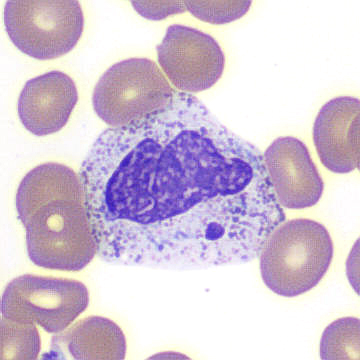
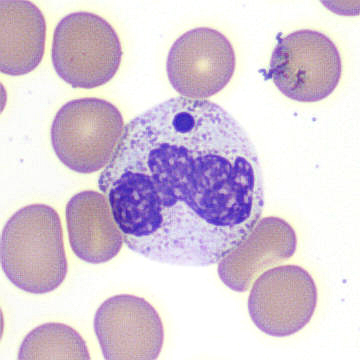
A 65-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease status post renal transplant 19 months ago was admitted with cough, fevers, and shortness of breath. Complete blood count (CBC) on admission showed the following: white blood cell (WBC) count, 1.41 K/mL; hemoglobin, 12.9 g/dL; mean corpuscular volume, 90 fL; and platelets, 163 K/mL. WBC differential was as follows: neutrophils, 55 percent; lymphocytes, including large granular forms, 30 percent; monocytes, 15 percent. Chest X-ray showed ill-defined patchy opacities in the lungs. Infectious work-up was positive for SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) by reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction and negative for all other infections. The figure shows three images from the peripheral blood.
Peripheral blood smear
Peripheral blood smear
Peripheral blood smear
A. Anaplasma spp. morulae
B. Döhle bodies
C. May-Hegglin anomaly
D. Howell-Jolly body–like inclusions
E. Blue-green inclusions
To complete the quiz, visit https://ic.hematology.org/Thehematologist/Image-Challenge/10411.aspx.
Dr. Pozdnyakova and Dr. Kim indicated no relevant conflicts of interest.