Abstract
von Willebrand factor (VWF) protects factor VIII (FVIII) from proteolysis and mediates the initial contact of platelets with the injured vessel wall, thus playing an important role in hemostasis and thrombosis. VWF is crucial for the formation of occlusive thrombi at arterial shear rates. However, with only a few conflicting studies published, the role of VWF in venous thrombosis is still unclear. Using gene-targeted mice, we show that in ferric chloride–injured veins platelet adhesion to subendothelium is decreased and thrombus growth is impaired in VWF−/− mice when compared with wild type (WT). We also observed increased embolization in the VWF−/− mice, which was due to lower FVIII levels in these mice as recombinant factor VIII (r-FVIII) restored thrombus stability. Despite normalization of blood clotting time and thrombus stability after r-FVIII infusion, the VWF−/− venules did not occlude. Transgenic platelets lacking the VWF receptor GPIbα extracellular domain showed decreased adhesion to injured veins. But, after a delay, all the injured venules occluded in these transgenic mice. Thus, VWF likely uses other adhesion receptors besides GPIbα in thrombus growth under venous shear conditions. Our studies document crucial roles for VWF and FVIII in experimental thrombosis under venous flow conditions in vivo.
Introduction
von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a large adhesive glycoprotein synthesized in megakaryocytes and endothelial cells and stored in platelet α-granules and Weibel-Palade bodies, respectively. VWF circulates in plasma as a series of multimers ranging from 500 to 20 000 kDa. The size of the multimers is regulated through proteolysis1,2 by a specific protease ADAMTS13 (adisintegrin-like and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type I repeats-13).3–5 There are 3 pools of VWF: (1) soluble plasma VWF, (2) subendothelial (ECM) VWF, and (3) cellular VWF in storage granules.6 VWF is a carrier for factor VIII (FVIII) and protects it from inactivation.7 The formation of a thrombus on an injured vessel wall is a complex process that involves multiple adhesion molecules (VWF, collagen, fibrinogen, and fibronectin) and their respective receptors on the platelet surface (GPIbα, GPVI, β1 and β3 integrins). VWF has 2 main receptors, GPIbα in the GPIb-IX-V complex and the integrin αIIbβ3. 8
Pathological thrombosis can occur in arteries and veins. Arterial thrombosis is often linked to inappropriate platelet activation and can result in myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke, while venous thrombosis (eg, deep vein thrombosis) is commonly linked to high procoagulant activity, which produces fibrin-rich thrombi. In the clinical setting, elevated levels of FVIII and VWF are associated with an increased risk of venous thrombosis. The Leiden Thrombophilia Study suggested that the effect of elevated VWF on the risk of venous thrombosis was due to increased FVIII levels.9 In contrast, the Longitudinal Investigation of Thromboembolism Etiology (LITE) Study showed FVIII and VWF were independently associated with venous thromboembolism.10
Under high shear, the VWF-GPIbα interaction is necessary for initial platelet contact with the subendothelium, while irreversible platelet aggregation also requires interaction between the VWF and integrin αIIbβ3.8,11–13 Although an important role for VWF in platelet-platelet cohesion and thrombus formation at arterial shear rates was demonstrated both in vitro13,14 and in vivo,15,16 its role in thrombus formation in vivo under venous shear conditions is unclear. Under flow using type I collagen–coated coverslips, inhibition of the A3 domain or the A1 domain of VWF had no effect on thrombus volume at shear rates of 500s−1 and 100s−1.13 On the other hand, using glass microcapillary tubes coated with a VWF-deficient platelet monolayer (prepared from individuals with type III von Willebrand disease [VWD]) and perfusing whole blood from VWD patients, it was shown that VWF was required in platelet tethering at a shear rate of 150 s−1.14 In vivo the formation of a thrombus can be different than in in vitro conditions; for example, fibrinogen is required for platelet aggregation in vitro, whereas in vivo thrombi form readily in fibrinogen-deficient mice.16
Therefore, in order to understand the in vivo role of VWF and FVIII in experimental thrombosis under venous flow conditions, we decided to evaluate thrombosis in VWF−/−, FVIII−/−, and transgenic mice lacking the GPIbα extracellular domain that was replaced by human interleukin-4 receptor (IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg).17 Our results suggest that optimal platelet adhesion to subendothelial matrix in injured veins requires VWF and that both VWF and FVIII are essential for the formation of occlusive thrombi in injured venules.
Materials and methods
Animals
The VWF−/−15 mice were on C57BL/6J background. The control wild-type (WT) mice of C57BL/6J background were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). Factor VIII−/−(FVIII−/−)18 and IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg17 mice were on mixed background and were a gift from Drs Haig Kazazian (University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA) and Zaverio Ruggeri/Jerry Ware (Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA), respectively. The mice used for intravital microscopy were approximately 4 weeks old, both males and females, and weighed 13 to 17 grams. Platelets were isolated from 4- to 6-month-old mice of the same genotype. Animals were bred at the CBR Institute for Biomedical Research, and the experimental procedures were approved by its Animal Care and Use Committee.
Platelet preparation
Blood was collected from the retro-orbital venous plexus by puncture and collected in polypropylene tubes containing 300 μL heparin (30 U/mL). Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was obtained by centrifugation at 100 g for 5 minutes. The PRP was transferred to fresh tubes containing 2 μL prostaglandin I2 (PGI2, 2 μg/mL) and incubated at 37°C for 5 minutes. After centrifugation at 600 g, pellets were resuspended in 1 mL modified Tyrode-HEPES buffer (137 mM NaCl, 0.3 mM Na2HPO4, 2 mM KCl, 12 mM NaHCO3, 5 mM HEPES, 5 mM glucose, 0.35% BSA, pH 7.2) containing 2 μL PGI2 and incubated at 37°C for 5 minutes. The suspended pellet was centrifuged at 600 g for 5 minutes. In order to remove PGI2, the washing step was repeated twice and platelets were fluorescently labeled with calcein AM 2.5 μg/mL (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) for 10 minutes at room temperature.
Intravital microscopy
Intravital microscopy was performed as described.19 Briefly, mice were anesthetized and an incision was made through the abdominal wall to expose the mesenteric venules of 200- to 300-μm in diameter. The shear rate was calculated using an optical Doppler velocimeter (Microcirculation Research Institute, Texas A&M College of Medicine, College Station, TX). Platelets were counted by a Beckman Coulter (Fullerton, CA) counter. Fluorescent platelets (2.5% of total count) were then infused intravenously. Whatman paper (Florham Park, NJ) soaked in a 10% FeCl3 solution was applied topically for 5 minutes on the venules, and the vessel was monitored for 40 minutes or until occlusion. One venule was selected per mouse.
Quantitative analysis of platelet adhesion and thrombi formation
Analysis of the recorded tapes was performed blinded to animal genotype. We evaluated (1) single platelet–vessel wall interaction determined as the number of fluorescent platelets that deposited on the injured vessel wall (250 μm) segment in the course of 1 minute (2-3 minutes after injury), (2) the time required to form thrombi of 30, 50, 100, and 150 μm in diameter, (3) the rate of thrombus growth by following the diameter of a 40-μm thrombus over a period of 10 minutes, (4) thrombus stability by determining the number of thrombi with a diameter larger than 30 μm embolizing before vessel occlusion, and (5) occlusion time of the vessel—that is, time required for blood to stop flowing for 30 seconds. To study the role of GPIbα in initial platelet tethering/adhesion to the extracellular matrix, we infused IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg or WT (control) platelets in WT mice. Because IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg platelets, but not WT platelets, are cleared after transfusion the number of fluorescent platelets present in blood was determined again by fluorescent-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis after the experiment. The single platelet–vessel wall interaction was normalized with actual number of fluorescent platelets present in blood.
Recombinant human factor VIII infusion
Recombinant human FVIII protein (r-hu-FVIII; gift from Fritz Scheiflinger, Baxter Bioscience, Vienna, Austria) was dissolved in 0.9% saline and injected intravenously at a dose of 200 U/kg mouse body weight.
Whole blood clotting time and clot rate
The whole blood clotting time was measured by a Sonoclot (Sienco, Arvada, CO) as described.20 Analysis was performed with 280 μL citrated (3.8%) blood recalcified with 20μL calcium chloride (150 mM). The following variables were analyzed: (1) the initial clot formation; and (2) the clot rate, the gradient of the primary slope measured as clot signal units per minute, which is an index of fibrinogen conversion into fibrin gel.
Statistical analysis
Results are reported as the mean ± SEM. The statistical significance of the difference between means was assessed by unpaired Student t test (for comparison of 2 groups) or by ANOVA with the Bonferroni test if more than 2 groups were compared. Values of P below .05 were considered significant.
Results
Platelet adhesion to the subendothelium is decreased in VWF−/− venules
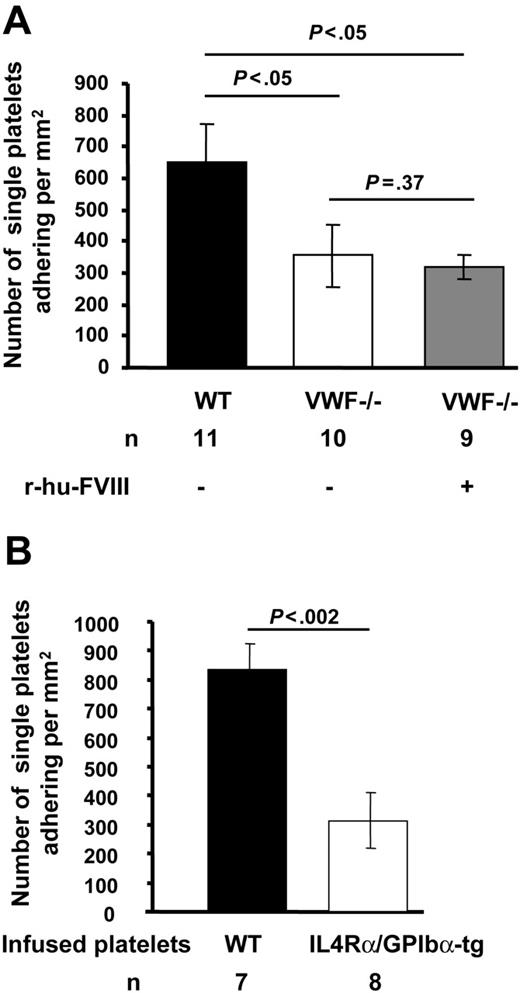
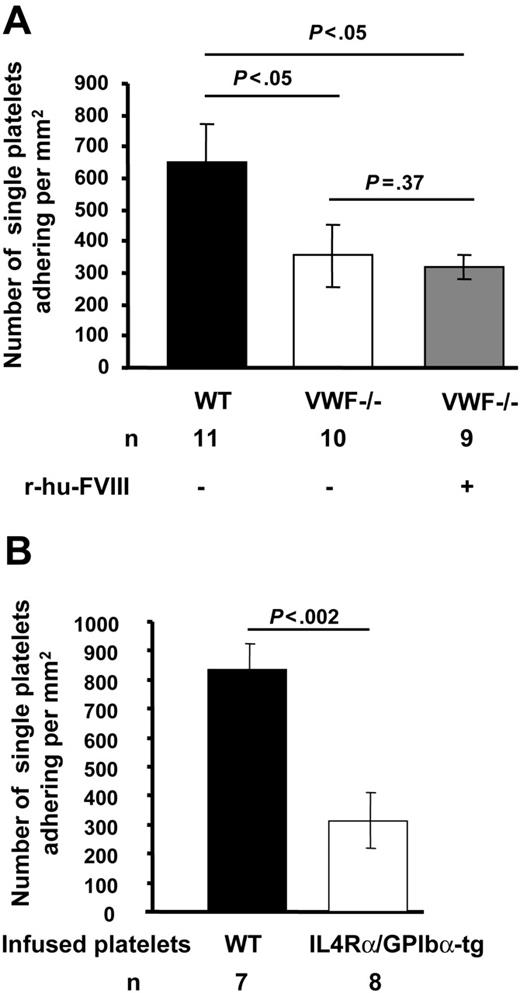
We first evaluated the role of VWF in platelet tethering to exposed subendothelium in ferric chloride–injured mesenteric venules of mice infused with fluorescently-labeled platelets of the same genotype. The shear rate (VWF−/− = 119.79 ± 0.74 s−1, WT = 115 ± 0.52 s−1, n = 10-11, P > .05) and diameter (VWF−/− = 287.5 ± 0.44 μm, WT = 278.40 ± 0.40 μm, n = 10-11, P > .05) of the mesenteric venules studied were similar for VWF−/− and WT mice. In the VWF−/− mice, the number of single fluorescent platelets transiently tethering and/or stable (355 ± 98/mm2) on the injured vessel wall was nearly half that seen in WT mice (650 ± 119/ mm2) (P < .05, Figure 1). Infusion of r-hu-FVIII in VWF−/− mice did not normalize the single platelet adhesion to WT count. This observation suggests that VWF is required for optimal platelet adhesion to injured vessel wall under venous shear conditions.
Platelet adhesion to subendothelium in the absence of VWF or functional GPIbα is decreased. Venules of approximately 200- to 300-μm in diameter were visualized in the mesentery of live mice after ferric-chloride injury. Numbers of single fluorescent platelets transiently tethering and/or stably adhering to vessel wall within 2 to 3 minutes after ferric-chloride injury were determined. (A) Significantly fewer platelets adhered in VWF−/− venules compared with WT. The infusion of r-hu-FVIII in VWF−/− mice did not increase platelet adhesion. (B) Fluorescent IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg or WT platelets were infused in WT mice. The adhesion of IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg fluorescent platelets to injured venules was significantly less than that of WT platelets. Error bars indicate SEM.
Platelet adhesion to subendothelium in the absence of VWF or functional GPIbα is decreased. Venules of approximately 200- to 300-μm in diameter were visualized in the mesentery of live mice after ferric-chloride injury. Numbers of single fluorescent platelets transiently tethering and/or stably adhering to vessel wall within 2 to 3 minutes after ferric-chloride injury were determined. (A) Significantly fewer platelets adhered in VWF−/− venules compared with WT. The infusion of r-hu-FVIII in VWF−/− mice did not increase platelet adhesion. (B) Fluorescent IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg or WT platelets were infused in WT mice. The adhesion of IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg fluorescent platelets to injured venules was significantly less than that of WT platelets. Error bars indicate SEM.
Impaired thrombus growth in injured venules of VWF−/− mice
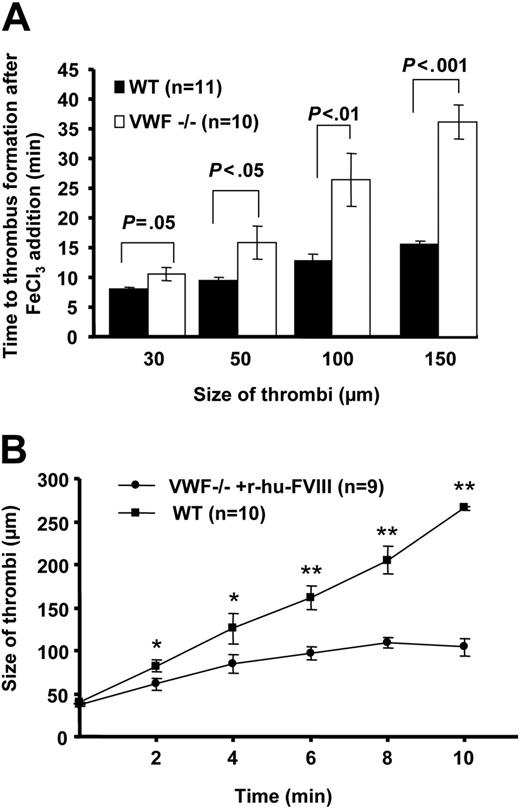
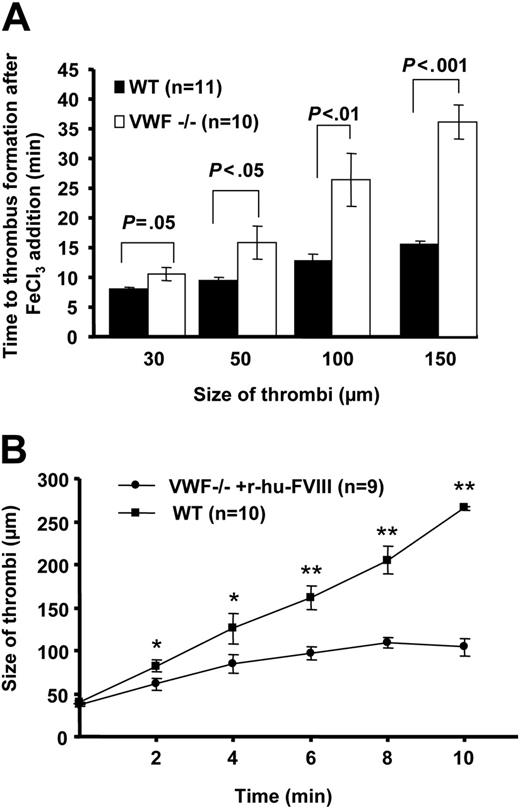
To examine the role of VWF in platelet-platelet cohesion under venous shear rate, we measured the time to form a thrombus of 30 μm to 150 μm in diameter upon acute injury. In the VWF−/− mice, thrombi formed but their growth was impaired compared with WT mice. The time to form the first thrombus of 30 μm in diameter in the VWF−/− mice was 10.68 ± 1.1 minutes compared with 8.05 ± 0.21 minutes in the WT mice (P < .05, Figure 2A). Although statistically significant, the observed time difference is small. Larger differences were observed when the thrombi grew to a size of 100 to 150 μm in diameter. In the VWF−/− venules, the mean time to form thrombi of 150 μm was twice that in WT (VWF−/− = 36.05 ± 2.98, WT = 15.55 ± 0.49 minutes, P < .001, Figure 2A). Thus, thrombi grew slowly in the absence of VWF. The thrombus growth was impaired due to platelet shedding and breakdown of platelet aggregates from the growing edge of the thrombus. The growing thrombus narrows the vessel, thus increasing the shear rate, which could be a reason for platelet shedding as VWF is required for platelet-platelet cohesion at high arterial shear rates.21 Indeed the shear rate increased to 585 ± 73 (n = 4, thrombi size 150 μm) but remained in venous shear rate range outside the growing thrombus.
VWF is required for thrombus growth under venous shear conditions. (A) Time to platelet thrombus formation (30-150 μm in diameter) was measured. In the absence of VWF, the thrombi growth was impaired. The time to form the first 150-μm thrombus in VWF−/− venules was nearly twice that in WT. (B) Rate of individual thrombus growth was determined in the VWF−/− mice infused with r-hu-FVIII and compared with WT. Time 0 was considered when thrombus reached approximately 40 μm in size and thrombi were followed for 10 minutes. In VWF−/− mice infused with r-hu-FVIII the thrombus grew significantly more slowly than in WT (*P < .05, **P < .001). Error bars indicate SEM.
VWF is required for thrombus growth under venous shear conditions. (A) Time to platelet thrombus formation (30-150 μm in diameter) was measured. In the absence of VWF, the thrombi growth was impaired. The time to form the first 150-μm thrombus in VWF−/− venules was nearly twice that in WT. (B) Rate of individual thrombus growth was determined in the VWF−/− mice infused with r-hu-FVIII and compared with WT. Time 0 was considered when thrombus reached approximately 40 μm in size and thrombi were followed for 10 minutes. In VWF−/− mice infused with r-hu-FVIII the thrombus grew significantly more slowly than in WT (*P < .05, **P < .001). Error bars indicate SEM.
FVIII restores thrombus stability in injured VWF−/− venules
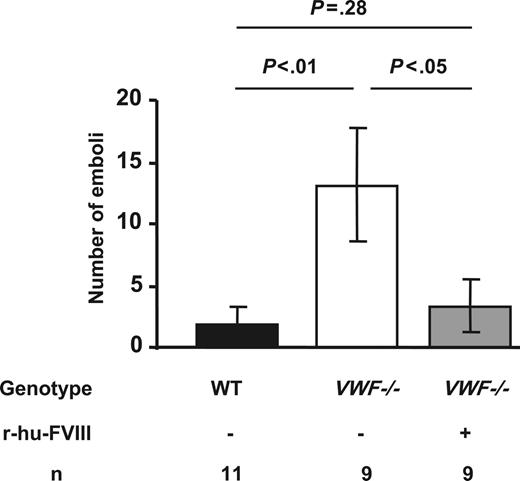
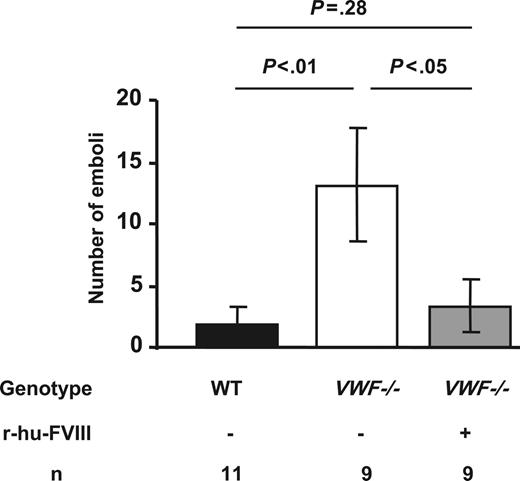
Since we noted that thrombi were not stable in VWF−/− mice during thrombus growth in injured veins, we quantified the number of emboli (platelet aggregates > 30μm in diameter broken off from the thrombus) formed in VWF−/− mice up to 19 minutes after injury (mean occlusion time of WT vessels). During this period, the number of emboli formed in WT mice was 2 ± 1 compared with 13 ± 4 in the VWF−/− mice (P < .01). We also observed frequent channel formation within the VWF−/− thrombi. The VWF−/− mice have only 20% the level of FVIII compared with the WT mice.15 Since we also observed frequent embolization in FVIII−/− mice (not shown), we thought that the unstable thrombi could be a consequence of the lower levels of FVIII since FVIII is needed for proper thrombin/fibrin formation. We infused r-hu-FVIII at a dose of 200 U/kg and this resulted in VWF−/− thrombi stabilization (Figure 3). These observations suggest that the observed thrombus fragility in VWF−/− mice was due to lower FVIII levels and reduced clotting ability in the VWF−/− mice. Indeed, when we examined whole blood clotting time (Table 1)we found that VWF−/− mice whole blood took one minute longer to clot compared with WT (P < .01). The clot rate in VWF−/− mice was also significantly decreased (Table 1). Infusion of r-hu-FVIII in VWF−/− mice normalized both the clotting time and clot rate for at least 20 minutes following infusion (Table 1).
Thrombus stability in VWF−/− venules is restored by recombinant FVIII. The number of emboli (> 30 μm in diameter) generated before 19 minutes (mean occlusion time for WT mice) of injury was determined. Five times more emboli were observed in VWF−/− mice compared with the WT. This was due to less FVIII, as reconstitution with r-hu-FVIII corrected the defect. Error bars indicate SEM.
Thrombus stability in VWF−/− venules is restored by recombinant FVIII. The number of emboli (> 30 μm in diameter) generated before 19 minutes (mean occlusion time for WT mice) of injury was determined. Five times more emboli were observed in VWF−/− mice compared with the WT. This was due to less FVIII, as reconstitution with r-hu-FVIII corrected the defect. Error bars indicate SEM.
We asked whether infusion of FVIII would normalize thrombus growth in the VWF−/− venules. We determined the rate of thrombus growth in VWF−/− mice reconstituted with r-hu-FVIII and compared with WT. On average, in VWF−/− mice infused with r-hu-FVIII the thrombus increased from 40 μm to 100 μm in 10 minutes, whereas in the same time period a 40-μm thrombus in the WT mice grew to 260 μm (Figure 2B). These results suggest that VWF promotes platelet aggregation/cohesion in the growing thrombus under venous shear rate.
Lack of vessel occlusion in VWF−/− and FVIII−/− mice
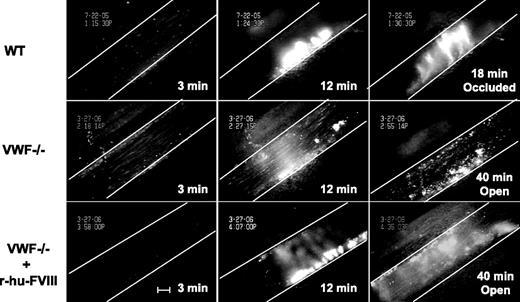
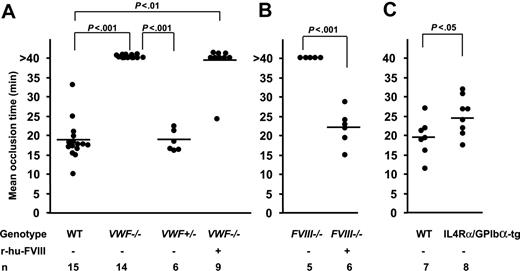
We measured the time to form an occlusive thrombus in the FeCl3-injured venules. In the WT mice thrombi grew to occlusive size in 18 minutes and all injured venules occluded, whereas in VWF−/− mice none of the vessels occluded by 40 minutes after injury, when observation was terminated (Figure 4, 5A). Venules of mice deficient in FVIII treated similarly also did not occlude (Figure 5B) because of embolization. The infusion of r-hu-FVIII in FVIII−/− mice normalized the occlusion time to WT values (Figure 5B), whereas in the VWF−/− mice infused with the same amount of r-hu FVIII, 8 of 9 vessels remained patent (Figure 5A). As would be expected from the asymptomatic state of human carriers of type 3 von Willebrand disease,22 venules in mice containing half the level of VWF (VWF+/− mice) occluded, at times similar to WT mice (Figure 5A).
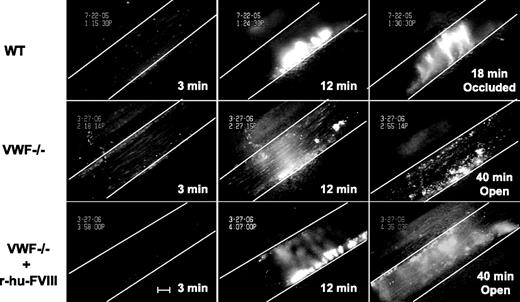
Injured VWF−/− venules do not occlude. Fluorescently-labeled platelets representing approximately 2.5% of total platelets were observed in mesenteric venules of live mice after ferric-chloride injury. Representative photographs of the injured venules are shown. At 3 minutes, the number of single platelets deposited on the injured vessel wall (Figure 1) in the WT mice (top panels) was more than in VWF−/− venules (middle panels) even if the mice were infused with r-hu-FVIII (bottom panels). The thrombus growth was significantly delayed at 12 minutes in the VWF−/− mice with or without r-hu-FVIII when compared with WT. The vessel occluded at 18 minutes in WT, whereas in the VWF−/− mice with or without r-hu-FVIII injured venules remained opened for the entire 40-minute observation time. Blood flow was from left to right. White line delineates the venules, and time after ferric-chloride application is indicated. Bar = 100 μm.
Injured VWF−/− venules do not occlude. Fluorescently-labeled platelets representing approximately 2.5% of total platelets were observed in mesenteric venules of live mice after ferric-chloride injury. Representative photographs of the injured venules are shown. At 3 minutes, the number of single platelets deposited on the injured vessel wall (Figure 1) in the WT mice (top panels) was more than in VWF−/− venules (middle panels) even if the mice were infused with r-hu-FVIII (bottom panels). The thrombus growth was significantly delayed at 12 minutes in the VWF−/− mice with or without r-hu-FVIII when compared with WT. The vessel occluded at 18 minutes in WT, whereas in the VWF−/− mice with or without r-hu-FVIII injured venules remained opened for the entire 40-minute observation time. Blood flow was from left to right. White line delineates the venules, and time after ferric-chloride application is indicated. Bar = 100 μm.
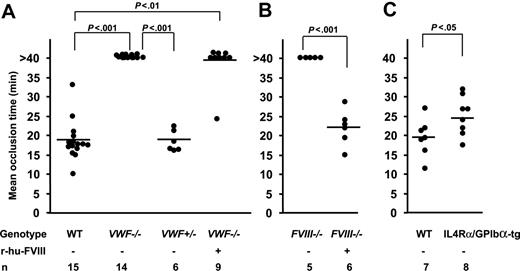
Mean occlusion time in injured veins depends on VWF and FVIII. The time to form an occlusive thrombus was determined. (A) Mean occlusion time in WT, VWF−/−, and VWF+/− mice. None of the injured vessels in the VWF−/− mice occluded during the 40-minute observation time, whereas all WT mice and VWF+/− occluded. Eight of 9 venules of VWF−/− mice infused with r-hu-FVIII did not occlude. (B) None of the injured vessels occluded during the 40-minute observation time in the FVIII−/− mice (n = 5). The infusion of r-hu-FVIII normalized the occlusion time in all FVIII−/− mice. (C) Mean occlusion time in IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg mice was 25 minutes compared with 19.5 minutes in the WT and all the IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg venules occluded at the site of injury.
Mean occlusion time in injured veins depends on VWF and FVIII. The time to form an occlusive thrombus was determined. (A) Mean occlusion time in WT, VWF−/−, and VWF+/− mice. None of the injured vessels in the VWF−/− mice occluded during the 40-minute observation time, whereas all WT mice and VWF+/− occluded. Eight of 9 venules of VWF−/− mice infused with r-hu-FVIII did not occlude. (B) None of the injured vessels occluded during the 40-minute observation time in the FVIII−/− mice (n = 5). The infusion of r-hu-FVIII normalized the occlusion time in all FVIII−/− mice. (C) Mean occlusion time in IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg mice was 25 minutes compared with 19.5 minutes in the WT and all the IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg venules occluded at the site of injury.
Role of GPIbα in venous thrombosis
To examine the role of GPIbα in platelet tethering and thrombus formation at venous shear rate, we used IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg mice.17 These transgenic mice lack the GPIbα extracellular domain, which is replaced by that of interleukin-4 receptor.17 We evaluated the role of GPIbα in platelet tethering to subendothelium. We infused fluorescent WT or IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg platelets in WT (c57BL/6) mice to study adhesion under identical conditions. The number of single IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg fluorescent platelets tethering or adhering was approximately 40% of WT (mean ± SEM: 834 ± 91 for WT, 313 ± 96 for IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg, Figure 1B). These results suggest that under venous shear rate VWF and GPIbα are similarly required for optimal platelet tethering (Figure 1). Since thrombosis is driven by endogenous platelets, this process had to be studied in the IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg mice of mixed genetic background. All the IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg mice occluded a few minutes later than WT mice (mean occlusion time: IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg = 25.06 ± 1.76 minutes, WT = 19.45 ± 1.85 minutes, P < .05, Figure 5C). This is in contrast to VWF−/− mice, which did not form occlusive thrombi in veins during the 40-minute observation period.
Discussion
Under arterial shear rates, VWF-GPIbα axis is necessary for initial platelet adhesion and subsequent thrombus formation.13,14,16 Our results now point to an important role of VWF in platelet adhesion, aggregation, and occlusive thrombus formation in an experimental injury model of thrombosis under venous shear conditions. We have demonstrated earlier an important role for VWF in promoting platelet endothelial interaction in vivo under venous conditions23 that was accentuated in mice lacking ADAMTS13, the enzyme cleaving VWF multimers.19,24 But the role of VWF-GPIbα in platelet adhesion to subendothelium and aggregation at low venous shear was unclear with conflicting conclusions from various in vitro models.13,14,21,25 In VWF-deficient mice we found that under low shear VWF was also required for optimal platelet adhesion to the injured vessel wall (Figure 1). This finding is consistent with 2 previously published reports where it was shown in vitro that VWF-GPIbα interaction participates in the adhesion process at venous shear rate. First, in an ex vivo study using blood from VWF-deficient pigs, a defect in platelet deposition at low shear rate (200 to 400 s−1) was demonstrated,26 and second, in a flow chamber coated with collagen type VI, platelet adhesion was shown to be VWF dependent at a shear rate of 100 s−1.27
In order to form a thrombus, the important parameter is not the number of transiently tethering platelets to the injured vessel wall but the number of platelets that are stably adherent because of αIIbβ3 activation. Previously, it was shown in vitro that on type I collagen fibrils thrombus growth at low shear is dependent on integrin αIIbβ3 and GPIbα and that VWF was less relevant.13 The role of β3 integrin in thrombus growth in vitro is in agreement with in vivo results. In the ferric-chloride injury model, β3 integrin is important for thrombus formation at venous flow conditions as mice deficient in β3 integrin slowly form platelet-poor mostly nonocclusive clots at the site of injury (D.D.W. and Richard Hynes, unpublished observation, January 2000). β3−/− mice are completely protected from the effect of ADP and partially protected from collagen plus epinephrine–induced thrombosis.28 In vivo, we found that VWF was critical for thrombus growth under venous flow conditions (Figure 2). The discrepancy in the role of VWF in thrombus growth between in vitro and in vivo results could be due to different adhesive substrates. Collagen type I fibrils are very potent in inducing integrin αIIbβ3 activation, thus perhaps promoting platelet aggregation with less dependence on VWF than in vivo. Our finding is consistent with another in vivo study where, in a crushed femoral vein model (hamster), it was shown that the presence of an antagonist to the VWF A1 domain decreased thrombus size.29
The key finding in our study is the essential role for VWF in forming an occlusive thrombus under venous flow conditions. The importance of VWF in occlusive thrombus formation at arterial shear conditions has been shown in vivo.15,16 The defect in experimental venous thrombosis in VWF−/− mice was striking since none of the vessels in the VWF−/− mice occluded in the ferric-chloride injury model (Figure 5A). Using the same model, it was shown previously that 50% of the arterioles occluded in VWF−/− mice.16 The difference observed in the percentage of occlusion between the 2 types of vessels could perhaps be due to the size of the vessels as the observed veins were larger in diameter than the arterioles, thus requiring larger thrombi for occlusion. VWF−/− mice have 20% of the WT level of FVIII,15 and as consequence the VWF−/− mice showed a defect in whole blood clotting time and clot rate. We thought that possibly the defect observed in experimental venous thrombosis in VWF−/− mice could be a consequence of low FVIII levels. However, our results suggest that this was not the case for the following reasons: Infusion of r-hu-FVIII in VWF−/− mice resulted in the complete recovery of thrombus stability and of the whole blood clotting parameters for at least 20 minutes after infusion (Figure 3; Table 1) but did not lead to formation of occlusive thrombi (Figure 4–5). Thus the adhesive function of VWF is important on its own merits.
VWF is a prominent ligand for GPIbα and the integrin αIIbβ3 on the platelet surface. In arterioles, thrombi do not form without functional GPIbα and thus its role far exceeds that of VWF.30 In veins we show that both GPIbα and VWF are important for optimal platelet adhesion to subendothelium, however injured venules occlude in all the mice lacking the GPIbα extracellular domain (Figure 5B) but not in mice lacking VWF (Figure 5A). Thus, GPIbα does not appear to be essential to form occlusive thrombi under venous shear conditions. This finding is consistent with the in vitro results published previously where blockade of GPIbα did not have an effect on thrombus volume at low shear of 100 s−1.13 Upon platelet activation, VWF released from the platelets and plasma VWF can compete for the integrin αIIbβ3 receptor with other adhesive proteins such as fibronectin and fibrinogen. Using the ferric-chloride injury model, our group has shown that under arterial conditions thrombosis depends on VWF, fibrinogen, and fibronectin in vivo.16,31 Using the same model, we have documented that the absence31 or lower levels (50%) of plasma fibronectin result in serious arterial thrombosis defect32 but not a venous thrombosis defect.32 Thus fibronectin is important in thrombosis only at arterial shear rates, while VWF plays an important role at both arterial and venous shear rates.
In conclusion, our results provide evidence for the in vivo role of VWF and GPIbα in platelet adhesion and also that of FVIII in subsequent thrombus growth in experimental thrombosis under venous flow conditions. The formation of occlusive thrombi in the IL4Rα/GPIbα-tg mice and not in VWF−/− mice shows that VWF likely uses other adhesion receptors besides GPIbα in thrombus growth under venous shear conditions. Our findings also suggest that the inhibition of VWF binding activity and/or specific VWF degradation have a therapeutic potential in pathological conditions related to venous thrombosis.
Authorship
Contribution: A.K.C. designed and performed most of the experiments and wrote the paper; J.K. measured all clotting parameters; C.B.L. analyzed all recordings; W.B. provided results concerning GPIb and helpful discussions; D.D.W. helped design the study, analyze the results, and write the paper. Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Denisa D. Wagner, CBR Institute for Biomedical Research and Department of Pathology, Harvard Medical School, 800 Huntington Ave, Boston, MA-02115; e-mail: wagner@cbr.med.harvard.edu.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health grant R37 HL41002 (D.D.W.).
We thank Janos Polgar for helpful discussions; Haig Kazazian, Jerry Ware, and Zaverio Ruggeri for genetically modified mice; and Lesley Cowan for help in preparing the paper.