Abstract
BACKGROUND: Despite advances in transplantation immunology, there is no clinically practical tool to predict acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Murine models indicate that aGVHD is promoted by interleukin-7 (IL-7), a homeostatic cytokine for naïve CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells. We hypothesized that serum IL-7 levels might be associated with the development of aGVHD in patients (pts) undergoing allogeneic HSCT, and evaluated this using serum samples obtained for this purpose in a prospective clinical trial.
METHODS: Thirty-one pts underwent allogeneic HSCT from HLA-identical siblings. Pts received 1 to 3 pre-transplant chemotherapy cycles to induce profound, uniform host lymphopenia (CD4<100), followed by fludarabine-based reduced-intensity conditioning. GVHD prophylaxis was cyclosporine & methotrexate. Serum IL-7 was measured by ELISA at baseline and multiple time points from the day of transplant through 1 year after allogeneic HSCT. IL-7 levels were evaluated for associations with blood lymphocyte counts, aGVHD, and survival. Other variables examined for association with aGVHD were pt and donor age; CD3+ and CD34+ cell doses; donor gender; donor-recipient gender mismatch; donor or recipient CMV status, prior rituximab therapy; donor lymphoid or myeloid chimerism >95% at day +14; serum IL-15 levels; and levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor-α receptors 1 and 2 (sTNFR1 and sTNFR2).
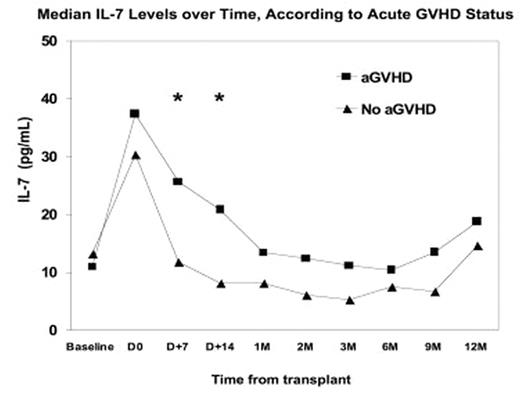
RESULTS: Grades I, II, and III aGVHD occurred in 3%, 23%, and 19%, respectively; none had grade IV. Median (range) IL-7 levels rose from baseline 12.1 (0–46.9) pg/ml to 37 (13.3–79.2) pg/ml on day 0 before allografting, then fell to 12.0 (1.3–74.7) pg/ml by day +14; these changes were inversely correlated with absolute lymphocyte counts, CD3, CD4, and CD8 counts at baseline and day +7. The development of aGVHD was associated with IL-7 levels at day +7 (p=0.01) and day +14 (p=0.000033) post-transplant (Figure), along with the allograft CD34+ cell dose (p=0.012). Higher IL-7 levels at day +14 corresponded to more severe grades of aGVHD (p<0.0001).
In logistic regression models, these factors jointly classified pts according to development or avoidance of aGVHD with a maximum sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 100%. IL-7 levels were more strongly associated with aGVHD than were sTNFR levels or other parameters.
CONCLUSIONS: Determination of serum IL-7 levels in the early post-transplant period accurately predicted the risk of developing aGVHD after allogeneic HSCT and holds promise as a simple, reproducible test to select pts for pre-emptive therapy. These data support preclinical observations that demonstrate a critical role for IL-7 in inducing aGVHD and provide a rational basis for novel approaches to GVHD prophylaxis through modulation of the IL-7 homeostatic pathway.
Author notes
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.