Abstract
The F-box protein S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2) is one of the positive regulators of the cell cycle that promote ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. In this study, we investigated the significance of Skp2 and p27 expression in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) treated with CHOP or CHOP-R. All patients (671) were diagnosed as having DLBCL at the twenty different hospitals and were treated with either CHOP (425) or CHOP-R (246) from 1996 to 2005. All specimens were histopathologically recomfirmed by one pathologist with expertise before entering into this study. Their clinical characteristics, including either the IPI or R-IPI factors, were evenly matched in both treatment groups. The median follow-up of living patients was 3.7 and 2.1 y for CHOP vs CHOP-R, respectively.
Survival analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method and the Cox regression model.
There were 257 patients with high Skp2 expression (cutoff value >40% positive cells) (257/671,39.0%). High Skp2 expression was found in all IPI groups. Expression of p27 (P<.001) was associated with better overall survival (OS), whereas expression of Skp2 was associated with worse OS in CHOP treatment groups (P<.001). We also examined the prognostic impact of Skp2 according to various expression degree of Skp2, Skp2 expression remained a significant predictor of survival (<40%,40–79%,≥80%, P<.001). The multivariant analysis revealed that both the IPI score and the expression of Skp2 and p27 were independent predictors of OS and PFS in both treatment groups (P<.001).
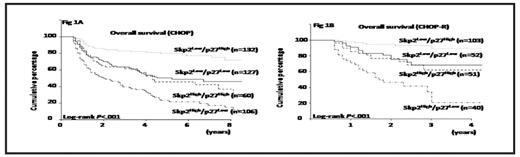
The patients with high Skp2 expression in combination with low p27 expression were related to worst survival in CHOP group (Fig1A). Interestingly, even in CHOP-R group, both high Skp2 expression and low p27 expression were the strong biomarker of worse prognosis (Fig 1B). DLBCL patients with high Skp2 expression did not benefit from the addition of R to CHOP.
Conclusion: Addition of rituximab did not provide a beneficial outcome to DLBCL with high Skp2 and low p27 expression. Therapeutic strategies other than CHOP-R will be needed for DLBCL patients exhibiting a high Skp2 and low p27 expression at the time of diagnosis.
Disclosures: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author