Abstract
Oxidative stress is a prominent contributor to the premature destruction of RBC as well as anemia in thalassemia and sickle cell anemia. The oxidative status within RBC is maintained by the balance between oxidative systems, such as Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), and antioxidative systems, such as reduced glutathione (GSH). Using flow cytometric methods, we previously showed that RBC obtained from patients with thalassemia (
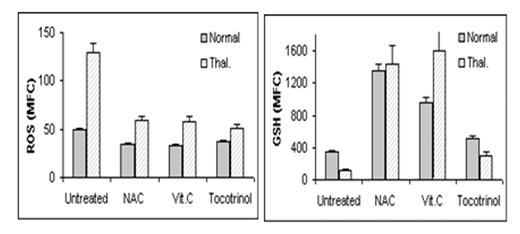
RBC were derived from normal and thalassemic mice before and 4 hours after i.p. injection of the antioxidants N-acetyl cysteine (NAC), vitamin C (Vit. C) or tocotrinol - a mixture of vitamin E derivatives, at a dose of 150 mg/kg. Intracellular ROS was determined in dichlorofluorescin diacetate-stained RBC following stimulation with 2 mM H2O2; GSH content was assessed in RBC stained with mercury orange. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry: RBC were gated according to size (forward light scatter) and granularity (side light scatter), their fluorescence was measured and the Mean Fluorescence Channel (MFC) was calculated. Fig. 1 shows the average MFC of ROS and GSH of normal and thalassemic mice treated or not treated with anti-oxidants (N=6 in each group).
The results show a significantly higher (2.6-fold) production of ROS and lower (three-fold) levels of GSH in RBC from the thalassemic mice versus those in RBC from normal mice. Administration of antioxidants decreased the ROS of normal and thalassemic RBC by 1.4-fold and 2.6-fold, respectively, whereas GSH levels were significantly increased both in the normal (2.7 fold) and in the thalassemic (9.4-fold) RBC. The results show that the RBC of thalassemic mice are under oxidative stress that could be ameliorated by a short antioxidant treatment. Hence, this mouse model recapitulates the oxidative stress found in thalassemic patients and can serve as a model for studying the effects of antioxidant therapy. The flow cytometry methodology used is helpful in following up the results of the treatment and in evaluating its efficacy in reducing oxidative stress.
Author notes
Corresponding author