Abstract
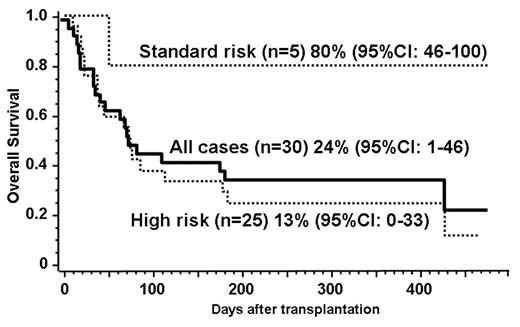
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation has been potentially curative approach for advanced malignant lymphoma. Unrelated umbilical cord blood cell has become a viable source of transplantation for those who lack suitable donors, but the outcome of the transplantation with reduced-intensity conditioning has not been clearly defined yet. We have therefore analysed the outcome of the patients with advanced malignant lymphoma who have undergone reduced-intensity unrelated cord blood transplantation (RI-UCBT). Thirty patients (median age, 47 years; range 27–69 years) underwent RI-UCBT with a preparative regimen consisting mainly of fludarabine 125 mg/m2, melphalan 80 mg/m2, and 4 Gy of total body irradiation since June 2002 to June 2005 with a mean follow-up of 353 days (59–621 days). The types of lymphoma included in this study were DLBCL (11 cases), PTCL (5), Hodgkin disease (5), Follicular lymphoma (5), AITL (2), ALCL (1), and nasal NK/T lymphoma (1). All the patients were heavily treated before proceeding to RI-UCBT, including 9 with prior autologous and 1 allogeneic transplantation. The median infused total cell dose was 2.71 x 107/kg (range, 1.76–4.76 x 107/kg). Graft-versus host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis was composed of cyclosporine or tacrolimus alone. Twenty-four patients (80%) achieved primary neutrophil engraftment at a median of 23 days (12–33 days), and 18 (60%) achieved platelet engraftment at a median of 40 days (26–77 days). Fourteen patients (57.1%) developed grade II to IV acute GVHD at a median of 31 days (15–59 days). Five patients subsequently relapsed and all died within 2 years. Fifteen patients died of non-relapse causes such as infection (8), GVHD (3), IP (2), and others (2). Transplant-related mortality (TRM) within 100 days was 54%. The estimated 1-year probability of overall survival was 24% (95%CI: 1–46%). In subgroup analyses, standard risk patients (CR1, CR2, PR1, n=5) showed 80% while high risk (n=25) showed 13% overall survival at 1 year. These data suggest that RI-UCBT is a feasible option for patients with refractory lymphoma who lack HLA-matched donors. Although the patients in standard risk can expect reasonably good overall survival, the beneficial effect is only limited to small part of the high risk patients. To further improve the outcome, RI-UCBT should be investigated among patients with less advanced diseases in a well-designed clinical trial.
Author notes
Corresponding author