Abstract
Background: Successful reconstitution of cellular immunity following allogeneic HPCT reduces the risk of relapse and confers protection against opportunistic infections. We performed an IRB-approved retrospective analysis of patients who underwent allogeneic HPCT and in whom the content of immune cells were measured in the graft and in post-transplant blood samples.
Methods: The study population consisted of 122 patients with hematologic disorders (71 acute leukemia; 14 chronic leukemia; 18 lymphoma, 12 MDS; 3 aplastic anemia; and 4 other) who underwent HPCT with a non-T cell depleted graft from an HLA matched related (73) or unrelated (49) donor. 47 patients had low risk disease (AA, ALL CR1, AML CR1, CML CP1), while 75 had high risk disease (all others). The conditioning regimen was non-myeloablative in 38 (31%), included ATG in 18 (15%), and included TBI in 54 (44%). Peripheral blood was drawn at a median of 101 days post-HPCT and analyzed for T-cell subsets, B-cells, NK cells, and dendritic cells. Subjects were divided into three strata based upon the maximal value for the content of each cell subset in the blood. Univariate and multi-variable stepwise logistic regression analyses were performed to test the association of pre-transplant clinical factors, the cells in the graft, and the numbers of immune cells in the blood post-transplant with overall survival.
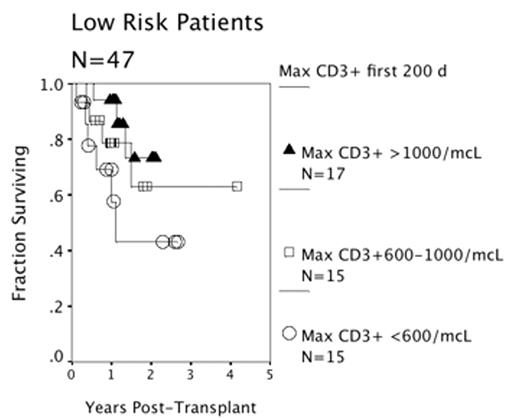
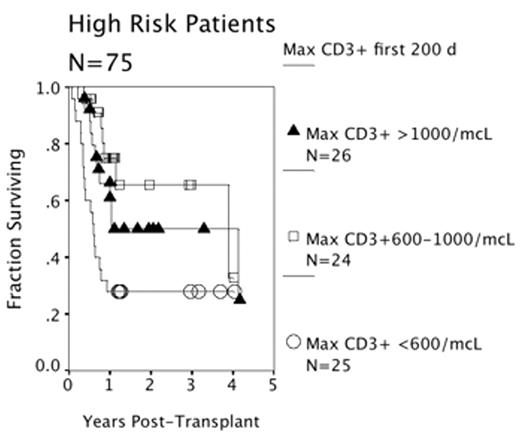
Results: The estimated three-year survival for all subjects was 53%, with death in 49/122 patients (40%) due to progressive disease (37%), infection (29%), GVHD (20%), and other causes (14%). Univariate factors associated with death included high risk, age, the use of reduced intensity conditioning regimen, the use of TBI, the use of ATG during conditioning and the measurement of lower numbers of total T-cells, CD4+ T-cells, CD8+ T-cells, γδ T-cells, DC1 and DC2 in the peripheral blood during the first 200 days post-transplant. A multi-variable Cox model identified non-myeloablative conditioning (HR 2.2, 95% CI 1.2–3.9), TBI (HR 1.9, 95% CI 1.1–3.3), transplant risk strata (HR 1.9, 95% CI 1.0–3.6), and a blood CD3+ T-cell count of less than 600 cells/mcL (HR 1.8, 95% CI 1.2–2.5) as independent risk factors for post-transplant death. The presence of acute GVHD (all grades) or graft constituents was not significantly associated with survival. Limiting the study population to those subjects who survived at least 100 days showed that blood CD3+ T-cells, non-myeloablative conditioning, the use of TBI remained significantly associated with survival.
Conclusions: Higher CD3+ counts in the early post-transplant period predict better survival. Patients who fail to achieve a blood CD3+ T-cell count of >600/mcL in the first 200 days post-transplant may be appropriate subjects for adoptive cellular immunotherapy.
Low Risk Patients
High Risk Patients
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author