Abstract
Despite the mature results of the new intensive treatments, ABVD is still considered the standard therapy of the HL. Here we report the 2-year results of a phase 2 study which explore the possibility to ameliorate the performance of this (g)old schedule. Primary End-Points: CR and early cardio-toxicity. Secondary End-Points: survival (FFP,OS) and late cardio-toxicity. 23/25 CR (CI 90%) to validate the study (80% standard vs 90% DD-DI ABVD, CI +/− 10% one tail test, 5% sig stat level). Modifications of the standard (st) ABVD and strategy concepts are summarized as follow:
Each patient received a total of 6 cycles without RT
Adryamicin (ADM) was escalated from 50 to 70 mg/m2 in the cycles 1,2,3,4. The cumulative dose of ADM was 380 mg/m2.
The intercycle period was shortened from 28 to 21 days for all 6 cycles; the 4 drugs were delivered at day 1 and 11 of each cycle
G-CSF was given from d4 to d8, and from d14 to d18 of each cycle
The therapy program was driven by dynamic indicators such as interim-PET and CT fusion images.
Normalisation of PET images at the end of 2nd cycles was indicator of early CR, while the persistence of PET+ lesion(s) at the end of the 4th cycle was indicator of failure and consequently the treatment was shift to a high-dose CT/CD34+ rescue program.
RT was eliminated. At the end of 6th cycle, PET- residual masses were monitored by PET/TC fusion images.
An historical group of 94 HL pts treated with 6–8 cycles of st-ABVD +/− RT was used to compare response, survival and toxicity data.
Compared to st-ABVD the theoretical relative dose-intensity (RDI) values of drugs were 1.86 for ADM, 1.33 for DTIC, Bleomycin and Vinblastine, and 1.46 for the entire schedule. Administered RDIs of the schedule (delivered cycles = 184) ranged between 1.10 to 1.55 (median value 1.39).
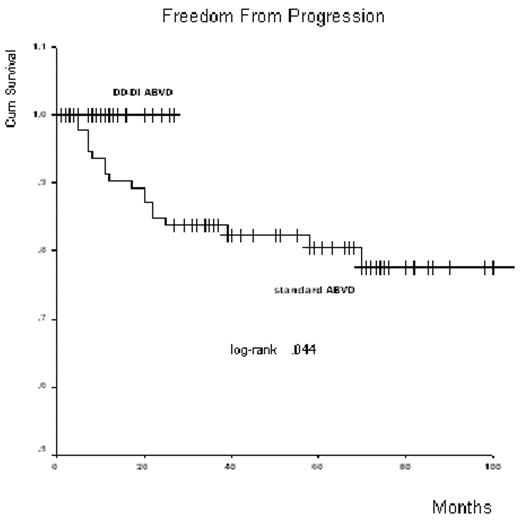
Results: from June 2004 to August 2006 thirty-nine pts were enrolled (tab1). As the 8th August 2006 thirty-five out of 39 pts have performed the interim-PET-TC fusion images and thirty-two completed the treatment: 100% of valuable pts obtained the early CR (35/35) and CR (32/32). All pts are alive and free of disease (tab2 and fig.1).
Cardiac functions were monitored by ECG, Ecography, MUGA scan, pro-BNP, and troponin T. Toxicity was mild and similar to standard ABVD.
Dose-dense and dose-intense ABVD is feasible, well tolerated and highly active in newly diagnosed patients with advanced/intermediated Hodgkin’s lymphoma: six cycles without RT seem superior to 6–8 cycles of ABVD +/− RT (fig 1) and may be a promising program for optimal long-term results.
presentation features
| Features . | . | . |
|---|---|---|
| total | 39 | 100% |
| Early unfavourable | 9 | 23% |
| Advanced | 30 | 77% |
| Age > 45 –yr | 4 | 10% |
| Bulky | 19 | 44% |
| Stage IV | 13 | 33% |
| B symptoms | 25 | 64% |
| Extranodal | 9 | 23% |
| VES > 50 mm | 20 | 51% |
| LDH Ratio > 1 | 15 | 38% |
| IPS ≥ 3 | 10 | 26% |
| N. Sites>3 | 28 | 72% |
| Male | 13 | 33% |
| Features . | . | . |
|---|---|---|
| total | 39 | 100% |
| Early unfavourable | 9 | 23% |
| Advanced | 30 | 77% |
| Age > 45 –yr | 4 | 10% |
| Bulky | 19 | 44% |
| Stage IV | 13 | 33% |
| B symptoms | 25 | 64% |
| Extranodal | 9 | 23% |
| VES > 50 mm | 20 | 51% |
| LDH Ratio > 1 | 15 | 38% |
| IPS ≥ 3 | 10 | 26% |
| N. Sites>3 | 28 | 72% |
| Male | 13 | 33% |
Response and Survival
| . | N. of patients . | percent . |
|---|---|---|
| *n°. of valuable pts as 8 August 2006 | ||
| Early CR | 35/35* | 100% |
| CR | 32/32* | 100% |
| FFP-2yr | 32/32* | 100% |
| OS-2yr | 32/32* | 100% |
| . | N. of patients . | percent . |
|---|---|---|
| *n°. of valuable pts as 8 August 2006 | ||
| Early CR | 35/35* | 100% |
| CR | 32/32* | 100% |
| FFP-2yr | 32/32* | 100% |
| OS-2yr | 32/32* | 100% |
Freedom From Progression
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author