Abstract
Effective immunotherapy must overcome tolerance toward tumor antigens and avoid subsequent inhibition of stimulated antitumor immunity. The specific contribution of immune regulatory mechanisms intrinsic to dendritic cells (DCs), especially with regard to regulatory T cells (T regs), is of emerging importance. We have found that all conventional, immunogenic human DCs express the immunomodulatory enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and that IDO protein expression and activity are markedly increased in mature compared with immature DCs. Priming of resting T cells with mature IDO+ DCs in an autologous mixed leukocyte reaction (MLR) increases the proportion of CD4+CD25+ T cells capable of suppressing allogeneic T cell proliferation in secondary MLRs as much as 10-fold above baseline (Figure 1A). Conversely, 1-methyl-tryptophan, a competitive inhibitor of IDO, dampens the inhibitory activity (Figure 1A). Further characterization of the suppressor T cells was performed after cytofluorographic sorting into CD4+CD25hi, CD4+CD25int, and CD4+CD25low/− subpopulations. Post-sort analysis revealed that the majority (>60%) of the CD4+CD25hi cells coexpressed Foxp3, which was absent in the CD4+CD25low/− cells. Separate studies showed that these Foxp3+ cells express little or no CD127 (IL-7R-alpha). Candidate CD4+CD25hi T regs inhibited DC-stimulated allogeneic T cell proliferation in a dose dependent manner, with >90% inhibition at a suppressor to responder T cell ratio of 1:1 and ∼50% inhibition at a ratio as low as 1:25 (Figure 1B). CD4+CD25low/− cells were not inhibitory, and CD4+CD25int cells exerted intermediate suppression depending on dose (Figure 1B). CD4+CD25hi T regs exert similar inhibition of autologous T cell responses to stimulation de novo by DCs. Both the priming and effector phases of T reg suppression were contact dependent. Moreover, depletion of the trace population of CD4+CD25hi T cells at the outset of autologous priming largely abolished the relative expansion of this population. These results clearly demonstrate that mature conventional human DCs support relative but significant expansion of autologous, constitutive CD4+CD25hi T cells, which coexpress Foxp3, express little or no CD127, and exert significant suppression of both allogeneic and autologous T cells stimulated de novo by DCs. Although contrary to the anticipated enrichment of IDO in immature DCs because of their expected tolerogenicity, these findings underscore the importance of regulatory mechanisms exerted by immunogenic cells like mature conventional DCs. While this may provide a physiologic means of turning off an otherwise unchecked immune response, this IDO-mediated pathway in DCs provides a rational target for optimizing host immune responses against tumor antigens. This should result in more sustained benefit from active immunotherapy with DC-based vaccines.
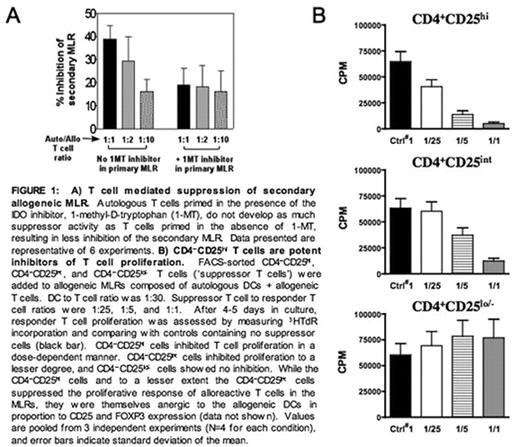
A) T cell mediated suppression of secondary allogeneic MLR. Autologous T eels primed in the presence of the IDO inhibitor. 1-metnyl-D-tryptophan (1-MT), do not develop as much suppressor activity as T cells primed in the absence of 1-MT, resulting in loss inhibition of the secondary MLR Data presented are representative of 6 experiments. B) CD4−CD25***** T cells art potent inhibitors of T cell proliferation. FACS-sorted CD4−CD25******, CD4−CD25*****, and CD4−CD25***** T cells (‘suppressor T cells’) were added to allogeneic MLRs composed of autologous DCs + allogeneic T cells. DC to T cell ratio was 1:30. Suppressor T cell to responder T cell ratios were 1:25, 1:5, and 1:1. After 4–5 days in culture, responder T cell proliferation was assessed by measuring 3HTdR incorporation and comparing with controls containing no suppressor cells (black bar). CD4−CD25***** cells inhibited T cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. CD4−CD25***** cells inhibited proliferation to a lesser degree, and CD4-CD25***** cells showed no inhibition. While the CD4−CD25***** cells and to a lesser extent the CD4−CD25***** cells suppressed the proliferative response of alloreactive T cells in the MLRs, they were themselves anergic to the allogeneic DCs in proportion to CD25 and FOXP3 expression (data not shown). Values are pooled from 3 independent experiments (N=4 for each condition), and error bars indicate standard deviation of the mean.
A) T cell mediated suppression of secondary allogeneic MLR. Autologous T eels primed in the presence of the IDO inhibitor. 1-metnyl-D-tryptophan (1-MT), do not develop as much suppressor activity as T cells primed in the absence of 1-MT, resulting in loss inhibition of the secondary MLR Data presented are representative of 6 experiments. B) CD4−CD25***** T cells art potent inhibitors of T cell proliferation. FACS-sorted CD4−CD25******, CD4−CD25*****, and CD4−CD25***** T cells (‘suppressor T cells’) were added to allogeneic MLRs composed of autologous DCs + allogeneic T cells. DC to T cell ratio was 1:30. Suppressor T cell to responder T cell ratios were 1:25, 1:5, and 1:1. After 4–5 days in culture, responder T cell proliferation was assessed by measuring 3HTdR incorporation and comparing with controls containing no suppressor cells (black bar). CD4−CD25***** cells inhibited T cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. CD4−CD25***** cells inhibited proliferation to a lesser degree, and CD4-CD25***** cells showed no inhibition. While the CD4−CD25***** cells and to a lesser extent the CD4−CD25***** cells suppressed the proliferative response of alloreactive T cells in the MLRs, they were themselves anergic to the allogeneic DCs in proportion to CD25 and FOXP3 expression (data not shown). Values are pooled from 3 independent experiments (N=4 for each condition), and error bars indicate standard deviation of the mean.
Author notes
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.