Abstract
Loss of a whole chromosome 5 or a deletion of the long arm, del(5q), is a recurring abnormality in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). To identify a leukemia-related gene on chromosome 5, we previously delineated a 970-kb segment of 5q31 that is deleted in all patients examined, and prepared a transcript map of this region. EGR1 is a candidate tumor suppressor gene within the commonly deleted segment of 5q, and encodes a zinc finger transcription factor. To test the hypothesis that loss of function of Egr1 is an initiating event in the pathogenesis of AML/MDS, Egr1-deficient mice were treated with a potent DNA alkylating agent, N-ethyl-nitrosourea (ENU), to induce secondary cooperating mutations. Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice treated with ENU developed immature T-cell lymphomas (CD4+, CD8+) or a myeloproliferative disorder (MPD) at increased rates and with shorter latencies than that of wild-type littermates. The MPD was characterized by an elevated white blood cell count, anemia, and thrombocytopenia with ineffective erythropoiesis. Biallelic mutations of Egr1 were not observed in MPDs in Egr1+/− mice. Our data suggest that haploinsufficiency for Egr1 plays a role in murine leukemogenesis, and in the development of AML/MDS characterized by abnormalities of chromosome 5.
Introduction
Loss of chromosome 5, or a del(5q), is a recurring abnormality observed in 10% of patients with a myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML) arising de novo, and in 40% of patients with therapy-related MDS or AML (t-MDS/t-AML).1 In previous studies, we delineated a 970-kb commonly deleted segment (CDS) of 5q31, and created a transcript map of the region.2 Molecular analysis of 20 candidate genes within the CDS of 5q did not reveal inactivating mutations in the remaining alleles, nor is there evidence of transcriptional silencing via DNA methylation.2,3 These observations are compatible with a haploinsufficiency model in which loss of 1 allele of the relevant gene(s) perturbs cell fate. One such candidate is the gene encoding the transcription factor, early growth response 1 (EGR1). EGR1 is a member of the WT-1 family of transcription factors and contains 3 Cys2His2 Zn fingers that bind the GC-rich consensus sequences, GCG(G/T)GGGCG.4 In the mouse, Egr1 has been shown to be an early response gene, and mediates the cellular response to growth factors, mitogens, and stress stimuli.5-8 Egr1+/− or Egr1−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) bypass senescence and have immortalized growth characteristics, suggesting a role for Egr1 as a “gatekeeper” of p53-dependent growth regulation.9
Egr1 has been shown to be a tumor suppressor in a 2-stage skin carcinogenesis mouse model. Egr1-null mice treated with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) developed skin tumors at an increased rate compared with that of wild-type and heterozygous littermates.10 EGR1 has also been shown to act as a tumor suppressor gene in human tumors. For example, deletion of EGR1 in estrogen receptor–negative (ER−) breast carcinomas correlated with a higher grade of tumor, suggesting that loss of EGR1 (and thereby loss of functioning EGR1) may contribute to the pathogenesis of ER− breast carcinomas.11 In non–small-cell lung cancer, low EGR1 expression was predicative of poor survival independent of tumor stage.12 Recently, EGR1 has been shown to be a direct transcriptional regulator of many known tumor suppressor genes (eg, TP53, CDKN1A/p21, TGFB, and PTEN), and loss of function of these tumor suppressors correlates with immortalized growth characteristics and escape from apoptosis (reviewed in Baron et al13 ).
We hypothesized that loss of function of EGR1 plays an initiating role in the development of primary MDS, AML de novo, and t-MDS/t-AML characterized by abnormalities of chromosome 5. To test this hypothesis, we characterized the hematopoietic potential of Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice. In addition, we treated wild-type (WT), Egr1+/−, and Egr1−/− mice with a potent DNA alkylating agent, N-ethyl-nitrosourea (ENU), to induce secondary cooperating mutations. Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice treated with ENU develop T-cell lymphoma or a myeloproliferative disorder (MPD) at an increased rate with a shorter latency period than that of WT littermates. Our data suggest that loss of a single allele of Egr1 cooperates with mutations induced by an alkylating agent in the development of malignant lymphoid and myeloid diseases in mice. The absence of biallelic loss of the genes within the CDS of 5q31 suggests that loss of a single allele of EGR1 as a result of the −5/del(5q) may play a role in the pathogenesis of MDS, AML de novo, and t-MDS/t-AML.
Materials and methods
Egr1 knockout mice
Egr1 knockout mice (C57BL/6) were generously provided by Dr Jeffrey Milbrandt (Washington University, St Louis, MO), and were bred to generate the cohorts used for all of these studies. Egr1 was disrupted by insertion of a neomycin resistance gene cassette into a unique NdeI site upstream of the DNA binding domain, which resulted in a complete loss of Egr1 protein expression.14 All mice used for this study were housed in a specific pathogen–free barrier facility in accordance with the University of Chicago Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) guidelines. WT, Egr1+/−, and Egr1−/− mice received intraperitoneal injections of 100 mg/kg ENU at either 4 or 20 weeks of age. ENU-treated mice were monitored for the onset of disease by performing complete blood counts (CBCs; Hemavet 850; CDC Technologies, Inc., Oxford, CT) at 6-week intervals and when the animals became moribund, and by monitoring weights weekly. All organs were recovered, fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 4 to 5 μm, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histologic examination by a pathologist. Bone marrow and spleen single-cell suspensions were prepared for spectral karyotyping analysis, flow cytometric analysis, or transplantation studies.
In vitro differentiation assays
Bone marrow from WT, Egr1+/−, and Egr1−/− mice was plated in duplicate in methylcellulose media containing murine stem cell factor (mSCF), murine interleukin-3 (mIL-3), mIL-6, and human erythropoietin (hEpo) (Stem Cell Technologies, Vancouver, BC) at a final concentration of 2 × 104 cells/mL. Colonies were enumerated as described by the manufacturer. The averages of duplicate platings, performed in triplicate for each genotype, were graphed as the number of colonies per 105 cells plated per mL of culture. A minimum of 3 mice for each genotype and timepoint were used to generate the mean colony number for each cohort.
Serial replating of murine bone marrow
Lineage depletion of bone marrow isolated from WT, Egr1+/−, and Egr1−/− mice was performed using a magnetic negative-selection hematopoietic progenitor enrichment cocktail (Stem Cell Technologies). Lineage-depleted bone marrow cells were added to methylcellulose media containing mSCF, mIL-3, mIL-6, and hEpo (Stem Cell Technologies) at a final concentration of 2 × 103 cells/mL and plated in duplicate. The plates were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2/95% air for 7 to 10 days to allow colony formation to occur. The cells were then collected, rinsed, and replated in new media at a final concentration of 2 × 104 cells/mL to test their potential to form colonies upon secondary plating. This process was repeated until colony forming potential was exhausted.
Analysis of stem cells
LSK analysis.
Stem and progenitor cells were purified from mouse bone marrow by negative selection (EasySep; Stem Cell Technologies). Lineage-depleted bone marrow was analyzed using immunophenotyping with Lin+ biotin antibody cocktail and streptavidin PerCP-Cy5.5 antibody, APC antimouse CD117 (Kit) antibody, and PE antimouse Ly6A/E (Sca-1) (BD Pharmingen, San Jose, CA). Lin−Sca-1+Kit+ (LSK) populations were identified using a fluorescence-activated cell-sorting (FACS) Canto FACS machine. LSK populations were scored as lineage−, Kit+, and Sca-1+ cells.
CAFC assay.
A stromal cell layer of FMBD-1 cells (kindly provided by Dr Gary van Zant, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY) was grown in 96-well tissue-culture plates using cobblestone area–forming cell (CAFC) media (Dulbecco modified Eagle medium, 10% fetal bovine serum, 5% horse serum, 10−5 M hydrocortisone, 3.3 mM leukemia, 80 U/mL penicillin, 80 μg/mL streptomycin, 10−4 M β-mercaptoethanol, and 25 mM NaHCO3; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). The stromal cells were grown to confluency, and were overlaid with bone marrow cell suspensions at 6 dilutions, 3-fold apart with 20 replicate wells (81 000, 27 000, 9000, 3000, 1000, and 333 cells/well). Once the bone marrow was added, the media were switched to 20% horse serum as the sole serum source. Cobblestone areas were evaluated 5 weeks after plating.
SKY and FISH analysis
Cytogenetic and spectral karyotyping (SKY) analysis was performed on spleen or bone marrow cells as described previously.15 A minimum of 10 metaphase cells were analyzed per sample. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed as described previously.16 A biotin-labeled P1 artificial chromosome (PAC) probe from mouse chromosome 15 containing the Myc gene (RPCI23–98D8) was prepared by nick-translation using Bio-16–dUTP (Enzo Diagnostics, Farmingdale, NY), and detected with fluorescein-conjugated avidin (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). Cells were stained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole-dihydrochloride (DAPI), and 100 interphase cells were scored for each sample.
SSCP analysis
Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis was performed as described previously.17 Pairs of primers were designed from intron sequences flanking each exon (Table S3, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). Samples showing mobility shifts were subjected to direct sequencing. Mutations were confirmed by performing independent sequencing reactions on a second set of amplified products.
Transplantation assays
Sublethally irradiated (2 × 450 rad) and lethally irradiated (1 × 960 rad) recipient mice (C57Bl/6, Ly5.1) received 107 bone marrow and 1.5 × 107 spleen cells (C57Bl/6, Ly5.2) from moribund mice presenting with a MPD, and were monitored for the onset of disease.
Flow cytometry
Single-cell suspensions of bone marrow and spleen were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and incubated on ice for 15 minutes with FACS media (PBS, 0.1% sodium azide) and 2.4G2 (BD Pharmingen) to block Fc receptors. After washing, cells were incubated with monoclonal antibodies (CD45R, CD4, CD8, CD71, Ter119, Gr-1, Mac-1, F4/80, Kit, and CD34) on ice for 30 minutes. After a final wash, cells were resuspended in FACS media and analyzed using a FACS Canto flow cytometer (BD Biosciences).
Results
Characterization of the hematopoietic potential of Egr1-deficient mice
To examine the role of Egr1 in hematopoiesis, we characterized Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice. Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice are viable with mild postnatal growth retardation. CBCs were performed every 6 weeks for 18 months on WT, Egr1+/−, and Egr1−/− mice (15 mice per cohort). Egr1−/− mice display mildly elevated white blood cell counts as a result of increased lymphocyte counts, compared with wild-type and heterozygous mice (Figure S1). In addition, we collected bone marrow at 6 month intervals, up to 18 months of age, for in vitro progenitor colony growth (burst-forming unit erythroid [BFU-E], colony-forming unit erythroid [CFU-E], CFU–granulocyte macrophage [GM], CFU-M, CFU-G, and CFU–granulocyte-erythroid-macrophage-megakaryocyte [GEMM]) and serial replating assays of lineage-depleted bone marrow in vitro. Although slight differences in the CFU-E and CFU-M colony numbers were noted, we did not observe any significant differences in the ability to give rise to all lineages analyzed (Figure S2). Moreover, there were no differences in the self-renewal potentials of WT, Egr1+/−, and Egr1−/− bone marrow as assessed by serial replating assays (data not shown).
To determine whether Egr1 deficiency results in alterations in the number or self-renewal capacity of hematopoietic stem cells, we compared stem cell populations in WT, Egr1+/−, and Egr1−/− mice using FACS analysis of LSK populations in lineage-depleted bone marrow cells, and we used the CAFC assay to enumerate stem cells (CAFC units were scored on day 35). There were no significant differences in the stem/progenitor populations. Moreover, bone marrow cells from Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice produced the same number of CAFC units as those from wild-type bone marrow, suggesting that loss of function of Egr1 does not affect the proliferative capacity of the hematopoietic stem cell pool in vivo. Thus, heterozygous or homozygous loss of Egr1 alone, under normal physiologic conditions, does not affect the hematopoietic potential of murine bone marrow.
Secondary mutations cooperate with loss of Egr1 in murine leukemogenesis
Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice monitored for over 18 months did not develop tumors spontaneously, and this may be due in part to compensation by other Egr family members.14 In addition, there is extensive evidence that the initiating mutations in leukemogenesis (eg, translocation fusion proteins) are required, but not sufficient, to induce leukemogenesis, and that secondary mutations cooperate to give rise to the disease. To investigate whether loss of Egr1 cooperates with secondary mutations to induce leukemia in the mouse, WT, Egr1+/−, and Egr1−/− mice were treated with a single dose of 100 mg/kg ENU at 4 weeks or 20 weeks of age. ENU was chosen because it is an alkylating agent, and may recapitulate the effects of alkylating agent chemotherapy in patients who develop t-AML.
ENU-treated Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice develop T-cell lymphomas.
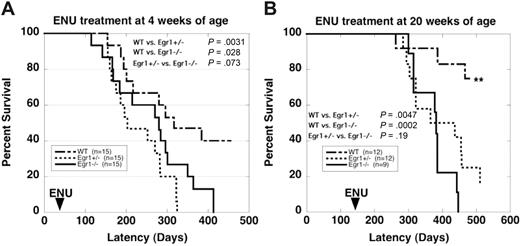
Based on studies in the literature using a similar dose of ENU,18 we expected that 20% to 30% of our wild-type mice would develop immature T-cell lymphomas. With ENU treatment at 4 weeks of age, 46% of Egr1+/− and 53% of Egr1−/− mice developed T-cell lymphomas compared with 26% of wild-type mice (Table 1; Figure 1A). Analysis of the spleen using flow cytometry revealed a high degree of infiltrating CD4+, CD8+ T-cell progenitors (data not shown), and histologic analysis of H&E-stained paraffin-embedded tissue sections confirmed a diagnosis of immature T-cell lymphoma (data not shown). In an effort to bypass this background incidence of T-cell lymphomas, we treated a second cohort of mice at 20 weeks of age, after thymic development is complete (Table 1; Figure 1B). The incidence of lymphoma in wild-type mice decreased to less than 10%, whereas the incidence of lymphoma in Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice was unchanged, with 50% of Egr1+/− and 44% of Egr1−/− mice developing lymphomas. These results suggest that loss of function of Egr1 plays a role in the development of T-cell lymphoma in the mouse.
Survival curves of WT and Egr1-deficient mice after ENU treatment. (A) 4 weeks of age. (B) 20 weeks of age. Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice developed T-cell lymphomas or MPD at a significantly increased rate and frequency compared with WT littermates. **Only 1 mouse from the WT cohort treated at 20 weeks developed a malignant disease (lymphoma). Two mice from this cohort were killed due to severe dermatitis. (Note that dermatitis is a common phenotype in C57BL/6 mice, and we observed no differences in the incidence or severity of dermatitis in WT versus Egr1-deficient mice, nor in healthy mice versus mice with lymphoma or MPD.)
Survival curves of WT and Egr1-deficient mice after ENU treatment. (A) 4 weeks of age. (B) 20 weeks of age. Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice developed T-cell lymphomas or MPD at a significantly increased rate and frequency compared with WT littermates. **Only 1 mouse from the WT cohort treated at 20 weeks developed a malignant disease (lymphoma). Two mice from this cohort were killed due to severe dermatitis. (Note that dermatitis is a common phenotype in C57BL/6 mice, and we observed no differences in the incidence or severity of dermatitis in WT versus Egr1-deficient mice, nor in healthy mice versus mice with lymphoma or MPD.)
ENU-treated Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice develop a MPD.
In addition to the increased rate of lymphomagenesis, Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice developed a MPD at an increased rate compared with wild-type littermates. The development of a MPD or lymphoma was mutually exclusive in that we did not observe both diseases in any mouse. With ENU treatment at 4 weeks of age, 33% of Egr1+/− mice and 40% of Egr1−/− mice developed a MPD, compared with only 13% of wild-type mice. With ENU treatment at 20 weeks of age, 25% of Egr1+/− mice and 33% of Egr1−/− mice developed a MPD (Table 1; Figure 1). Wild-type mice did not develop MPD in this cohort. Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice developed MPD at the same rate, suggesting that loss of a single allele is sufficient for disease predisposition. The development of a MPD after ENU treatment is notable in that MPD has not been observed previously in the C57BL/6 strain, or in 19 other inbred strains treated with ENU.18
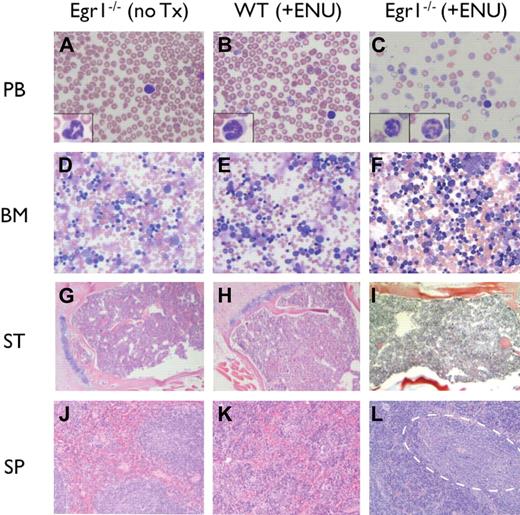
The MPD was characterized by elevated white blood cell counts (WBC > 19 × 109/L), anemia (Hb < 75g/L), and thrombocytopenia (platelets < 800 × 109/L), with ineffective erythropoiesis in the bone marrow and spleen (Table 2; Figure 2). Microscopic analysis of peripheral blood revealed marked anemia in all genotypes, and thrombocytopenia in Egr1-null mice. Dysplastic neutrophils were observed in the bone marrow and peripheral blood with hypersegmented and atypical nuclei and a hypogranular cytoplasm. The bone marrow was hypercellular with full maturation of all lineages, but no increase in blasts. The mice presented with severe splenomegaly (15- to 20-fold increase in spleen weight), and histologic analysis revealed a dramatic increase in erythropoiesis, with areas of immature and maturing myeloid elements. By flow cytometric analysis, there was an expansion of erythroid (Ter119+,CD71+) and myeloid (Gr1+, Mac1+) populations in the spleen; immature cells (Kit+, CD34+), however, were not increased (Table 3). Following the Bethesda Criteria,33 we classify this disease as an MPD with ineffective erythropoiesis. This MPD also resembles human MDS/MPD overlap disorders.
Histologic analysis of MPDs. (A-C) Peripheral blood (PB) smears stained with Wright-Giemsa; insets show high-magnification images of representative neutrophils. (D-F) Bone marrow (BM) aspirates stained with Wright-Giemsa. (G-I) Paraffin-embedded sections of sternum (ST) stained with H&E. (J-L) Paraffin-embedded sections of spleen (SP) stained with H&E. (L) Dashed outline encompasses pockets of immature and maturing myeloid elements. Images were obtained using an Olympus microscope (Model BX45, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with an Olympus DP12 digital camera (top row: 40× Plan Air objective/0.6NA (insets, 100× oil objective/1.26 NA), middle row: 10× Plan air objective/0.3 NA, bottom two rows: 4× Plan air objective/0.1NA), and processed using Microsoft PowerPoint (Redmond, WA).
Histologic analysis of MPDs. (A-C) Peripheral blood (PB) smears stained with Wright-Giemsa; insets show high-magnification images of representative neutrophils. (D-F) Bone marrow (BM) aspirates stained with Wright-Giemsa. (G-I) Paraffin-embedded sections of sternum (ST) stained with H&E. (J-L) Paraffin-embedded sections of spleen (SP) stained with H&E. (L) Dashed outline encompasses pockets of immature and maturing myeloid elements. Images were obtained using an Olympus microscope (Model BX45, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with an Olympus DP12 digital camera (top row: 40× Plan Air objective/0.6NA (insets, 100× oil objective/1.26 NA), middle row: 10× Plan air objective/0.3 NA, bottom two rows: 4× Plan air objective/0.1NA), and processed using Microsoft PowerPoint (Redmond, WA).
Loss of a single allele of Egr1 is sufficient for disease predisposition
To date, we have not identified mutations in any of the genes located within the CDS of chromosome 5 in leukemia cells from patients with AML de novo or t-MDS/t-AML, nor have we observed homozygous deletions or gene silencing via DNA methylation (L. Godley et al, unpublished data, June 2002).2 These data suggest that the proposed tumor suppressor gene within the CDS is acting through haploinsufficiency. As described here, Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice develop T-cell lymphoma or MPD at the same rate and with a similar latency period, suggesting that loss of a single allele of Egr1 is sufficient for disease predisposition. To determine whether the remaining allele of Egr1 was mutated as a result of ENU treatment, we performed SSCP analysis of the coding sequence and intron-exon junctions of Egr1 in lymphomas (WT, 2 cases; Egr1−/−, 5 cases) or MPDs (WT, 1 case; Egr1+/−, 3 cases; Table S1). To date, we have not identified Egr1 mutations in malignant cells from wild-type or Egr1+/− mice.
Secondary mutations are required for disease progression
The characterization of a number of mouse models that recapitulate the genetic changes in human leukemias (eg, RUNX1-ETO and CBFB-MYH11 fusions) has shown that secondary cooperating mutations are required for the development of disease.19-22 At typical doses (100–400 mg/kg), ENU induces point mutations at a rate of 1 in 1.01 Mb, of which 1 in 1.82 Mb are potentially functional.23 The actual number or combination of genes that must be mutated to cooperate with heterozygous or homozygous loss of Egr1 is not known.
To identify genes that cooperate with loss of Egr1 in murine leukemogenesis, we performed SSCP analysis on candidate genes that are known to be involved in primary MDS, AML de novo, or t-MDS/t-AML, including Tp53 (exons 4–9), Nras and Kras1 (exons 1–3 encoding amino acids 12, 13, 59, and 61), and Jak2 (exon 13 encompassing the codon for amino acid 617). Approximately 25% of patients with t-AML have small insertions or deletions of TP53 that result in frameshifts, missense mutations, and splice site mutations.24 Moreover, mutations of TP53 in t-MDS/t-AML are associated with abnormalities of chromosome 5. RAS gene mutations are found in approximately 30% of patients with t-AML, and correlate with −7/del(7q).25 Missense mutations of JAK2 (a valine to phenylalanine shift at amino acid 617) that result in a constitutively active tyrosine kinase have been described in patients with myeloproliferative disorders, including polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET), and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis (MMM).26 The JAK2 kinase is downstream of several cytokine receptors, including the Epo receptor (EPOR), and plays a role in hematopoietic cytokine signaling pathways. Amino acid 617 is conserved between mouse and humans (data not shown).
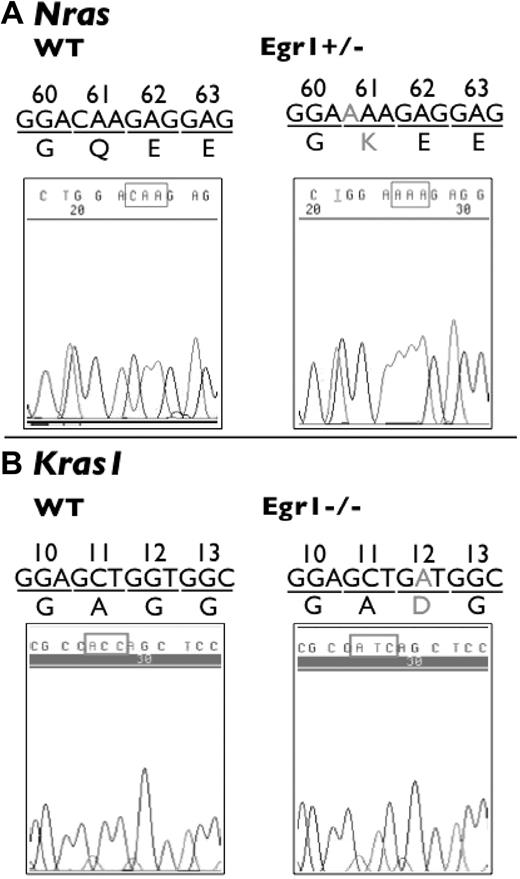
This analysis revealed that there are no mutations in the Tp53 or Jak2 sequences analyzed in the lymphomas or MPDs arising in Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice treated with ENU. However, we identified 1 transversion mutation at the first base of codon 61 (CAA > AAA) of Nras, resulting in a change from glutamine to lysine in a lymphoma sample from an Egr1+/− mouse (Figure 3). We also identified 1 transition mutation at the first base of codon 12 (GGT > GAT) of Kras1, resulting in a glycine to asparagine change in a lymphoma sample from an Egr1−/− mouse (Figure 3). Mutations of Nras and Kras1 have been reported previously in mice treated with ENU.27,28
Mutations of Nras and Kras 1 in ENU-induced lymphomas. Mutations of Nras and Kras1 were identified in T-cell lymphomas in Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice. (A) SSCP analysis revealed a transversion mutation at the first base of codon 61 (CAA > AAA) of Nras in a lymphoma sample from an Egr1+/− mouse. (B) SSCP revealed a transition mutation at the second base of codon 12 (GGT > GAT) of Kras1 in a lymphoma sample from an Egr1−/− mouse. The DNA trace of Kras1 is the sequence from the reverse strand.
Mutations of Nras and Kras 1 in ENU-induced lymphomas. Mutations of Nras and Kras1 were identified in T-cell lymphomas in Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice. (A) SSCP analysis revealed a transversion mutation at the first base of codon 61 (CAA > AAA) of Nras in a lymphoma sample from an Egr1+/− mouse. (B) SSCP revealed a transition mutation at the second base of codon 12 (GGT > GAT) of Kras1 in a lymphoma sample from an Egr1−/− mouse. The DNA trace of Kras1 is the sequence from the reverse strand.
Recently, Laslo et al demonstrated functional redundancy of Egr1 and Egr2 in regulating macrophage cell fate.29 Hematopoietic progenitors from Egr1−/−, Egr2+/− compound mutant mice are defective in undergoing macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF)–induced differentiation, compared with hematopoietic progenitors from Egr1−/− or Egr2−/− mice. In addition, the authors noted that Egr1 and Egr2 function redundantly, not only in positively regulating macrophage differentiation, but also in the repression of the alternate lineage neutrophil genes.29 At present, our understanding of the functional redundancy among the Egr family members in the regulation of hematopoiesis and lineage determination is incomplete. To determine whether Egr2 cooperates with loss of 1 Egr1 allele, and is a target of ENU mutagenesis, we performed SSCP analysis of the coding sequences of Egr2. Our analysis revealed that Egr2 is not mutated in any of the lymphomas or MPDs examined (data not shown).
To determine whether T-cell lymphomas or MPDs arising in Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice have acquired clonal chromosomal abnormalities, we performed SKY analysis (Table 4). One of 7 lymphomas analyzed had a clonal abnormaility (+mar), and the remainder had a normal karyotype. Of 6 MPDs examined, 5 had a normal karyotype, and 1 had a clonal abnormality, characterized by trisomy 15 (mouse no. 95). Trisomy 15 is the most common abnormality in murine T-cell lymphomas and in murine B-cell leukemias arising in irradiated Eμ-BCL2 transgenic mice.30,31 Moreover, we have detected trisomy 15 in myeloid neoplasms arising in a number of murine models that recapitulate the genetic mutations in human myeloid leukemias.32 To determine whether other MPDs arising in Egr1−/− and Egr1−/− mice were characterized by trisomy 15, we performed interphase FISH analysis using a PAC clone containing the mouse Myc gene on chromosome 15 (Table S2). Of 7 mice analyzed, 4 had a normal karyotype, 1 had +15, and 2 had an insufficient number of metaphase cells for SKY analysis (Table S2). We did not detect trisomy 15 by FISH analysis in any of the MPDs, including the disease in mouse no. 95, which had a low percentage clone with +15 by SKY analysis.
Transplantability
The ability to give rise to transplantable tumors can be helpful in distinguishing neoplasms from a reactive condition. Although transplantability often correlates with the degree of malignancy, not all malignancies are transplantable.33 To determine whether the MPDs arising in Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice were transplantable, we transplanted bone marrow and spleen cells from Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice (Ly5.2) with a MPD into lethally irradiated (7 mice) or sublethally irradiated (7 mice) syngeneic recipients (Ly5.1). Recipient mice were monitored for engraftment and the onset of disease by performing CBCs every 14 days after transplantation. All mice that received cells recovered fully from sublethal or lethal irradiation, and all mice have shown long-term engraftment of the donor cells. To date, we have not observed the onset of disease in any mice (median follow-up, 32 weeks; range, 29–37 weeks).
Discussion
Despite intensive analysis by a number of laboratories, the genes involved in the pathogenesis of AML associated with a −5/del(5q) have not been identified. Moreover, the available data suggest that 1 or more of the candidate tumor suppressor genes in the CDS of 5q31 acts through haploinsufficiency to initiate the development of MDS/AML. One candidate is EGR1, a tumor suppressor gene within the CDS of 5q. EGR1 is a member of the WT-1 family of transcription factors and mediates the cellular response to mitogens, stress stimuli, and growth factors.5-8 In mice, Egr1 acts though haploinsufficiency in regulating p53-dependent growth,9 and EGR1 has been shown to act as a classical (2-hit) tumor suppressor gene in the mouse and in humans.10-13
In this report, we demonstrate that heterozygous or homozygous loss of Egr1 cooperates with secondary mutations induced by ENU to induce neoplasms in mice. Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice develop T-cell lymphoma or MPD at an increased rate and reduced latency over that observed in wild-type littermates. Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice develop T-cell lymphoma or MPD at the same rate and latency, suggesting that loss of a single allele of Egr1 is sufficient for disease predisposition. This is consistent with observations in patients with MDS/AML characterized by abnormalities of chromosome 5, in that only 1 EGR1 allele is affected. Together, these results suggest that EGR1 may be acting though haploinsufficiency to initiate the development of MDS/AML.
In Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice, the MPD was characterized by elevated WBC counts, anemia, and thrombocytopenia, with ineffective erythropoiesis in the bone marrow and spleen. The disease recapitulates some, but not all, of the clinical features seen in patients who present with primary MDS, AML de novo, or t-AML with a −5/del(5q). Both diseases present with a proliferative and dysplastic component involving multiple lineages, and both are ultimately fatal. The absence of a blast cell component in the Egr1+/− and Egr1−/− mice could suggest that additional cooperating mutations are required for progression to acute leukemia. Alternatively, genetic and physiologic differences between humans and mice may influence the phenotype of the disease. Activating mutations of Kras1 and Flt3, as well as inactivating Nf1 mutations, result in MPD in mouse models, implicating deregulated cytokine-signaling pathways in the pathogenesis of these disorders. Although we did not observe mutations of Kras1 or Nras in the MPDs arising in Egr1+/− or Egr1−/− mice, oncogenic Hras signaling suppresses Egr1 transcription in NIH3T3 cells, raising the possibility that Ras gene mutations would be redundant in this model.34
Characterization of the mutations that cooperate with loss of function of Egr1, as well as the identification of transcriptional targets of Egr1 in hematopoietic cells, holds great promise to expand our understanding of leukemogenesis in this mouse model, as well as in patients with AML characterized by −5/del(5q). Patients with AML de novo or t-MDS/t-AML have a 5-year survival rate of less that 10%, and a median survival of approximately 6 months.35 Characterization of the molecular pathways that lead to the development of MDS/AML may facilitate the identification of new targeted therapies for these patients.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this article.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Jeffery Milbrandt for generously providing Egr1 knockout mice for this study, the Animal Resource Center at the University of Chicago for the care of the mice used in this study, and the Shared Research Facilities of the University of Chicago Cancer Research Center for technical assistance. We also thank Dr Theodore Karrison for assistance with statistical analysis, Dr Kevin Shannon, and members of the Le Beau laboratory for helpful discussions.
This work was supported by US Public Health Service grants CA40046 and CA84221.
Authorship
Contribution: J.M.J. designed experiments, performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; A.A.F., T.R.T., and E.M.D. performed research; S.C.K. and J.A. performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; J.D.C. designed experiments, and wrote the paper; and M.M.L. designed research, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Michelle M. Le Beau, Section of Hematology/Oncology, University of Chicago, 5841 S Maryland Ave, MC2115, Chicago, IL 60637; e-mail: mlebeau@medicine.bsd.uchicago.edu.