analysis of the trial in all 440 patients.
Material and methods
Patient selection
Patients aged 18 to 70 years with newly diagnosed AML with a FLT3-ITD and considered fit for intensive chemotherapy were eligible. Diagnoses included de novo AML, secondary AML following an antecedent myeloid neoplasm, and therapy-related AML. Patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia and core-binding factor (CBF) AML were not eligible. All patients gave written informed consent. The clinical trial was approved by the ethics committees. The historical control cohort consisted of 415 patients aged 18 to 70 years with newly diagnosed AML and a FLT3-ITD who had received intensive chemotherapy within 5 AMLSG trials conducted between 1993 and 2009 (supplemental Table 1). As a second, more contemporary historical cohort, we used 273 patients treated on the placebo arm of the CALGB 10603/RATIFY trial.13
Molecular screening
Rapid molecular screening was performed centrally within our AMLSG BiO Registry5 using the previously described clinical trial assay.13 A FLT3-ITD mutant-to-wild-type AR of ≥0.05 was considered positive; AML were categorized into cases with low (<0.5) and high (≥0.5) AR.16 Samples were also analyzed for FLT3-TKD mutations (codons D835/I836) and for NPM1 mutations.10 Cytogenetic risk was categorized according to 2010 European LeukemiaNet (ELN) recommendations.17
Trial design
AMLSG 16-10 was a single-arm, phase 2 study conducted at 54 study sites in Germany and Austria (see also supplemental Material for further information on trial design). Compared with the CALGB 10603/RATIFY trial, the design of the AMLSG 16-10 trial differed with regard to the following aspects: (1) only patients with FLT3-ITD-positive AML were included; (2) AMLSG 16-10 allowed for inclusion of older patients 60 to 70 years of age; (3) all patients were intended to receive allogeneic matched-related donor (MRD) or matched-unrelated donor hematopoietic-cell transplantation (HCT) for consolidation; (4) a 1-year maintenance treatment with midostaurin was included also after allogeneic HCT; (5) patients with CBF-AML were excluded; (6) patients with therapy-related AML were eligible (except CBF-AML); and (7) a continuous dosing schedule of midostaurin was applied with the aim of achieving a better target inhibition.
Statistical analysis
The primary efficacy endpoint of the AMLSG 16-10 trial was EFS, defined as the time from enrollment to induction failure (ie, failure to achieve complete remission [CR] or complete remission with incomplete hematologic recovery [CRi], death or relapse, whichever occurred first, based on response assessed by the investigator); patients not known to have any of these events were censored on the date they were last examined. The key secondary efficacy endpoint was OS, defined as the time from enrollment to death from any cause, patients not known to have died at last follow-up are censored on the date they were last known to be alive. Overall and predefined subgroup analyses in the age groups 18 to 60 years and 61 to 70 years were performed for EFS and OS. Other secondary endpoints included rates of CR/CRi, cumulative incidence of relapse, cumulative incidence of death in remission, relapse-free survival, as defined in the 2017 ELN recommendations,16 the impact of allogeneic HCT in first CR/CRi analyzed as time-dependent intervention on EFS, and FLT3 target inhibition by measuring the FLT3 plasma inhibitory activity (the latter to be reported elsewhere). The safety endpoint evaluated toxicity assessed according to the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), version 3.0.
The analyses for the primary and key secondary endpoints addressed the null hypotheses of “no treatment effect,” whereby treatments compared were midostaurin in addition to standard chemotherapy (AMLSG 16-10) vs standard chemotherapy without midostaurin (AMLSG historical control population). To reduce confounding bias originating from structural differences in prognostic factors between the 2 cohorts, a double-robust adjustment strategy was used to account for age (as continuous variable), sex, log10 white blood cell (WBC) count, bone marrow blasts, NPM1 mutational status, and FLT3-ITD AR. More specifically, these clinical variables were included as covariates in a (weighted) Cox proportional hazards model as well as for the calculation of propensity score weights via logistic regression for midostaurin treatment. Missing values of the covariates were addressed via multiple imputation by chained equations.18
The Wald test for the treatment group comparison resulting from these analyses were used to test the “local” null hypotheses concerning the primary and key secondary endpoints of the study, EFS and OS:
- 1.
H0(EFS): “no treatment effect” for the entire efficacy population
- 2.
H01(EFS): “no treatment effect” for the subset of patients 18 to 60 years
- 3.
H02(EFS): “no treatment effect” for the subset of patients 61 to 70 years
- 4.
H0(OS): “no treatment effect” for the entire efficacy population
- 5.
H01(OS): “no treatment effect” for the subset of patients 18 to 60 years
- 6.
H02(OS): “no treatment effect” for the subset of patients 61 to 70 years
Within the final analysis, the 6 null hypotheses were tested sequentially according to a predefined algorithm which allows reallocation of local significance levels whenever 1 of the hypotheses is rejected.19 More details about the testing procedure as well as details about sensitivity analyses and analyses of secondary endpoints can be found in the supplemental Material.
Because patients of the historical control were treated about 1 decade earlier, we also compared the results from this study with those of the CALGB 10603/RATIFY study with regard to OS. To this aim, patients to be included in this analysis were selected according to the inclusion/exclusion criteria of both trials (AMLSG 16-10, n = 300 patients; CALGB 10603/RATIFY study, n = 273 patients; see also supplemental Material).
For testing differences in baseline characteristics between the AMLSG 16-10 study population and the historical cohort, Fisher exact test and Cochran-Armitage test were used for nominal and ordinal data, respectively; and Mann-Whitney test for 2-group comparisons of continuous data and Kruskal-Wallis test for comparison of continuous data for more than 2 groups. Statistical analyses were performed with the statistical software environment R, version 4.0.2, using the R packages survival, version 3.1-12; mice,18 version 3.11.0; gMCP, version 2.2-10; rms, version 6.0-1; and riskRegression, version 2020.02.05.
Results
Patient and disease characteristics
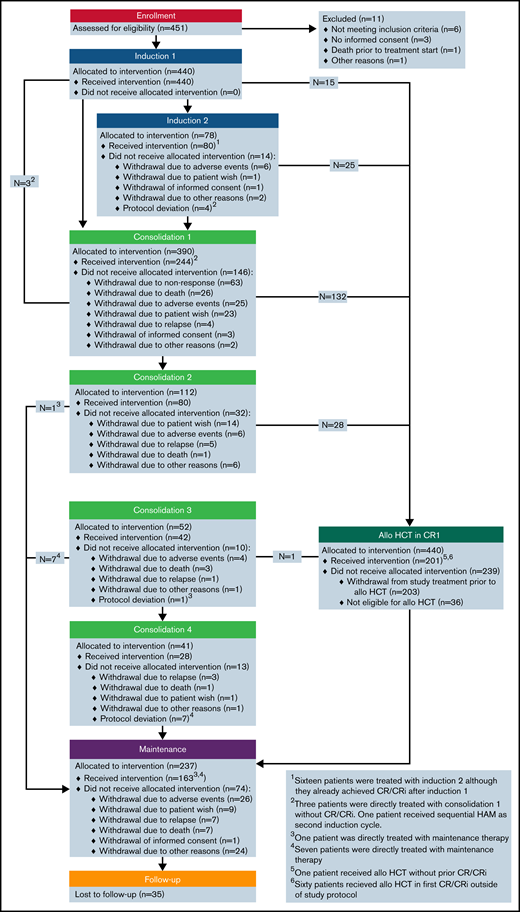
Between June 2012 and February 2018, 451 patients were enrolled; of these, 11 patients were excluded from the analysis, resulting in 440 evaluable patients (Figure 1). The full analysis set for the analyses of all efficacy endpoints comprised 855 patients, 440 patients from the AMLSG 16-10 trial and 415 patients from the AMLSG historical control group. Patient baseline characteristics by cohort are given in Table 1 and by cohort and age group in supplemental Table 2.
Patient and disease characteristics
| . | AMLSG 16-10 . | Historical controls . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | n = 440 . | n = 415 . | . |
| Age, y | <.001 | ||
| Median (range) | 54.1 (18-70) | 50.5 (18-70) | |
| Sex, n (%) | .37 | ||
| Male | 191 (43) | 193 (46) | |
| Female | 249 (57) | 222 (54) | |
| ECOG PS, n (%) | <.0001 | ||
| 0 | 169 (38) | 92 (22) | |
| 1 | 218 (50) | 255 (62) | |
| 2 | 53 (12) | 68 (16) | |
| WBC, 109/L | .40 | ||
| Median (range) | 41.8 (0.3-420) | 44.8 (0.2-439) | |
| Missing | 3 | 3 | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | .79 | ||
| Median (range) | 9.0 (4.1-18.1) | 9.0 (3.1-16.6) | |
| Missing | 4 | 3 | |
| Platelets, 109/L | .37 | ||
| Median (range) | 59 (5-681) | 58 (6-734) | |
| Missing | 3 | 2 | |
| BM blasts, % | .22 | ||
| Median (range) | 80 (0-100) | 85 (2-100) | |
| Missing | 46 | 25 | |
| PB blasts, % | .08 | ||
| Median (range) | 52 (0-100) | 60 (0-100) | |
| Missing | 30 | 20 | |
| AML type, n (%) | <.0001 | ||
| De novo | 390 (89) | 396 (96) | |
| Secondary | 31 (7) | 6 (1) | |
| Therapy-related | 19 (4) | 12 (3) | |
| Missing | — | 1 | |
| Cytogenetics, n (%)* | .02 | ||
| Intermediate I | 285 (69) | 321 (78) | |
| Intermediate II | 101 (25) | 72 (17) | |
| Adverse | 26 (6) | 22 (5) | |
| Missing | 28 | 0 | |
| FLT3-ITD, n (%) | .67 | ||
| Allelic ratio <0.5 | 196 (45) | 129 (44) | |
| Allelic ratio ≥0.5 | 242 (55) | 165 (56) | |
| Missing | 2 | 121 | |
| FLT3-TKD,† n (%) | .86 | ||
| Yes | 16 (4) | 16 (4) | |
| No | 424 (96) | 377 (96) | |
| Missing | — | 22 | |
| Mutated NPM1, n (%) | .24 | ||
| Yes | 266 (60) | 229 (56) | |
| No | 174 (40) | 178 (44) | |
| Missing | — | 8 |
| . | AMLSG 16-10 . | Historical controls . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | n = 440 . | n = 415 . | . |
| Age, y | <.001 | ||
| Median (range) | 54.1 (18-70) | 50.5 (18-70) | |
| Sex, n (%) | .37 | ||
| Male | 191 (43) | 193 (46) | |
| Female | 249 (57) | 222 (54) | |
| ECOG PS, n (%) | <.0001 | ||
| 0 | 169 (38) | 92 (22) | |
| 1 | 218 (50) | 255 (62) | |
| 2 | 53 (12) | 68 (16) | |
| WBC, 109/L | .40 | ||
| Median (range) | 41.8 (0.3-420) | 44.8 (0.2-439) | |
| Missing | 3 | 3 | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | .79 | ||
| Median (range) | 9.0 (4.1-18.1) | 9.0 (3.1-16.6) | |
| Missing | 4 | 3 | |
| Platelets, 109/L | .37 | ||
| Median (range) | 59 (5-681) | 58 (6-734) | |
| Missing | 3 | 2 | |
| BM blasts, % | .22 | ||
| Median (range) | 80 (0-100) | 85 (2-100) | |
| Missing | 46 | 25 | |
| PB blasts, % | .08 | ||
| Median (range) | 52 (0-100) | 60 (0-100) | |
| Missing | 30 | 20 | |
| AML type, n (%) | <.0001 | ||
| De novo | 390 (89) | 396 (96) | |
| Secondary | 31 (7) | 6 (1) | |
| Therapy-related | 19 (4) | 12 (3) | |
| Missing | — | 1 | |
| Cytogenetics, n (%)* | .02 | ||
| Intermediate I | 285 (69) | 321 (78) | |
| Intermediate II | 101 (25) | 72 (17) | |
| Adverse | 26 (6) | 22 (5) | |
| Missing | 28 | 0 | |
| FLT3-ITD, n (%) | .67 | ||
| Allelic ratio <0.5 | 196 (45) | 129 (44) | |
| Allelic ratio ≥0.5 | 242 (55) | 165 (56) | |
| Missing | 2 | 121 | |
| FLT3-TKD,† n (%) | .86 | ||
| Yes | 16 (4) | 16 (4) | |
| No | 424 (96) | 377 (96) | |
| Missing | — | 22 | |
| Mutated NPM1, n (%) | .24 | ||
| Yes | 266 (60) | 229 (56) | |
| No | 174 (40) | 178 (44) | |
| Missing | — | 8 |
Abbreviations: BM, bone marrow; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; PB, peripheral blood.
Cytogenetics categorization according to 2010 European LeukemiaNet categories.16
FLT3-TKD mutation concurrent to a FLT3-ITD.
Patient disposition
Figure 1 shows details regarding patient disposition within the AMLSG 16-10 trial.
Allogeneic HCT.
Transplantation was intended in all patients achieving CR/CRi after induction therapy. Overall, 199 (45%) patients received allogeneic HCT in first CR/CRi, 150 (48%) and 49 (38%) patients in the younger and older cohort, respectively (Table 2). Most patients >55 years of age received reduced-intensity conditioning regimens. Eighty-three patients received consolidation with high-dose cytarabine (1 cycle [n = 32]; 2 cycles [n = 10]; 3 cycles [n = 13]; 4 cycles [n = 28]).
Response to induction therapy, rates of allogeneic HCT, and efficacy outcomes
| . | AMLSG 16-10 . | Historical controls . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | All (N = 440) . | 18-60 y (312) . | 61-70 y (n = 128) . | All (N = 415) . | 18-60 y (n = 352) . | 61-70 y (n = 63) . |
| Response to induction therapy | ||||||
| CR, % | 37.0 | 37.6 | 35.4 | 49.2 | 49.4 | 47.6 |
| CRi, % | 37.9 | 38.3 | 37.0 | 15.4 | 17.1 | 6.3 |
| CR/CRi, % | 74.9 | 75.9 | 72.4 | 64.6 | 66.5 | 54.0 |
| RD, % | 19.2 | 20.6 | 15.8 | 30.6 | 28.4 | 42.9 |
| ED/HD, % | 5.9 | 3.5 | 11.8 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 3.2 |
| Missing | 2 | 1 | 1 | — | — | — |
| Allogeneic HCT | ||||||
| HCT in CR/CRi, n (%) | 199 (45.2) | 150 (48.1) | 49 (38.3) | 94 (22.7) | 89 (25.3) | 5 (7.9) |
| MRD, n (%) | 51 (26) | 40 (27) | 11 (22) | 48 (51) | 46 (52) | 2 (40) |
| MUD, n (%) | 148 (74) | 110 (73) | 38 (78) | 46 (49) | 43 (48) | 3 (60) |
| Time to HCT, d (range) | 98 (49-202) | 98 (53-202) | 99 (49-186) | 135 (61-288) | 135 (61-237) | 148 (95-288) |
| Any HCT during disease course | 321 (72.9) | 241 (77.2) | 80 (62.5) | 237 (57.1) | 222 (63.1) | 15 (23.8) |
| Follow-up time | ||||||
| Median, mo | 40.4 | — | — | 76.3 | — | — |
| Outcomes | ||||||
| Median EFS, mo | 13.6 (10.4-17.9) | 14.5 (10.5-23.1) | 11.7 (8.5-17.7) | 5.3 (4.4-6.7) | 6.03 (5.03-7.1) | 2.53 (0.03-5.0) |
| 2-y EFS rate | 0.41 (0.36-0.46) | 0.43 (0.38-0.49) | 0.34 (0.27-0.44) | 0.21 (0.17-0.25) | 0.23 (0.19-0.28) | 0.10 (0.04-0.20) |
| Median OS-mo | 36.2 (24.6-57.3) | 57.3 (28.4-NA) | 22.7 (14.7-36.7) | 13.2 (11.9-15.7) | 14.9 (12.9-18.2) | 8.4 (7.1-11.7) |
| 2-y OS rate | 0.55 (0.50-0.60) | 0.57 (0.52-0.63) | 0.50 (0.41-0.59) | 0.38 (0.33-0.43) | 0.41 (0.36,0.47) | 0.18 (0.10-0.31) |
| 2-y CIR | 0.28 (0.23-0.33) | 0.24 (0.19-0.3) | 0.37 (0.27-0.47) | 0.57 (0.51-0.63) | 0.54 (0.48-0.61) | 0.74 (0.59-0.88) |
| 2-y CID | 0.20 (0.16-0.25) | 0.20 (0.15-0.26) | 0.19 (0.11-0.28) | 0.12 (0.08-0.15) | 0.12 (0.07-0.16) | 0.12 (0.01-0.23) |
| . | AMLSG 16-10 . | Historical controls . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | All (N = 440) . | 18-60 y (312) . | 61-70 y (n = 128) . | All (N = 415) . | 18-60 y (n = 352) . | 61-70 y (n = 63) . |
| Response to induction therapy | ||||||
| CR, % | 37.0 | 37.6 | 35.4 | 49.2 | 49.4 | 47.6 |
| CRi, % | 37.9 | 38.3 | 37.0 | 15.4 | 17.1 | 6.3 |
| CR/CRi, % | 74.9 | 75.9 | 72.4 | 64.6 | 66.5 | 54.0 |
| RD, % | 19.2 | 20.6 | 15.8 | 30.6 | 28.4 | 42.9 |
| ED/HD, % | 5.9 | 3.5 | 11.8 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 3.2 |
| Missing | 2 | 1 | 1 | — | — | — |
| Allogeneic HCT | ||||||
| HCT in CR/CRi, n (%) | 199 (45.2) | 150 (48.1) | 49 (38.3) | 94 (22.7) | 89 (25.3) | 5 (7.9) |
| MRD, n (%) | 51 (26) | 40 (27) | 11 (22) | 48 (51) | 46 (52) | 2 (40) |
| MUD, n (%) | 148 (74) | 110 (73) | 38 (78) | 46 (49) | 43 (48) | 3 (60) |
| Time to HCT, d (range) | 98 (49-202) | 98 (53-202) | 99 (49-186) | 135 (61-288) | 135 (61-237) | 148 (95-288) |
| Any HCT during disease course | 321 (72.9) | 241 (77.2) | 80 (62.5) | 237 (57.1) | 222 (63.1) | 15 (23.8) |
| Follow-up time | ||||||
| Median, mo | 40.4 | — | — | 76.3 | — | — |
| Outcomes | ||||||
| Median EFS, mo | 13.6 (10.4-17.9) | 14.5 (10.5-23.1) | 11.7 (8.5-17.7) | 5.3 (4.4-6.7) | 6.03 (5.03-7.1) | 2.53 (0.03-5.0) |
| 2-y EFS rate | 0.41 (0.36-0.46) | 0.43 (0.38-0.49) | 0.34 (0.27-0.44) | 0.21 (0.17-0.25) | 0.23 (0.19-0.28) | 0.10 (0.04-0.20) |
| Median OS-mo | 36.2 (24.6-57.3) | 57.3 (28.4-NA) | 22.7 (14.7-36.7) | 13.2 (11.9-15.7) | 14.9 (12.9-18.2) | 8.4 (7.1-11.7) |
| 2-y OS rate | 0.55 (0.50-0.60) | 0.57 (0.52-0.63) | 0.50 (0.41-0.59) | 0.38 (0.33-0.43) | 0.41 (0.36,0.47) | 0.18 (0.10-0.31) |
| 2-y CIR | 0.28 (0.23-0.33) | 0.24 (0.19-0.3) | 0.37 (0.27-0.47) | 0.57 (0.51-0.63) | 0.54 (0.48-0.61) | 0.74 (0.59-0.88) |
| 2-y CID | 0.20 (0.16-0.25) | 0.20 (0.15-0.26) | 0.19 (0.11-0.28) | 0.12 (0.08-0.15) | 0.12 (0.07-0.16) | 0.12 (0.01-0.23) |
CID, cumulative incidence of relapse; CIR, cumulative incidence of relapse; ED, early death; HD, hypoplastic death; MUD, matched-unrelated donor; RD, refractory disease.
Maintenance therapy.
Of 237 patients allocated to midostaurin maintenance therapy, 163 actually started maintenance (Figure 1), 128 of 201 (64%) after allogeneic HCT and 35 of 83 (42%) after cytarabine consolidation; maintenance therapy was started after allogeneic HCT in median at day 54 (range, 24-167). Reasons for not starting maintenance treatment are provided in supplemental Table 3.
Efficacy outcomes: primary and key secondary endpoints
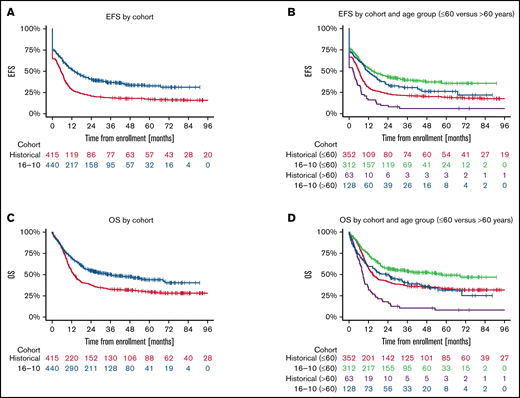
The median follow-up times of the patients in the AMLSG 16-10 trial and the historical control group were 40.4 months and 76.3 months, respectively. The 2-year EFS rate was 0.41 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.36-0.46) in the AMLSG 16-10 trial and 0.21 (95% CI, 0.17-0.25) in the AMLSG historical population (Table 2). The 2-year OS was 0.55 (95% CI, 0.50-0.60) in the AMLSG 16-10 trial and 0.38 (95% CI, 0.33-0.43) in the historical population (Figure 2). Median survival times and 1- to 5-year survival rates are given in supplemental Table 4.
Survival distribution for the primary endpoint event-free survival (EFS) and key secondary endpoint overall survival (OS) according to study population and age group. (A) Median EFS times of the 440 patients from the AMLSG 16-10 trial and the 415 patients from the historical control group were 13.6 months and 5.3 months, respectively; and the 2- and 4-year EFS rates 0.41/0.34 and 0.21/0.18, respectively. (B) EFS by cohort age group ≤60 vs >60 years (for median EFS times and EFS rates, see supplemental Table 3). (C) Median OS times of the 440 patients from the AMLSG 16-10 trial and the 415 patients from the historical control group were 36.2 months and 13.2 months, respectively; and the 2- and 4-year OS rates 0.55/0.47 and 0.38/0.31, respectively. (D) OS by age group ≤60 vs >60 years (for median OS times and OS rates, see supplemental Table 4).
Survival distribution for the primary endpoint event-free survival (EFS) and key secondary endpoint overall survival (OS) according to study population and age group. (A) Median EFS times of the 440 patients from the AMLSG 16-10 trial and the 415 patients from the historical control group were 13.6 months and 5.3 months, respectively; and the 2- and 4-year EFS rates 0.41/0.34 and 0.21/0.18, respectively. (B) EFS by cohort age group ≤60 vs >60 years (for median EFS times and EFS rates, see supplemental Table 3). (C) Median OS times of the 440 patients from the AMLSG 16-10 trial and the 415 patients from the historical control group were 36.2 months and 13.2 months, respectively; and the 2- and 4-year OS rates 0.55/0.47 and 0.38/0.31, respectively. (D) OS by age group ≤60 vs >60 years (for median OS times and OS rates, see supplemental Table 4).
Propensity-score-based comparative analysis to historical controls (before adjustment for multiple testing).
Multivariate analysis of EFS showed a highly significant hazard reduction for an event for patients treated within the AMLSG 16-10 trial compared with the AMLSG historical control group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.55; P < .001); this effect was significant both in the younger (HR, 0.59; P < .001) and the older patient cohort (HR, 0.41; P < .001) (Table 3). In context with this treatment effect of midostaurin, the presence of the NPM1 mutation was another favorable prognostic factor (HR, 0.48; P < .001), whereas older age (HR for 10-year increase, 1.02; P < .001) and a higher WBC (HR, 1.21 for 10-fold increase; P = .011) were significant unfavorable factors. There was a trend for a higher event hazard for patients with a FLT3-ITD AR ≥ 0.5 (HR, 1.21; P = .052).
Results from the multivariate regression models (before adjustment for multiple testing via gatekeeping procedure) using multiple imputation of missing values and double-robust adjustment for EFS and OS in the full analysis set
| . | EFS . | . | OS . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . | Variable . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . |
| Entire cohort (N = 855) | |||||||
| AMLSG 16-10 | 0.55 | 0.47-0.65 | <.001 | AMLSG 16-10 | 0.56 | 0.47-0.68 | <.001 |
| Age (10-y increase) | 1.17 | 1.09-1.25 | <.001 | Age, y | 1.33 | 1.23-1.44 | <.001 |
| Female | 0.91 | 0.78-1.07 | .255 | Female | 0.90 | 0.75-1.07 | .241 |
| NPM1-mutated | 0.48 | 0.41-0.57 | <.001 | NPM1-mutated | 0.76 | 0.63-0.91 | .002 |
| WBC (log10) | 1.21 | 1.05-1.40 | .011 | WBC (log10) | 1.23 | 1.04-1.44 | .015 |
| BM blasts | 0.94 | 0.62-1.44 | .788 | BM blasts | 1.16 | 0.73-1.87 | .528 |
| FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.21 | 1.00-1.48 | .052 | FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.20 | 0.98-1.47 | .082 |
| Younger patients (18-60 y) (n = 664) | |||||||
| AMLSG 16-10 | 0.59 | 0.49-0.71 | <.001 | AMLSG 16-10 | 0.59 | 0.47-0.73 | <.001 |
| Age (10-y increase) | 1.16 | 1.06-1.27 | <.001 | Age, y | 1.30 | 1.17-1.45 | <.001 |
| Female | 0.97 | 0.80-1.16 | .709 | Female | 0.99 | 0.80-1,22 | .893 |
| NPM1-mutated | 0.47 | 0.39-0.56 | <.001 | NPM1-mutated | 0.76 | 0.61-0.94 | .010 |
| WBC (log10) | 1.24 | 1.04-1.47 | .014 | WBC (log10) | 1.23 | 1.01-1.49 | .037 |
| BM blasts | 0.99 | 0.62-1.60 | .978 | BM blasts | 1.41 | 0.81-2.45 | .219 |
| FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.15 | 0.93-1.42 | .194 | FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.14 | 0.90-1.45 | .284 |
| Older patients (61-70 y) (n = 191) | |||||||
| AMLSG 16-10 | 0.41 | 0.29-0.59 | <.001 | AMLSG 16-10 | 0.47 | 0.33-0.67 | <.001 |
| Age (10-y increase) | 1.36 | 0.75-2.47 | .301 | Age, y | 1.27 | 0.67-2.40 | .456 |
| Female | 0.74 | 0.53-1.04 | .082 | Female | 0.70 | 0.49-0.99 | .042 |
| NPM1-mutated | 0.53 | 0.38-0.74 | <.001 | NPM1-mutated | 0.75 | 0.53-1.08 | .118 |
| WBC (log10) | 1.09 | 0.82-1.44 | .550 | WBC (log10) | 1.15 | 0.84-1.56 | .378 |
| BM blasts | 0.65 | 0.27-1.56 | .329 | BM blasts | 0.57 | 0.22-1.47 | .245 |
| FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.48 | 0.96-2.29 | .078 | FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.44 | 0.92-2.27 | .111 |
| . | EFS . | . | OS . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . | Variable . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . |
| Entire cohort (N = 855) | |||||||
| AMLSG 16-10 | 0.55 | 0.47-0.65 | <.001 | AMLSG 16-10 | 0.56 | 0.47-0.68 | <.001 |
| Age (10-y increase) | 1.17 | 1.09-1.25 | <.001 | Age, y | 1.33 | 1.23-1.44 | <.001 |
| Female | 0.91 | 0.78-1.07 | .255 | Female | 0.90 | 0.75-1.07 | .241 |
| NPM1-mutated | 0.48 | 0.41-0.57 | <.001 | NPM1-mutated | 0.76 | 0.63-0.91 | .002 |
| WBC (log10) | 1.21 | 1.05-1.40 | .011 | WBC (log10) | 1.23 | 1.04-1.44 | .015 |
| BM blasts | 0.94 | 0.62-1.44 | .788 | BM blasts | 1.16 | 0.73-1.87 | .528 |
| FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.21 | 1.00-1.48 | .052 | FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.20 | 0.98-1.47 | .082 |
| Younger patients (18-60 y) (n = 664) | |||||||
| AMLSG 16-10 | 0.59 | 0.49-0.71 | <.001 | AMLSG 16-10 | 0.59 | 0.47-0.73 | <.001 |
| Age (10-y increase) | 1.16 | 1.06-1.27 | <.001 | Age, y | 1.30 | 1.17-1.45 | <.001 |
| Female | 0.97 | 0.80-1.16 | .709 | Female | 0.99 | 0.80-1,22 | .893 |
| NPM1-mutated | 0.47 | 0.39-0.56 | <.001 | NPM1-mutated | 0.76 | 0.61-0.94 | .010 |
| WBC (log10) | 1.24 | 1.04-1.47 | .014 | WBC (log10) | 1.23 | 1.01-1.49 | .037 |
| BM blasts | 0.99 | 0.62-1.60 | .978 | BM blasts | 1.41 | 0.81-2.45 | .219 |
| FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.15 | 0.93-1.42 | .194 | FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.14 | 0.90-1.45 | .284 |
| Older patients (61-70 y) (n = 191) | |||||||
| AMLSG 16-10 | 0.41 | 0.29-0.59 | <.001 | AMLSG 16-10 | 0.47 | 0.33-0.67 | <.001 |
| Age (10-y increase) | 1.36 | 0.75-2.47 | .301 | Age, y | 1.27 | 0.67-2.40 | .456 |
| Female | 0.74 | 0.53-1.04 | .082 | Female | 0.70 | 0.49-0.99 | .042 |
| NPM1-mutated | 0.53 | 0.38-0.74 | <.001 | NPM1-mutated | 0.75 | 0.53-1.08 | .118 |
| WBC (log10) | 1.09 | 0.82-1.44 | .550 | WBC (log10) | 1.15 | 0.84-1.56 | .378 |
| BM blasts | 0.65 | 0.27-1.56 | .329 | BM blasts | 0.57 | 0.22-1.47 | .245 |
| FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.48 | 0.96-2.29 | .078 | FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.44 | 0.92-2.27 | .111 |
BM, bone marrow.
Multivariate analysis also showed a highly significant beneficial effect on OS for patients treated within the AMLSG 16-10 trial compared with the historical control group (HR, 0.56; P < .001); this effect was again significant both in the younger and the older patient cohort. With regard to treatment with midostaurin, the same prognostic factors as for EFS were identified for OS (Table 3).
The results described in the previous paragraph provided the basis for the primary analysis of primary and key secondary endpoints. After correction for multiple testing using a gatekeeping procedure (see supplemental Material), the conclusions remained valid, and the results showed a significantly better outcome for patients in the AMLSG 16-10 population compared with the AMLSG historical control. All null hypotheses were rejected at the final significance levels, which implies that the study was successful. The adjusted 95% confidence limits for the hazard ratios and P values associated with each of the 6 null hypotheses are listed in supplemental Table 5.
Sensitivity analyses.
Two types of sensitivity analyses were performed, 1 including allogeneic HCT as a time-dependent covariate in the model (Table 4) and another considering allogeneic HCT as a competing event (supplemental Table 6). For both endpoints EFS and OS, treatment effect of midostaurin remained significant. In general, adjusting for allogeneic HCT slightly reduced the treatment effect compared with the multivariate model without considering allogeneic HCT (EFS: HR, 0.63 and 0.62 compared with 0.55; OS: HR, 0.72 and 0.66 compared with 0.57).
Results of multivariate analysis using multiple imputation of missing values and double-robust adjustment for EFS and OS with allogeneic HCT in first CR or CRi used as a time-dependent variable in the full analysis set
| . | EFS . | OS . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . |
| AMLSG 16-10 | 0.62 | 0.52-0.73 | <.001 | 0.66 | 0.55-0.80 | <.001 |
| Age (10-y increase) | 1.15 | 1.08-1.23 | <.001 | 1.31 | 1.21-1.41 | <.001 |
| Female | 0.89 | 0.76-1.05 | .161 | 0.88 | 0.74-1.05 | .169 |
| NPM1-mutated | 0.48 | 0.41-0.57 | <.001 | 0.77 | 0.64-0.92 | .004 |
| WBC (log10) | 1.21 | 1.05-1.40 | 011 | 1.21 | 1.03-1.43 | .021 |
| BM blasts | 0.91 | 0.60-1.39 | 0.672 | 1.16 | 0.73-1.86 | .533 |
| FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.25 | 1.02-1.53 | .028 | 1.23 | 1.00-1.51 | .050 |
| HCT | 0.55 | 0.44-0.70 | <.001 | 0.58 | 0.47-0.72 | 0.001 |
| . | EFS . | OS . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . |
| AMLSG 16-10 | 0.62 | 0.52-0.73 | <.001 | 0.66 | 0.55-0.80 | <.001 |
| Age (10-y increase) | 1.15 | 1.08-1.23 | <.001 | 1.31 | 1.21-1.41 | <.001 |
| Female | 0.89 | 0.76-1.05 | .161 | 0.88 | 0.74-1.05 | .169 |
| NPM1-mutated | 0.48 | 0.41-0.57 | <.001 | 0.77 | 0.64-0.92 | .004 |
| WBC (log10) | 1.21 | 1.05-1.40 | 011 | 1.21 | 1.03-1.43 | .021 |
| BM blasts | 0.91 | 0.60-1.39 | 0.672 | 1.16 | 0.73-1.86 | .533 |
| FLT3-ITDhigh | 1.25 | 1.02-1.53 | .028 | 1.23 | 1.00-1.51 | .050 |
| HCT | 0.55 | 0.44-0.70 | <.001 | 0.58 | 0.47-0.72 | 0.001 |
BM, bone marrow.
Comparison with outcome data from CALGB 10603/RATIFY trial.
Supplemental Table 7 provides the results from multivariate analysis for OS using the placebo arm of CALGB 10603/RATIFY instead of the AMLSG historical control as reference. The treatment effect of AMLSG 16-10 trial remained significant (HR 0.71; P = .005). Supplemental Figure 1 shows OS curves for the comparison AMLSG 16-10 versus placebo arm CALGB 10603/RATIFY (panel A), AMLSG 16-10 versus midostaurin arm CALGB 10603/RATIFY (panel B), and AMLSG historical controls versus placebo arm CALGB 10603/RATIFY (panel C).
Efficacy outcomes: other secondary endpoints
Response to therapy.
The overall CR/CRi rate in the AMLSG 16-10 trial was 74.9%, with no difference between the 2 age groups (18-60 years: 75.9%; 61-70 years: 72.4%); these response rates were superior to those of the historical control group with 64.6% (18-60 years: 66.5%; 61-70 years: 54.0%) (Table 2). Using a logistic regression model in the full analysis set, factors favorably affecting response were treatment within AMLSG 16-10 trial (odds ratio [OR], 1.70; P < .001) and presence of NPM1 mutation (OR, 3.76; P < .001); adverse factors were older age (OR for a 10-year increase, 0.98; P = .013) and higher WBC (OR for a 10-fold increase, 0.68; P = .009) (supplemental Table 8).
Relapse-free survival, cumulative incidence of relapse and death.
The 2-year relapse-free survival was 0.52 in the AMLSG 16-10 trial and 0.32 in the historical population (supplemental Figure 2). Multivariate analysis revealed treatment within the AMLSG 16-10 trial (HR, 0.50; P < .001) and NPM1 mutation (HR, 0.63; P < .001) as significant favorable factors, and older age (HR for a 10-year increase, 1.02; P < .001) as adverse factor. There was a trend for a higher relapse hazard for patients with a FLT3-ITD AR ≥0.5 (HR, 1.22; P = .104) (supplemental Table 9). Results for cumulative incidence of relapse and cumulative incidence of relapse are provided in supplemental Tables 4 and 10 and in supplemental Figure 3.
Effect of allogeneic HCT on EFS within AMLSG 16-10 trial.
The effect of HCT in first CR/CRi on EFS was considered as a time-dependent covariate in a multivariate Cox model in 2 ways, overall and by donor type (MRD vs matched-unrelated donor). In both models, allogeneic HCT had a significantly beneficial effect on EFS (supplemental Table 11); presence of NPM1 mutation was the other variable reducing the risk (supplemental Figure 4).
Study drug exposure and toxicity
Study drug exposure.
In 8 patients, midostaurin was not administered at all. The median number of days on midostaurin treatment in the 432 patients was 61 days (range, 1-557). Exposure to and cumulative doses of midostaurin were comparable for both age groups (supplemental Table 12). During maintenance therapy, median days on treatment and the median cumulative dose of midostaurin were 225 days (207 and 259 days for the younger and older patient cohort, respectively) and 14.825 mg (14.350 and 16.300 mg) (supplemental Table 3).
Dose of midostaurin was reduced at least once in 365 (84%) patients, most commonly because of toxicity (74%). Co-medication (eg, strong CYP3A4 inhibitors) contributed to 19% of dose reductions. Midostaurin administration was interrupted at least once in 40% of the patients, again mostly because of toxicity (73%). The percentage of dose reductions and dose interruptions was comparable between both age groups. The most frequent adverse events (AEs) resulting in discontinuation were thrombocytopenia, nausea/vomiting, graft-versus-host disease, hepatobiliary disease/increase of transaminases, and infections. The frequencies of discontinuation from AEs were similar in both age groups.
Adverse events.
The overall frequencies of AEs with CTCAE grade ≥3 by system organ classes are given in supplemental Table 13. System organ classes affected more frequently in older patients were metabolism and nutrition disorders (P = .003), vascular disorders (P = .04), and in trend cardiac disorders (P = .08) and respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders (P = .07). Cardiac arrhythmias CTCAE grade ≥3 occurred in 17 (4%) patients (10 younger and 7 older patients) and QTc prolongations in 16 (4%) patients (8 younger and 8 older patients). AEs specifically occurring during maintenance treatment and reasons for early termination of maintenance therapy are provided in supplemental Tables 3 and 14 , respectively.
Discussion
Within the AMLSG 16-10 trial, the addition of midostaurin to intensive therapy led to a significant improvement in outcome in younger and older patients with AML and FLT3-ITD in comparison with historical controls. Importantly, the results from the AMLSG 16-10 trial not only confirm the results for the younger patients but also show that treatment with midostaurin in older patients 60 to 70 years of age is safe and leads to a statistically significant improvement in response rates and all survival endpoints in comparison with an AMLSG historical control population. Patients with AML and FLT3-TKD mutations were not eligible because the trial was designed to evaluate the concept of both FLT3 inhibition and early allogeneic HCT and patients with FLT3-TKD mutations were commonly not considered for transplant.16
Results from multivariate analyses showed a highly significant beneficial effect of midostaurin on EFS and OS in patients with FLT3-ITD AML. Of note, the improvement in EFS and OS was even more pronounced in older (61-70 years) compared with younger (18-60 years) patients (Table 3). In the context of this treatment effect of midostaurin, the concurrent presence of NPM1 mutation was a favorable prognostic factor for all survival endpoints, a finding that is consistent with previous reports.8,10-12 Older age and higher WBC counts were consistent unfavorable factors.
We acknowledge the limitations inherent in a single-arm trial with a historical cohort as a control. To address these limitations, we used a double-robust adjustment, that is, propensity score weighting and covariate adjustment in all regression models. Because the treatment period of the historical control was approximately 1 decade earlier compared with the AMLSG 16-10 trial, we also evaluated outcome data of AMLSG 16-10 vs the more contemporary placebo arm of the CALGB 10603/RATIFY trial as a reference matching all eligibility criteria. This comparison confirmed the significant midostaurin treatment effect with a somewhat higher HR for OS (0.71 and 0.59 for AMLSG 16 vs placebo arm of CALGB 10603/RATIFY and AMLSG 16-10 vs our historical controls, respectively; supplemental Table 7; Figure 1).
Allogeneic HCT has been shown to improve outcome of patients with FLT3-ITD-positive AML, although a number of more recent studies have shown that patients of the favorable 2017 ELN risk category may not derive a benefit.11,12,16,20 To address the influence of allogeneic HCT, we performed sensitivity analyses, 1 including HCT as a time-dependent covariate and a second considering HCT as a competing event. In both analyses, the treatment effect of midostaurin remained significant for EFS and OS; other significant variables were allogeneic HCT, age, NPM1 mutation, WBC counts, and a high FLT3-ITD AR (Table 4). In addition, we evaluated the effect of allogeneic HCT in first CR/CRi on EFS using a multivariate Cox model. We restricted this analysis to patients from the AMLSG 16-10 trial because in this trial all patients were assigned to HCT, whereas the algorithms in the historical controls followed a more conservative approach. In this analysis, allogeneic HCT had a significant beneficial effect on EFS, demonstrating that allogeneic HCT both from related and unrelated donors remains an important pillar for the treatment of patients with FLT3-ITD AML (supplemental Figure 4; supplemental Table 11).
With regard to safety, dose of midostaurin was reduced in 84% patients, most commonly because of toxicity (74%); co-medication (eg, strong CYP3A4 inhibitors) contributed to 19% of dose reductions (supplemental Table 3). Dose modifications in the RATIFY trial were necessary in 74.1% of the patients; thus, the rate of dose modifications observed in our study appears comparable, in particular if one considers that in the RATIFY trial midostaurin was not given after allogeneic HCT, but only during induction and conventional consolidation therapy. Midostaurin administration was interrupted in 40% of the patients, again mostly because of toxicity (73%). The most frequent AEs resulting in discontinuation were thrombocytopenia, nausea/vomiting, graft-versus-host disease, hepatobiliary disease/increase of transaminases, and infections. Because AMLSG 16-10 was not a placebo-controlled randomized trial, it is not possible to assess whether dose reductions and interruptions were due to midostaurin per se or to consequences of intensive chemotherapy and/or co-medications. In fact, the RATIFY trial showed a favorable safety profile for midostaurin with no significant differences in grade 3, 4, or 5 nonhematologic AEs between midostaurin and placebo, except for a higher rate of grade ≥3 rash or desquamation.
There has been increasing interest in using FLT3 inhibitors for maintenance treatment, both after conventional consolidation and after allogeneic HCT. The effect of maintenance treatment with midostaurin after conventional consolidation within the CALGB 10603/RATIFY remained inconclusive because there was no second randomization for maintenance.21 Similarly, in our trial, interpretation of results for maintenance treatment is limited to feasibility and safety. Of 237 patients assigned to maintenance, 163 (69%) actually started maintenance, 128 of 201 (64%) after allogeneic HCT and 35 of 83 (42%) after consolidation. The most common reasons for not starting maintenance were AEs. Of note, maintenance therapy appeared to be equally tolerated in younger and older patients, with cumulative doses of midostaurin being even slightly higher in older patients (supplemental Table 3). Two recent studies randomizing sorafenib for maintenance after allogeneic HCT showed a significant survival advantage for patients receiving the TKI.22,23 There are 2 ongoing randomized maintenance studies with gilteritinib, 1 after conventional consolidation (NCT02927262) and another after allogeneic HCT (NCT02997202), which should provide a more definite answer as to the value of TKI maintenance therapy.
The results from this study provide important confirmatory data for those of the pivotal CALGB 10603/RATIFY study in younger adult patients, but importantly extend beyond these previous data in showing a marked survival advantage and a favorable safety profile of midostaurin also in older patients, providing evidence for midostaurin as the new standard of care for these patients. Despite these clinically relevant improvements, outcome of patients with FLT3-ITD-positive AML remains unsatisfactory, with only ∼50% of younger and 30% of older patients experiencing long-term survival. Studies on clonal evolution will be instrumental in elucidating primary and secondary resistance mechanisms under TKI treatment.24,25 Furthermore, the development of sensitive next-generation sequencing-based assays for the detection of measurable residual disease will help in monitoring treatment effects.26,27 Whether the combination of next-generation FLT3 inhibitors with intensive chemotherapy will improve on these results is currently being tested in prospective randomized clinical trials (NCT04027309; NCT03258931).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all members of the German-Austrian AML Study Group (AMLSG) for participation in the trial; a list of AMLSG institutions and investigators appears in the supplemental Material. They also thank Carina Morlok and Margit Mössner for their support in data management. The authors thank additional members of the CALGB 10603/RATIFY Correlative Science Committee (Sergio Amadori, Christian Thiede, Maria Teresa Voso; and Insa Gathmann, Hans Menssen, Celine Pallaud from Novartis) for supporting the study. H.D., K.D., and L.B. are supported by Collaborative Research Center SFB 1074 (project B3, B12, Z02), and by Research Group FOR 2674 (project A02).
Novartis provided financial support and the study drug midostaurin.
Authorship
Contribution: H.D., D.W., R.F.S., A.B., and A.G. undertook study conception and design; H.D. wrote the first draft of the manuscript; and all authors collected, assembled, analyzed and interpretated data, undertook manuscript writing, editing, and approval, revised the manuscript, and reviewed and approved the final version. The AMLSG Clinical Trial Office and the AMLSG statistical team collected and analyzed data in conjunction with all authors.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: H.D. reports an advisory role for AbbVie, Agios, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Berlin-Chemie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, GEMoaB, Gilead, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Syndax and research funding from AbbVie, Agios, Amgen, Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Kronos-Bio, and Novartis. W.F. reports membership on an entity’s board of directors or advisory committee for AbbVie, Amgen, ARIAD/Incyte, Celgene, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, and Pfizer; patents and royalties from Amgen; support for meeting attendance from Amgen, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Servier; and research funding from Amgen and Pfizer. G.W. reports consultancy for Clinigen and Novartis and honoraria from Novartis, Gilead, and Takeda. Helmut Salih reports an advisory role for Synimmune GmbH, Pfizer, Novartis, Celgene, and BMS. M.L. reports an advisory role for AbbVie, Astex Pharmaceuticals, Hexal, Imago BioSciences, Janssen, Pfizer, and Syros and research funding from Janssen, Aristopharm, Cheplapharm, Janssen, and TEVA. M.W.M.K. reports consulting for AbbVie, Kura-Oncology, and Pfizer; travel support from AbbVie, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo; and research funding from Kura-Oncology. T.S. reports an advisory role for AbbVie, Astellas, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Takeda, and Pfizer and speakers honoraria from AbbVie, Astellas, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis. H. Salwender reports honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Chugai, GSK, Janssen, Oncopeptides, Sanofi, Sebia, and Takeda and travel support from Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Janssen, and Sanofi. K.G. reports advisory roles for Celgene/BMS, AbbVie, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals and research funding from Celgene/BMS. J.W. reports an advisory role for Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Amgen, AbbVie, Agios, Jazz, Pfizer, Sanofi, Sobi, and Astellas. L.F. reports an advisory role for AbbVie, Amgen, Medac, Novartis, and Takeda; research funding from Kite and AbbVie; and speaker’s bureau for Celgene. K.M. reports travel support from Novartis, Celgene, Roche, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Astellas. B.H. reports an advisory role for Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Novartis, and Sanofi. H.J.T. reports travel support from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Janssen-Cilag, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi-Aventis, and AbbVie. P.P. reports an advisory role for AbbVie, Agios, Astellas, Astex Pharmaceuticals, Celgene, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Otsuka Pharma, Pfizer, and Sunesis; speakers bureau for Agios, Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Pfizer; and travel support from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, and Takeda. V.I.G. reports an advisory role for AbbVie and Pfizer and speakers bureau for Pfizer and Janssen. F.T. reports an advisory role for AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Pfizer. M.H. reports an advisory role for AbbVie, BMS/Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Tolremo; honoraria from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, and Novartis; and research funding to institution from Astellas, Bayer Pharma AG, BergenBio, Daiichi Sankyo, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Karyopharm, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. R.S.S. reports an advisory role for AbbVie, Agios, Astellas, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Hexal, Neovio Biotech, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; research funding from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, and Roche; and speakers bureau for Astellas and Pfizer. L.B. reports an advisory role for Abbvie, Amgen, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Hexal, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Menarini, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Seattle Genetics, and research funding from Bayer and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. R.L. reports being a consultant or advisor to Novartis, Amgen, Ariad/Takeda, Astellas, Celgene/BMS, CVS/Caremark, Epizyme, and MorphoSys; clinical research support from Novartis, Astellas, Celgene, Cellectis, Daiichi Sankyo, Forty Seven/Gilead, and Rafael Pharmaceuticals; and royalties from UpToDate. R.S. reports an advisory role for Abbvie, Actinium, Agios, Astellas, Biolinerx, Celgene, Daiichi-Sankyo, Elevate, GEMoaB, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Macrogenix, Novartis, OncoNova, Syndax, Syntrix, Syros, Takeda, Trovagen, BerGenBio, Foghorn Therapeutics, Glaxo Smith Kline, Aprea, Innate, Amgen, CTI Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Boston Pharmaceuticals and research funding from Abbvie, Agios, Arog, and Novartis. K.D. reports an advisory role for Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Roche, and Daiichi Sankyo and research funding from: Agios, Astex, Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, and Novartis. A.G. reports an advisory role for Celgene, JAZZ Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Hartmut Döhner, Department of Internal Medicine III, University Hospital of Ulm, Albert-Einstein-Allee 23, 89081 Ulm, Germany; e-mail: hartmut.doehner@uniklinik-ulm.de.
References
Author notes
This clinical trial data can be requested by qualified researchers who perform rigorous, independent research; data will be provided following review and approval of a research proposal and Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP) and execution of a Data Sharing Agreement (DSA). Data will be accessible for 12 months, with possible extensions considered.
The full-text version of this article contains a data supplement.