Abstract
The role of angiogenesis in lymphoproliferative diseases is not well established. We demonstrate here that human lymphoma cells secrete vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and express VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR-1) and VEGFR-2. Proliferation of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) cells under serum-free conditions was enhanced by the addition of VEGF and was blocked by VEGFR-1– and VEGFR-2–specific antibodies. To differentiate between VEGF-mediated autocrine and paracrine effects on lymphoma growth, NOD/SCID mice engrafted with human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) were treated with species-specific antibodies against human VEGFR-1 (6.12), human VEGFR-2 (IMC-1C11), murine VEGFR-1 (MF-1), or murine VEGFR-2 (DC101). Treatment with 6.12 or DC101 (targeting tumor VEGFR-1 and host VEGFR-2) reduced established DLBCL xenograft growth, whereas treatment with IMC-1C11 or MF-1 (targeting tumor VEGFR-1 and host VEGFR-1) had no effect. Decreased tumor volumes after 6.12 and DC101 treatment correlated with increased tumor apoptosis and reduced vascularization, respectively, supporting the presence of autocrine VEGFR-1– and paracrine VEGFR-2–mediated pathways in lymphomagenesis. Inhibition of paracrine VEGF interactions (DC101) in these models was equivalent to their inhibition with rituximab. Combining DC101 with therapeutic agents (rituximab, 6.12, methotrexate) consistently improved tumor responses over those of single-agent therapy. These data support the further clinical development of VEGFR-targeted approaches for the therapy of aggressive DLBCL.
Introduction
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is the fifth most common cancer in the United States, with an age-adjusted incidence that has increased more than 80% since 1973. Although many patients with lymphoma are cured, more than half eventually die of their disease, making it important to elucidate the specific pathways involved in lymphomagenesis to develop effective novel therapies.1 Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is crucial for solid tumor growth, invasion, and metastases. To date, however, the role of angiogenesis in lymphomagenesis is not well understood. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is the most important proangiogenic factor involved in normal and pathologic angiogenesis.2 The VEGF family is composed of 5 structurally related members— VEGF-A, -B, -C, and -D, and placenta growth factor (PlGF)— whose biologic functions are mediated by the activation of 3 structurally homologous tyrosine kinase receptors: VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3. Most VEGF effects on vascular endothelium in solid tumor angiogenesis are mediated through VEGF/VEGFR-2 interactions, making this receptor the focus of numerous antiangiogenic agents currently in clinical trials. However, recent data have suggested that PlGF, a VEGFR-1–specific ligand, regulates the interaction between VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 by amplifying VEGF-mediated angiogenesis through VEGFR-2, stimulating downstream targets of VEGFR-1, and forming VEGF/PlGF heterodimers capable of stimulating angiogenesis in VEGF-nonresponsive ischemic tissues.3
Previous studies have strongly implicated VEGF and VEGFR in lymphomagenesis. VEGF protein and mRNA have been identified in Hodgkin disease,4 diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL),5 mantle cell lymphoma,6 and virus-related lymphomas.7,8 In indolent lymphoma, increased VEGF expression has been associated with areas of transformation to aggressive DLBCL.5 Elevated VEGF gene expression also correlates with DLBCL subtypes of poor prognosis on microarray analysis.9,10 In patients with lymphoma, high circulating serum VEGF levels have been strongly associated with poor clinical outcomes independent of other predictive factors.11,12 In addition, VEGF has been prominently identified in extranodal sites of lymphoma. High VEGF levels have been found in lymphomatous involvement of bone marrow, central nervous system,13 and pleural effusions.14 Increased in vitro VEGF secretion by high-grade Burkitt lymphoma cells correlates with enhanced tumor engraftment in mouse models,15 and pretreatment with anti-VEGF antibody prevents the development of effusions from VEGF-secreting lymphomas in mice.14,16 Although these studies all implicate VEGF as an important biologic mediator of lymphoma growth, until now there have been no data on the mechanisms behind VEGF-mediated effects, the role of VEGFR in lymphoma, or the potential therapeutic efficacy of VEGF/VEGFR inhibition.
We examined the role of VEGF and VEGFR in promoting NHL growth using a panel of human lymphoma cell lines and human DLBCL xenograft models established in NOD/SCID mice. To differentiate between autocrine and paracrine VEGF/VEGFR path-ways in vivo, human DLBCL xenografts in mice were treated with species-specific, noncross-reactive antibodies for human and murine VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2. We also investigated the effects of combining antiangiogenic antibodies with rituximab (RTX) and chemotherapy on lymphoma xenograft growth. The results presented here confirm the importance of VEGF/VEGFR–mediated pathways in lymphoma growth and support the further development of anti-VEGFR–targeted approaches, alone or in combination regimens, as novel therapeutic agents for aggressive lymphoma.
Materials and methods
Human lymphoma cell lines
Eight human B-cell NHL lines were obtained from the American Tissue Culture Collection (Manassas, VA) and from colleagues at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (New York, NY). All lines have been described previously. Five cell lines (DoHHT, OCI-Ly2, HT, RL, SKI-DLBCL1) represent DLBCL.17-19 The Raji and Ramos cell lines represent Burkitt lymphoma, and the Hs602 cell line represents a nonspecific B-cell lymphoma.20 Known genetic abnormalities in these cells include mutated p53 (HT, RL), t(14;18) (RL), and t(1;14)(q21;q32) (SKI-DLBCL1).18,19 The RL and SKI-DLBCL1 cell lines used in xenografts were of the germinal cell (GC)–like DLBCL subtype based on cluster analysis in comparison with the Lymphochip cDNA array data (data not shown). Cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium with 10% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, 4.5 g/L glucose, 1.5 g sodium bicarbonate, 1 U/mL penicillin/streptomycin, 10 mM HEPES (N-2-hydroxyethylenepiperazine-N-2′-ethanesulfonic acid), and 1 nM sodium pyruvate. Cells were maintained in humidified incubators at 37°C with 5% CO2.
VEGFR antibodies
Species-specific, noncross-reactive neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against human and murine VEGFR were provided by ImClone Systems Inc (New York, NY) and have been previously described in the literature.21-25 Antibodies included murine anti–human VEGFR-1 (clone 6.12), rat anti–murine VEGFR-1 (clone MF-1), rat anti–mouse VEGFR-2 (clone DC101), and human anti–VEGFR-2 antibodies (IMC-1C11, IMC-2C6) derived from Fab′ fragments originally isolated from a large antibody phage display library. Human immunoglobulin (Sandoglobulin; Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Summit, NJ) was the negative control.
Antibody-binding assay procedures
To determine the specificity of anti–VEGFR-1 and -2 monoclonal antibodies to respective receptors, 1 mg/mL recombinant human VEGFR-1 Fc, mouse VEGFR-1 Fc, mouse VEGFR-2 Fc (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN), or recombinant human VEGFR-2, alkaline phosphatase (ImClone Systems) was coated in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) in 96-well microtiter plates at 4°C overnight. After washing with PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20 (Sigma, St Louis, MO), the receptor-coated plates were blocked with PBS containing 5% dry milk (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) and 0.05% Tween 20 (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [ELISA] buffer). Serial dilutions of the primary antibody MF-1 (rat IgG1), DC101 (rat immunoglobulin G1 [IgG1]), 6.12 (mouse IgG1), and 1C11 (human IgG1) were incubated with ELISA buffer in receptor-coated plates for 30 minutes. The plates were washed 4 times. Goat anti–mouse immunoglobulin, anti–human κ (BioSource International, Camarillo, CA), or goat anti–rat IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch Labs, West Grove, PA) horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugate for each respective primary antibody was diluted in ELISA buffer and incubated in plates for 30 minutes. After washing, TMB (3,3′, 5,5′-tetra-methylbenzidine) substrate (Kirkegaard and Perry Laboratories, Gaithersburg, MD) was added in the plate for color development according to the manufacturer's instruction. Absorbance (450 nm) was read on a microtiter plate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA) for quantification of antibody-binding activity.
VEGF immunocytochemistry
Cytospin preparations of cells were dried, fixed in cold acetone, and evaluated for cytoplasmic VEGF using polyclonal rabbit anti–human VEGF antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) as previously described.26
Expression of VEGFR
VEGFR expression was determined by flow cytometry using human VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 antibodies (ImClone Systems) conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) with commercial reagents. Lymphoma cells were fixed and stained for VEGFR on the cell surface and after membrane permeabilization (IntraPrep Permeabilization Reagent; Immunotech, Marseille, France). Percentages of cells expressing VEGFR were quantitated using Cell Quest software with mean ± SE expression from 3 experiments shown.
Production of human VEGF under serum starvation conditions
Lymphoma cells (1 × 106) were incubated in 5 mL serum-free media for 24 hours before measurement of human VEGF, PlGF, and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in the cell-free supernatant using commercial ELISA kits (R&D Systems). Samples were plated in triplicate wells. Experiments were repeated 3 times.
Proliferation assays
Cells were incubated at 2 × 104 cells/well in triplicate in 96-well, round-bottom plates for 48 hours under different conditions: serum-free media alone, VEGF165 (50 ng/mL) (R&D Systems), PlGF (200 ng/mL) (R&D Systems), 6.12 antibody (10 μg/mL), IMC-1C11 or IMC-2C6 antibody (10 μg/mL), and combinations of growth factors with antibodies. [3H]-Thymidine (0.5 μCi/well [0.0185 MBq/well]) (Perkin Elmer, Boston, MA) was added for 18 hours, and [3H]-thymidine incorporation was assayed by scintillation counting using a β-counter (Packard Instrument, Meriden, CT). Experiments were repeated at least 3 times.
Lymphoma xenograft experiments
Eight-week-old female nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mice (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME) were sublethally irradiated with 3 cGy and inoculated with 10 × 106 lymphoma cells (RL, SKI-DLBCL1) under the skin, as described previously, according to an institute-approved animal protocol.27 When tumor volumes approached 100 mm3, mice were divided into experimental groups of 5 to 10 mice per group and were treated by intraperitoneal injection with 800 μg immunoglobulin (IVIG) 3 times a week, 400 μg IMC-1C11 or IMC-2C6 twice a week, 400 μg DC101 3 times a week, 800 μg MF-1 twice a week, 800 μg 6.12 twice a week, and 25 mg/kg chimeric murine/human monoclonal antibody against CD20 antigen twice a week (Rituxan; IDEC Pharmaceuticals, San Diego, CA).28 Methotrexate (MTX) was given at the maximally tolerated dose of 40 mg/kg intraperitoneally twice weekly for 4 doses based on previous data.29,30 Combination regimens of antibodies and chemotherapy used the same dosing regimens and intervals. Mice were routinely assessed for weight loss, anorexia, and other clinical signs. The 2 largest perpendicular axes of each tumor xenograft (l indicates length; w, width) were measured 3 times weekly with calipers, and tumor volume (TV) was calculated using the formula: TV (mm3) = 4/3πr3, where r = (l + w)/4. Animals were killed when they became moribund from progressive tumor-related signs or when the 1-dimensional tumor diameter exceeded 2.0 cm (according to the guidelines of the animal core facilities).
Results of xenograft experiments are shown as mean tumor volume (mTV) ± SE) at each time point for treatment groups of at least 5 to 10 mice. Statistical evaluation of differences in mTV between groups was performed using 2-tailed student t test analysis with unequal variance. P < .05 was considered significant.
Immunohistochemistry of tumor xenografts
Tumor-bearing mice were killed at the end of treatment. Lymphoma xenografts harvested at necropsy were evaluated by immunohistochemistry after fixation in 10% formalin-and-paraffin embedding. Four-micron–thick sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Giemsa for histologic examination. Apoptotic cells were identified using TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling) staining. Slides were deparaffinized, rehydrated, and digested in 20 μg/mL proteinase K for 15 minutes at room temperature. The slides were then washed in PBS and refixed in 4% formalin, washed again in PBS, and equilibrated. Biotinylated nucleotide mix and TdT enzyme were added and incubated for 90 minutes at 37°C. Slides were washed in PBS, blocked in 2% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBS, and incubated in ABC vector reagent for 1 hour at room temperature. Slides were developed in 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) and counterstained with Harris hematoxylin before dehydration and mounting. Numbers of apoptotic cells per low-power field (40 ×) were quantitated in triplicate. Microvessel density was quantified in multiple low-power fields with light microscopy after immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of tissues using antibodies against factor VIII (FVIII; von Willebrand factor; DAKO, Carpinteria, CA), CD31 (1:200; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), CD34 (1:200; PharMingen, San Diego, CA), and reticulin fibers. For FVIII staining, tissues were incubated with 3% hydrogen peroxide, PBS, and 0.05% Pronase E (Sigma) for 10 minutes before incubation with anti–FVIII-HRP (DAKO) for 1 hour, followed by chromogenic substrate solution (DAB) counterstaining. Evaluation of tissue proliferation rates was performed with the monoclonal MIB-1 (Ki-67) antibody (1:200 dilution; DAKO) using antigen retrieval. Slides were evaluated using an Olympus B × 40 light microscope with 10 × /0.30, 20 × /0.50, and 40 × /0.75 lenses and photographed with a Hitachi HV-C20U color camera using Image Pro Plus software (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD) for acquisition and Adobe Photoshop software (Adobe Systems, Mountain View, CA) for processing.
Results
Lymphoma cells produce VEGF
Immunohistochemical staining for VEGF protein was performed on cytospins of cultured lymphoma cells. Strong intracytoplasmic staining for VEGF protein was noted in all cell lines (Figure 1A). Most NHL cell lines also secreted measurable VEGF levels under serum starvation conditions in vitro with significant levels of VEGF production (greater than 50 pg/106 cells) seen in 4 of the 8 cell lines (Table 1), consistent with data demonstrating high engraftment rates of these cell lines in NOD/SCID mice.15 Of note, no measurable PlGF or bFGF production was detected under identical conditions (data not shown).
NHL cell lines express VEGF and VEGFR. (A) Representative results of immunohistochemistry staining for cytoplasmic VEGF in lymphoma cell cytospins. VEGF-positive control is on the top, and RL lymphoma cells are on the bottom (original magnification × 20). Results of (B) surface and (C) intracytoplasmic VEGFR expression as determined by flow cytometry on RL and SKI-DLBCL1 cells are shown.
NHL cell lines express VEGF and VEGFR. (A) Representative results of immunohistochemistry staining for cytoplasmic VEGF in lymphoma cell cytospins. VEGF-positive control is on the top, and RL lymphoma cells are on the bottom (original magnification × 20). Results of (B) surface and (C) intracytoplasmic VEGFR expression as determined by flow cytometry on RL and SKI-DLBCL1 cells are shown.
Lymphoma cells express surface and intracellular VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2
For systemically administered anti-VEGFR antibodies to inhibit malignant growth, tumor cells must express surface VEGFR accessible for antibody binding. Flow cytometry analysis of a panel of human lymphoma cell lines was performed using anti–VEGFR-1 and anti–VEGFR-2 antibodies conjugated to fluorescent dyes. Most lymphoma cells expressed more VEGFR-1 than VEGFR-2 on the cell surface. Because surface receptor expression can fluctuate to some degree depending on growth conditions, intracellular levels of VEGFR were also measured to determine whether a pool of quiescent receptors was present in the cytoplasm for up-regulation. High levels of VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 were readily identified in the cytoplasm of most lymphoma cells with the same antibodies (Figure 1B-C; Table 1).
Species specificity of anti-VEGFR antibodies
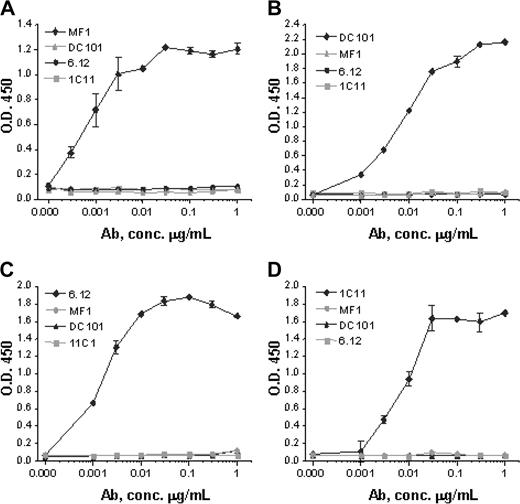
Monoclonal antibodies specific for murine VEGFR-1 (MF-1), murine VEGFR-2 (DC101), human VEGFR-1 (6.12), and human VEGFR-2 (IMC-1C11) were generated as previously described.21-25 Anti-VEGFR antibody assays using plates coated with recombinant human VEGFR-1 Fc, mouse VEGFR-1 Fc, human VEGFR-2 Fc, or mouse VEGFR-2 Fc demonstrated that each antibody strictly bound to its respective receptor with no cross-reactivity (Figure 2).
Anti-VEGFR antibody specificity. Monoclonal antibodies MF-1 against mouse VEGFR-1, DC101 against mouse VEGFR-2, 6.12 against human VEGFR-1, and IMC-1C11 (abbreviated 1C11) against human VEGFR-2 specifically bind in dose-response fashion to (A) mouse VEGFR-1, (B) mouse VEGFR-2, (C) human VEGFR-1, and (D) human VEGFR-2, respectively. No antibody shows cross-reactivity with any other VEGFR or with the same receptor from the other species. These results indicate that each antibody has a strict binding specificity with its respective receptor. Error bars indicate standard error of mean absorbance.
Anti-VEGFR antibody specificity. Monoclonal antibodies MF-1 against mouse VEGFR-1, DC101 against mouse VEGFR-2, 6.12 against human VEGFR-1, and IMC-1C11 (abbreviated 1C11) against human VEGFR-2 specifically bind in dose-response fashion to (A) mouse VEGFR-1, (B) mouse VEGFR-2, (C) human VEGFR-1, and (D) human VEGFR-2, respectively. No antibody shows cross-reactivity with any other VEGFR or with the same receptor from the other species. These results indicate that each antibody has a strict binding specificity with its respective receptor. Error bars indicate standard error of mean absorbance.
Autocrine VEGF/VEGFR-1 and VEGF/VEGFR-2 growth pathways are present in lymphoma cells in vitro
Because autocrine growth pathways mediated by VEGF are known to occur in solid tumor cells overexpressing VEGFR,31-33 we evaluated the proliferation of serum-starved lymphoma cells in the presence of exogenous VEGF and exogenous PlGF using [3H]-thymidine incorporation assays. Growth of lymphoma cell lines was enhanced in the presence of exogenous VEGF (P < .05) and was inhibited in the presence of neutralizing antibody against VEGFR-2 (IMC-1C11) (Figure 3A). Because these cells are known to secrete VEGF under culture conditions, serum-starved lymphoma cells were exposed to 2 anti–VEGFR-2 antibodies (IMC-1C11 and IMC-2C6) in the absence of exogenous VEGF, with further reduction in proliferation noted when compared with controls. The proliferative effects of VEGF on human lymphoma, therefore, appeared to be mediated in part by VEGFR-2 interactions (Figure 3A; data not shown).
Lymphoma proliferation experiments. Cells (RL, SKI-DLBCL) were plated at 2 × 104 cells/well in triplicate in 96-well, round-bottom plates and were incubated for 48 hours in the presence of serum-free media, growth factors, or VEGFR antibodies. [3H]-Tritiated thymidine (0.5 μCi/well [0.0185 MBq/well]) was added, and radioisotope incorporation into cells after 18 hours of exposure was measured. Experiments were performed at least 3 times, and results of 1 representative experiment are shown. Because of variations in baseline [3H]-tritiated thymidine incorporation between experiments, data are expressed as fold change of the serum-free control for each experiment. (A) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, VEGF (50 ng/mL), anti–human VEGFR-2 antibody (IMC-1C11 10 μg/mL), or VEGF + IMC-1C11 (same concentrations). (B) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, PlGF (200 ng/mL), anti–human VEGFR-1 antibody (6.12 10 μg/mL), or PlGF + 6.12 (same concentrations). (C) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, VEGF (50 ng/mL), 6.12 (10 μg/mL), or VEGF + 6.12 (same concentrations).
Lymphoma proliferation experiments. Cells (RL, SKI-DLBCL) were plated at 2 × 104 cells/well in triplicate in 96-well, round-bottom plates and were incubated for 48 hours in the presence of serum-free media, growth factors, or VEGFR antibodies. [3H]-Tritiated thymidine (0.5 μCi/well [0.0185 MBq/well]) was added, and radioisotope incorporation into cells after 18 hours of exposure was measured. Experiments were performed at least 3 times, and results of 1 representative experiment are shown. Because of variations in baseline [3H]-tritiated thymidine incorporation between experiments, data are expressed as fold change of the serum-free control for each experiment. (A) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, VEGF (50 ng/mL), anti–human VEGFR-2 antibody (IMC-1C11 10 μg/mL), or VEGF + IMC-1C11 (same concentrations). (B) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, PlGF (200 ng/mL), anti–human VEGFR-1 antibody (6.12 10 μg/mL), or PlGF + 6.12 (same concentrations). (C) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, VEGF (50 ng/mL), 6.12 (10 μg/mL), or VEGF + 6.12 (same concentrations).
Adding exogenous PlGF to serum-starved lymphoma cells under the same conditions enhanced the proliferation measured by [3H]-thymidine uptake. This proliferation was decreased in the presence of anti–VEGFR-1 antibody (6.12) in DLBCL cell lines, possibly through the inhibition of autocrine endogenous VEGF effects mediated by VEGFR-1 and PlGF/VEGFR-1 interactions because these cell lines did not secrete measurable PlGF under these culture conditions (data not shown) (Figure 3B). Exposing lymphoma cells to either 6.12 (anti–VEGFR-1) or IMC-1C11 (anti–VEGFR-2) antibodies inhibited proliferation stimulated by exogenous VEGF, suggesting that the VEGF ligand may function through either VEGFR-1– or VEGFR-2–mediated pathways to promote growth (Figure 3A-C). These data could be interpreted as supporting the presence of 2 independent autocrine pathways regulating VEGF effects in a redundant fashion under hypoxic conditions; alternatively, these receptors may exist as heterodimers or may mediate similar responses by crosstalk between the receptors.3
Inhibiting autocrine VEGFR-1–mediated pathways decreases growth of lymphoma xenografts
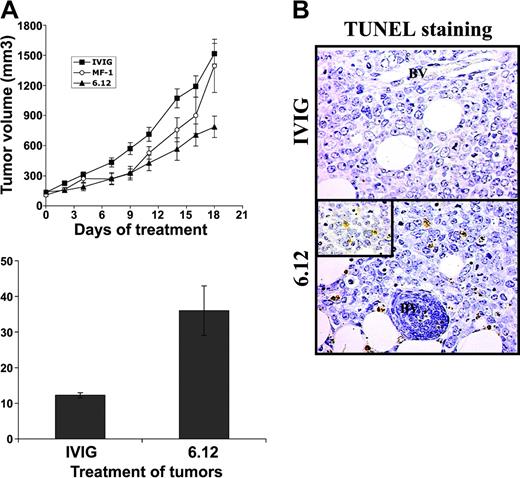
To determine the relative contribution of autocrine VEGF/VEGFR autocrine pathways compared with VEGF-mediated paracrine effects mediated by host endothelial cells on lymphoma growth, additional experiments were performed using NOD/SCID mice engrafted with 2 human DLBCL cell lines (RL, SKI-DLBCL) used in vitro.27 The effects of VEGF/VEGFR-1 autocrine pathways and paracrine pathways were examined and compared by treating mice engrafted with human lymphoma with species-specific, noncross-reactive antibodies directed against human (6.12) and mouse (MF-1) VEGFR-1 for 3 weeks.34 Inhibiting human VEGFR-1 resulted in more than 50% decreased tumor growth compared with controls, whereas treatment with MF-1 had no significant antitumor effect (P < .05) for IVIG compared with 6.12 on days 2 to 19 (Figure 4A). Paraffin sections from tumor xenografts collected from animals after the completion of treatment demonstrated markedly higher numbers of apoptotic lymphoma cells (by TUNEL staining per low-power field) after 6.12 (36 ± 6.9 cells) compared with controls (12 ± 0.8 cells) (Figure 4B-C).
Inhibition of autocrine VEGFR-1 pathways reduces growth of established lymphoma xenografts in NOD/SCID mice and correlates with increased tumor apoptosis. Sublethally irradiated NOD/SCID mice were engrafted with subcutaneous RL lymphoma xenografts and were treated by intraperitoneal injection 3 times weekly with human immunoglobulin (IVIG), anti–human VEGFR-1 (6.12), or anti–murine VEGFR-2 (MF-1) antibodies. (A) Mean tumor volumes (± SE) are shown for experimental groups of 5 to 10 mice. Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for IVIG compared with 6.12 on days 2 to 19. (B) Immunohistochemical staining of xenografts following treatment demonstrated increased tumor apoptosis after VEGFR-1 (6.12) treatment compared with controls (BV = blood vessels). Inset shows TUNEL+ apoptotic lymphoma cells at 40 × magnification. (C) Quantification of the mean number of TUNEL+ cells (± SE) per low-power field (10 ×) in treated xenografts is shown (P < .05).
Inhibition of autocrine VEGFR-1 pathways reduces growth of established lymphoma xenografts in NOD/SCID mice and correlates with increased tumor apoptosis. Sublethally irradiated NOD/SCID mice were engrafted with subcutaneous RL lymphoma xenografts and were treated by intraperitoneal injection 3 times weekly with human immunoglobulin (IVIG), anti–human VEGFR-1 (6.12), or anti–murine VEGFR-2 (MF-1) antibodies. (A) Mean tumor volumes (± SE) are shown for experimental groups of 5 to 10 mice. Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for IVIG compared with 6.12 on days 2 to 19. (B) Immunohistochemical staining of xenografts following treatment demonstrated increased tumor apoptosis after VEGFR-1 (6.12) treatment compared with controls (BV = blood vessels). Inset shows TUNEL+ apoptotic lymphoma cells at 40 × magnification. (C) Quantification of the mean number of TUNEL+ cells (± SE) per low-power field (10 ×) in treated xenografts is shown (P < .05).
Inhibiting paracrine VEGFR-2–mediated pathways decreases growth of established DLBCL lymphoma xenografts
To differentiate between tumor versus host VEGF/VEGFR-2–mediated effects on lymphomagenesis, mice engrafted with human lymphoma (RL, SKI-DLBCL1) were treated with species-specific antibodies against human VEGFR-2 (IMC-1C11), murine VEGFR-2 (DC101), or IMC-1C11 + DC101.25 Inhibiting host VEGFR-2 interactions (DC101 therapy) alone reduced established tumor volumes by more than 50% (SKI-DLBCL1, day 21 mTV: IVIG = 1333 ± 172 mm3; DC101 = 741 ± 94 mm3; IVIG vs DC101, P < .05 on days 15-21). In contrast, treatment with anti–human VEGFR-2 antibody (IMC-1C11) had no antitumor effects (SKI-DLBCL1, day 21 mTV: IVIG = 1333 ± 172 mm3; IMC-1C11 = 1604 ± 197 mm3; P > .05). Experiments were repeated using an anti–human VEGFR-2 antibody (IMC-2C6) with higher receptor-binding affinity than IMC-1C11, with no difference in results (data not shown).24 Results were similar in RL and SKI-DLBCL1 xenograft models (Figure 5A).
Inhibition of paracrine VEGFR-2 pathway reduces growth of established lymphoma xenografts in NOD/SCID mice and correlates with decreased tumor angiogenesis. (A) NOD/SCID mice engrafted with subcutaneous RL and SKI-DLBCL1 lymphoma tumors were treated with IVIG, anti–human VEGFR-2 (IMC-1C11), anti–murine VEGFR-2 (DC101), or DC101 + IMC-1C11 antibodies (n = 5-10 mice/group). Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for IVIG compared with DC101 on days 15 to 21 in both models. (B, C) Lymphoma xenografts from mice treated with IVIG, IMC-1C11, DC101, or DC101 + IMC-1C11 were stained with antibodies for CD34 (10 ×,20 ×), FVIII (von Willebrand factor 10 ×), and CD31 (10 ×). DC101 treatment decreased the number of vascular endothelial cells in vessels (von Willebrand factor and CD34 expression) and overall microvessel density (CD31+ and CD34+ vessels) compared with IVIG or IMC-1C11 treatment. Error bars indicate standard error of mean tumor volume.
Inhibition of paracrine VEGFR-2 pathway reduces growth of established lymphoma xenografts in NOD/SCID mice and correlates with decreased tumor angiogenesis. (A) NOD/SCID mice engrafted with subcutaneous RL and SKI-DLBCL1 lymphoma tumors were treated with IVIG, anti–human VEGFR-2 (IMC-1C11), anti–murine VEGFR-2 (DC101), or DC101 + IMC-1C11 antibodies (n = 5-10 mice/group). Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for IVIG compared with DC101 on days 15 to 21 in both models. (B, C) Lymphoma xenografts from mice treated with IVIG, IMC-1C11, DC101, or DC101 + IMC-1C11 were stained with antibodies for CD34 (10 ×,20 ×), FVIII (von Willebrand factor 10 ×), and CD31 (10 ×). DC101 treatment decreased the number of vascular endothelial cells in vessels (von Willebrand factor and CD34 expression) and overall microvessel density (CD31+ and CD34+ vessels) compared with IVIG or IMC-1C11 treatment. Error bars indicate standard error of mean tumor volume.
Immunohistochemical examination of tumors collected after the completion of therapy demonstrated marked differences in tumor angiogenesis between treatment groups. DC101-treated tumors exhibited marked areas of necrosis, with large cystic areas in tumors surrounded by rims of viable cells compared with dense, rapidly proliferating control tumors (not shown). Overall microvessel density of lymphoma tumors, determined by CD31, CD34, and reticulin staining, was reduced in DC101-treated tumors with 2- to 3-fold fewer blood vessels per tissue section than with IVIG- or IMC-1C11–treated tumors (Figure 5B-C; data not shown). DC101 treatment also decreased endothelial cell staining in capillaries (CD34) and larger blood vessels (FVIII) compared with controls, suggesting a decrease in the number of vascular endothelial cells (Figure 5B-C). DC101 antibody therapy has been shown to inhibit murine endothelial cell migration and proliferation and to enhance endothelial cell apoptosis in Matrigel assays.21,35,36 In solid tumor xenografts, DC101 treatment has also been reported to decrease microvessel density and to increase endothelial apoptosis in a similar fashion21,36 ; however, these are the first data to demonstrate these antiangiogenic effects in lymphoma.
Combining antiangiogenic treatment with other agents targeting lymphoma growth (RTX, 6.12, MTX) consistently improves tumor responses over single-agent therapy
These data demonstrate the presence of tumor-specific autocrine VEGF/VEGFR-1 pathways and paracrine VEGF/VEGFR-2 loops between lymphoma cells and the host endothelium. Antiangiogenic therapy aimed at inhibiting the interactions between tumors and vascular endothelial cells are promising for antitumor manipulation because endothelial cells are genetically more stable than rapidly proliferating malignant cells. In addition, therapies targeting the tumor microenvironment are likely to complement conventional agents (ie, cytotoxic agents aimed at cycling cells).
We investigated the efficacy of combining an antiangiogenic agent (DC101) with other therapeutic agents targeting autocrine growth pathways on established RL lymphoma xenografts in mice. Combining anti–human VEGFR-1 antibody (6.12) with DC101 resulted in additive effects with improvement in antitumor effects (ie, more than 70% inhibition of established xenograft growth) compared with antibody monotherapy (P < .05 for 6.12 vs 6.12 + DC101 days 16-21, DC101 vs 6.12 + DC101 days 18-21) (Table 2). Immunohistochemistry of tumors harvested at treatment completion demonstrated increased apoptotic tumor cells (35 ± 5.4 per low-power field) after DC101 + 6.12 treatment than after 6.12 (23 ± 1.2 or DC101 21 ± 2.2 treatment alone or control 10 ± 0.9) (Figure 6A; data not shown).
Combining antiangiogenic (DC101) therapy with anti–VEGFR-1 (6.12) antibody, chemotherapy, or RTX therapy enhances antitumor effects. NOD/SCID mice engrafted with subcutaneous human lymphoma xenografts were treated with antibodies through intraperitoneal injection for 3 weeks. Comparison of results on treatment day 21 is shown. (A) Tumor growth curves of RL lymphoma xenografts treated with immunoglobulin (IVIG), anti–human VEGFR-1 (6.12), anti–murine VEGFR-2 (DC101), or both antibodies (6.12 + DC101) (n = 9-16 mice/group). Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for 6.12 vs 6.12 + DC101 on days 16 to 21 and for DC101 vs 6.12 + DC101 on days 18 to 21. (B) Tumor growth curves of RL lymphoma xenografts treated with immunoglobulin (IVIG), maximally tolerated MTX, DC101, or MTX + DC101 (n = 8-10 mice/group). Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for IVIG compared with MTX + DC101 on days 4 to 21 and for DC101 compared with MTX + DC101 on days 16, 18, and 21. (C) Tumor growth curves of SKI-DLBCL1 lymphoma xenografts treated with IVIG, RTX, DC101, and RTX + DC101 (n = 10 mice/group). Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for DC101 compared with RTX + DC101 and for RTX vs RTX + DC101 on days 19 to 21. Error bars indicate standard error of mean tumor volume.
Combining antiangiogenic (DC101) therapy with anti–VEGFR-1 (6.12) antibody, chemotherapy, or RTX therapy enhances antitumor effects. NOD/SCID mice engrafted with subcutaneous human lymphoma xenografts were treated with antibodies through intraperitoneal injection for 3 weeks. Comparison of results on treatment day 21 is shown. (A) Tumor growth curves of RL lymphoma xenografts treated with immunoglobulin (IVIG), anti–human VEGFR-1 (6.12), anti–murine VEGFR-2 (DC101), or both antibodies (6.12 + DC101) (n = 9-16 mice/group). Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for 6.12 vs 6.12 + DC101 on days 16 to 21 and for DC101 vs 6.12 + DC101 on days 18 to 21. (B) Tumor growth curves of RL lymphoma xenografts treated with immunoglobulin (IVIG), maximally tolerated MTX, DC101, or MTX + DC101 (n = 8-10 mice/group). Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for IVIG compared with MTX + DC101 on days 4 to 21 and for DC101 compared with MTX + DC101 on days 16, 18, and 21. (C) Tumor growth curves of SKI-DLBCL1 lymphoma xenografts treated with IVIG, RTX, DC101, and RTX + DC101 (n = 10 mice/group). Results were statistically significant (P < .05) for DC101 compared with RTX + DC101 and for RTX vs RTX + DC101 on days 19 to 21. Error bars indicate standard error of mean tumor volume.
DC101 therapy was also combined with MTX, an antimetabolite chemotherapeutic agent, in the treatment of RL xenografts previously shown to be resistant to MTX.27 DC101 monotherapy was more effective than MTX in inhibiting xenograft growth (day 21 mTV: IVIG = 1774 ± 493 mm3, DC101 = 972 ± 112 mm3, P < .002; MTX = 1341 ± 145 mm3, P = .07). Combination DC101 + MTX had synergistic effects, and tumor volumes were reduced by 70% to 80% (day 21 mTV: DC101 + MTX = 530 ± 113 mm3; P < .0001) (DC101 vs DC101 + MTX days 16-21; P < .05) (Figure 6B and Table 3).
Anti–VEGFR-2 antibody treatment was administered concomitantly with RTX, a chimeric murine/human monoclonal antibody against CD20 used to treat aggressive DLBCL,37 in SKI-DLBCL1 lymphoma xenograft models. DC101 monotherapy was as effective as RTX in inhibiting the growth of established tumors (SKI-DLBCL1 day 21 mTV: IVIG = 1083 ± 113 mm3, RTX = 568 ± 92 mm3, DC101 = 566 ± 95 mm3; P < .003) (Table 4). Combination RTX + DC101 therapy had additive antitumor effects, effectively reducing tumor volumes by 75% (day 21 mTV: IVIG = 1083 ± 113 mm3, DC101 + RTX = 298 ± 36 mm3; P < .0001) with improved efficacy compared with monotherapy (RTX vs RTX + DC101 days 12-21, DC101 vs DC101 + RTX days 19-21; P < .05) (Figure 6C and Table 4).
Discussion
Antiangiogenic approaches as a means to control malignant growth have been explored extensively in solid tumors and leukemia38 but to date have not been documented in lymphoid malignancies. Several studies have demonstrated that high levels of VEGF protein and mRNA expression in primary lymphoma samples correlate with advanced tumor grade and higher risk for relapsed/refractory disease after standard chemotherapy.5,9 The goal of this study was to define the role of VEGF and VEGFR in lymphomagenesis and to target these pathways for potential therapeutic effects. Here we confirm the presence of high VEGF, VEGFR-1, and VEGFR-2 levels in human lymphoma cells, and we demonstrate that inhibiting autocrine VEGFR-1– or paracrine VEGFR-2–mediated loops with receptor-specific antibodies suppressed the growth of established DLBCL tumors by increasing tumor apoptosis and decreasing vascularization, respectively. Furthermore, inhibiting VEGF/VEGFR-2 interactions between tumor and host endothelia potentiated the effects of antimetabolite chemotherapy and RTX. These results confirm the role of VEGF in lymphomagenesis and support the targeting of VEGFR pathways as a novel therapeutic approach for aggressive lymphoma.
Although VEGFR is normally found only on vascular endothelial cells, aberrant expression of this tyrosine receptor kinase has been found on tumor cells, possibly as a result of malignant transformation events.31 Accumulating data suggest that for cells with VEGFR, VEGF is capable of functioning through autocrine growth mechanisms to promote tumor survival in certain environments.31 For example, VEGF interacts with functional VEGFR2/KDR receptors on the surfaces of HL60 leukemia cells to stimulate downstream antiapoptotic bcl-2 and hsp90-mediated pathways to enhance tumor growth.39 VEGF-mediated autocrine loops have also been identified in breast, prostate, sarcoma, and other solid tumor cell lines (Y.W., C. Costa, A. Hooper, et al, manuscript submitted).40,41 High VEGF expression has been correlated with higher tumor grade, increased lymphatic and vascular permeability of tumors,42 oncogenic transformation,43 and enhanced metastases.44 Although VEGF may function in a host of different pathways to promote tumorigenesis, tumors of different tissue origins tend to use specific VEGF-mediated mechanisms to facilitate growth in vivo.45-47
The finding of high levels of VEGF and its receptors (VEGFR-1 and -2) in lymphoma cells supports the existence of VEGF ligand/VEGFR–mediated autocrine loops. To confirm this, serumstarved NHL cell lines were treated with exogenous PlGF or VEGF in vitro and were found to have higher levels of DNA synthesis in the presence of these factors than controls. Blocking VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 pathways using receptor-specific neutralizing antibodies abolished PlGF- or VEGF-induced proliferation, respectively, suggesting that in vitro lymphoma growth was mediated in an autocrine fashion by VEGF/PlGF/VEGFR-1 and VEGF/VEGFR-2 interactions. These results are consistent with reports that VEGF binding to VEGFR-2/KDR promotes tumor growth31 and that VEGF and PlGF binding to VEGFR-1 are critical in inducing vasculogenesis in pathologic angiogenic states such as malignancy.22
In vivo experiments to corroborate these findings were performed in established tumor xenografts with the same anti–human VEGFR-1 and anti–human VEGFR-2 antibodies used in proliferation assays. In these studies, inhibiting human VEGFR-1 decreased lymphoma growth to 50% that of controls, whereas inhibiting human VEGFR-2 pathways did not. Experiments were repeated in 2 different xenograft models with similar results. These data highlight the need to assess the effects of biologic agents in vivo because signaling pathway dependence of tumor cells may be altered significantly in the presence or absence of the extracellular matrix or the microenvironment.48
Discovering an autocrine VEGFR-1–mediated loop in lymphoma is not surprising because VEGFR-1– and PlGF-mediated growth pathways have been found in human breast cancer and melanoma.40 VEGF and PlGF are known to work synergistically to promote vasculogenesis in epithelial tumor formation.49 However, this is the first time these pathways have been identified in hematologic malignancies. The VEGFR-1 ligand system is routinely involved in the regulation of hematopoietic and inflammatory cells,50 and it is possible that malignant B lymphocytes have retained this pathway to regulate the migration and proliferation of cells in extranodal sites. VEGF and VEGFR-1/flt-1 receptors have been identified in most primary B-cell lymphoma samples (including marrow samples) and cell lines.5,6,16 Our data showing that neutralizing this VEGFR-1 pathway reduces the growth of established lymphoma xenografts is also consistent with reports in which the inhibition of VEGFR-1 using genetically modified mice lacking flt-1 kinase domains,51 exogenous catalytic RNA molecules,52 or exogenous anti–flt-1 antibody22 markedly inhibited the growth of breast and epithelial tumors.
Although VEGF/VEGFR-2–mediated interactions between tumor and vascular endothelial cells are known to be critical for angiogenesis in solid tumors,21 similar pathways have not been described in lymphoma until now. In addition, high serum VEGF levels have recently been shown to recruit circulating hematopoietic VEGFR-1+VEGFR-2+ endothelial precursor cells from host bone marrow to localized tumors to enhance tumor neovascularization.34 Although these phenomena have been demonstrated convincingly in murine tumor models, the clinical significance of these mechanisms is not yet clear and is under intensive investigation.53 To distinguish between the relative contributions of host VEGFR-1– and VEGFR-2–mediated effects to lymphoma growth in vivo, NOD/SCID mice engrafted with human DLBCL were treated with specific anti–mouse VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 antibodies. Inhibiting paracrine VEGFR-2 interactions (DC101) reduced tumor growth, whereas inhibiting paracrine VEGFR-1 pathways (MF-1) did not, suggesting that though VEGFR-2+ vascular endothelial and precursor cells are important for lymphomagenesis,34 VEGFR-1+ hematopoietic precursors from the bone marrow are not, at least in these models.54 One possible explanation is that these xenotransplanted human lymphoma cells did not secrete high enough circulating VEGF levels (as evidenced by nondetectable serum human VEGF levels in these mice; data not shown) to mobilize hematopoietic precursors at distant marrow sites.55 Mice treated with DC101 or MF-1 also exhibited little evidence of marrow or hematologic toxicity, as assessed by peripheral blood cell counts obtained from treated and control mice during and after treatment (data not shown).54 However, similar to results seen in solid tumors,21 our results showed that inhibiting VEGF/VEGFR-2 paracrine interactions (DC101 antibody) effectively suppressed lymphoma xenograft growth by decreasing tumor vascularization (microvessel density) and endothelial cell number.
Identifying angiogenic pathways contributing to lymphoma growth not only provides insight into disease biology, it offers the opportunity to therapeutically target these pathways to improve clinical outcomes. Current therapy for aggressive B-cell NHL consists of cytotoxic chemotherapy and anti-CD20 antibody (RTX).1 Preclinical solid tumor studies in mice and humans have demonstrated enhanced antitumor effects through the addition of antiangiogenic agents (including DC101) to chemotherapy and radiation therapy.56,57 However, to date, none of these studies have examined lymphoma. In our experiments, DC101 resulted in antitumor effects comparable to those of RTX monotherapy. In combination regimens, DC101 potentiated the effects of chemotherapy and RTX on established DLBCL xenografts. The lymphoma xenografts used in these studies have been shown to be relatively insensitive to MTX therapy27 ; therefore, the marked synergistic improvement in antitumor effects when MTX was combined with DC101 was impressive and might have resulted from improved drug distribution into bulky tumors. Imaging studies (MRI and positron-emission tomography [PET]) to evaluate the effects of antiangiogenic therapy on tumor vasculature are now under way. By comparison, concomitant DC101 and RTX therapy resulted in only additive effects, suggesting that the antitumor activity mediated by these 2 antibodies occurred by separate complementary mechanisms and not by improved drug pharmacokinetics. These data imply that combining antiangiogenic agents with conventional lymphoma therapies may result in enhanced efficacy with minimization of the effects of acquired chemotherapy or RTX drug resistance and other angiogenic pathways.
Multiple targeted anti–VEGF/VEGFR agents—including human or chimeric monoclonal antibodies, small-molecular–weight receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and mRNA ribozyme—are in clinical trial for malignancies.38 The clinical efficacy of antiangiogenic approaches has recently been demonstrated in a phase 3 study demonstrating substantially longer overall survival times in patients with metastatic colon cancer who received bevacizumab (anti-VEGF antibody) along with combination IFL chemotherapy than were achieved in patients who received placebo and IFL.58 However, nonspecific inhibition of normal VEGF activity or of non-VEGFR tyrosine kinases may account for the unusual toxicities (pulmonary or gastroin-testinal hemorrhage) noted with these agents, and more selective strategies may minimize these adverse effects.59 Treatment with an anti–VEGFR-2 monoclonal antibody in a phase 1 trial was well tolerated; the only adverse effects were disease related.60 Fully humanized anti-VEGFR antibodies without immunogenic properties are in clinical development. The observation that PlGF-mediated effects in adults are restricted to disease sites (eg, inflammation, atherosclerosis, tumors) and not to normal angiogenic processes (eg, wound healing, neovasculogenesis) suggests that targeted inhibition of VEGFR-1 pathways with antibodies or other agents theoretically may result in less toxicity to normal tissues than pan-VEGF–targeted approaches.22 Bertolini et al28 showed that administering endostatin after chemotherapy or RTX treatment stabilized the growth of Burkitt lymphoma in preclinical models. However, the potential clinical benefits of endostatin as an antiangiogenic agent for lymphoma are unclear because elevated serum endostatin levels in lymphoma patients correlated with poor overall survival.61
In summary, these data identify 2 distinct VEGFR-1– and VEGFR-2–mediated pathways promoting lymphoma growth in vivo through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms, respectively. Disrupting these pathways with targeted anti-VEGFR agents effectively inhibits the growth of aggressive human DLBCL in preclinical models. Antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF/VEGFR-2 tumor–endothelial cell interactions were as effective as RTX therapy in inhibiting lymphoma growth and potentiated the effects of chemotherapy and RTX in combination regimens. These results provide the rationale to develop clinical VEGFR-targeted therapies for aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, July 6, 2004; DOI 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0226.
Supported in part by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Young Investigator Award (E.S.W.), National Institutes of Health grant CA-09207-24 (E.S.W.), the Charles H. Revson Foundation (E.S.W.), Mr William H. Goodwin and Mrs Alice Goodwin and the Commonwealth Cancer Foundation for Research (M.A.S.M.), Experimental Therapeutics Center of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (M.A.S.M.), and the Gar Reichman Fund of the Cancer Research Institute (M.A.S.M.).
Several authors (Y.W., Z.Z., D.J.H.) are employed by ImClone Systems, whose antibodies were studied in the present work.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
We thank Kang Zhang, Diane Domingo, Craig Farrell, and the personnel at the Molecular Cytology Core Facility (Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center) for excellent technical assistance. We also thank Drs A.D. Zelenetz, R. Brentjens, J. Houldsworth, and R.K. Chaganti for providing cell lines.


![Figure 3. Lymphoma proliferation experiments. Cells (RL, SKI-DLBCL) were plated at 2 × 104 cells/well in triplicate in 96-well, round-bottom plates and were incubated for 48 hours in the presence of serum-free media, growth factors, or VEGFR antibodies. [3H]-Tritiated thymidine (0.5 μCi/well [0.0185 MBq/well]) was added, and radioisotope incorporation into cells after 18 hours of exposure was measured. Experiments were performed at least 3 times, and results of 1 representative experiment are shown. Because of variations in baseline [3H]-tritiated thymidine incorporation between experiments, data are expressed as fold change of the serum-free control for each experiment. (A) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, VEGF (50 ng/mL), anti–human VEGFR-2 antibody (IMC-1C11 10 μg/mL), or VEGF + IMC-1C11 (same concentrations). (B) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, PlGF (200 ng/mL), anti–human VEGFR-1 antibody (6.12 10 μg/mL), or PlGF + 6.12 (same concentrations). (C) Growth of lymphoma cells in the presence of serum-free media, VEGF (50 ng/mL), 6.12 (10 μg/mL), or VEGF + 6.12 (same concentrations).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/104/9/10.1182_blood-2004-01-0226/6/m_zh80210468660003.jpeg?Expires=1766094045&Signature=ra28udeIxUqGNXtF4zetiAUhj1ABYLFBdodSlsKFZrL16ZXdmUs4zBWg7pxSFW23U2UThm7qOBORuM8Sx4CNrsCXjthSGjC6GH5BqsmsiLXsdzi6M6NA3RHraCmn3Rwc0QMGXcpxSbr08pBwGDH8A~GWFLGYBtCY8~Q9PsXRvazv3Z-h0wmaR6Xzo6emgrpWiSain57Atd6qrwt6A9gx69TaK~qEvmoVjf0C3DDFewnIjXJzTrEEmZKRJHSPuGKfhWnXULrlmwpIkWQeupaOQdmi708Yhw-U63Cgg-2CKQTtf6Geb5aIlMj63pC6~~jXX1VFXPn7x0tUHkXmS-YFuA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)