Abstract
CD33, a 67-kDa sialoglycoprotein expressed on the cell surface of monocytic/myeloid lineage and early hematopoietic progenitor cells, is frequently expressed in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (GO), an immunoconjugate consisting of a humanized anti-CD33 antibody and a cytotoxic compound (N-acetyl-γ-calicheamicin dimethylhydrazine), targets CD33 and has shown promising results in patients with AML. No evidence of a relationship between the levels of CD33-positive leukemic cells and clinical response has been found. We investigated the possibility that cell-free circulating CD33 (cCD33) might be useful as a marker of clinical behavior. We used a newly developed bead-based immunoassay to measure cCD33 in the plasma of patients with AML (n = 97) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS; n = 44). All patients were treated with standard therapy including idarubicin and ara-C. cCD33 levels were significantly higher in patients with MDS (median, 1600 U/μL; range, 102–791,350 U/μL) than in those with AML (median, 2709 U/μL; range: 62–263,349 U/μL) (P = 0.004). High-risk cytogenetic abnormalities were associated with higher cCD33 levels in patients with MDS (P = 0.04) but not in patients with AML (P = 0.72). cCD33 levels correlated with WBC count and % monocytes in patients with AML (R >0.35) but not in patients with MDS. cCD33 levels correlated with clinical behavior only among AML patients with intermediate-risk cytogenetic abnormalities (n = 56); those with cCD33 levels above the median had longer survival (P = 0.04). These data confirm the presence of cCD33 in AML and MDS and also suggest that cCD33 can be used as a tumor marker in patients with AML. Although further study is needed for confirmation, cCD33 appears to result from turnover of leukemic cells, may play a role in patients being treated with GO, and should be considered in the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of such therapy.
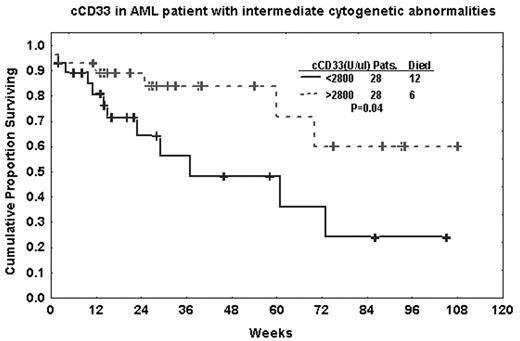
cCD33 in AML patient with intermediate cytogenetic abnormalities
cCD33 in AML patient with intermediate cytogenetic abnormalities
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author