Abstract
Canonical Wnt signaling is central to normal bone homeostasis, and secretion of Wnt signaling inhibitors by multiple myeloma (MM) cells contributes to MM-related bone resorption and disease progression. The aim of this study was to test the effect of Wnt3a on bone disease and growth of MM cells in vitro and in vivo. Although Wnt3a activated canonical signaling in the majority of MM cell lines and primary cells tested, Wnt3a had no effect on MM cell growth in vitro. Moreover, forced expression of Wnt3a in H929 MM cells conferred no growth advantage over empty vector-transfected cells in vitro or importantly when grown subcutaneously in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. Importantly, although H929 cells stably expressing an empty vector injected into human bone grew rapidly and induced a marked reduction in bone mineral density, bones engrafted with Wnt3a-expressing H929 cells were preserved, exhibited increased osteoblast-to-osteoclast ratios, and reduced tumor burden. Likewise, treatment of myelomatous SCID-hu mice, carrying primary disease, with recombinant Wnt3a stimulated bone formation and attenuated MM growth. These results provide further support of the potential anabolic and anti-MM effects of enhancing Wnt signaling in the bone.
Introduction
Wnts comprise a highly conserved family of secreted glycoproteins, consisting of 19 members, that bind to the Frizzled receptors alone or complexed with the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins (LRPs) 5/6. In vertebrates, Wnts can activate a “canonical” β-catenin–dependent pathway or several β-catenin–independent “noncanonical” pathways.1,2 The canonical pathway is normally repressed at several levels. An intracellular complex, including GSK-3, axin, and the tumor suppressor gene product APC, functions to phosphorylate β-catenin, which in turn targets it for ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation. On Wnt binding, β-catenin degradation is blocked, leading to its accumulation and translocation to the nucleus, where it binds the TCF/LEF family of transcription repressors, turning them into transcriptional activators.1,3
Mounting evidence suggests that canonical Wnt signaling is central to normal skeletogenesis4-6 and cancer-related bone diseases.7,8 The first direct evidence of a role for Wnt signaling in human bone formation came from observations that inactivating mutations of the LRP5 gene, a coreceptor for Wnt, causes a syndrome associated with early-onset osteoporosis.9 Subsequently, it was shown that a separate and distinct mutation in the same gene results in high bone density.10,11 Expression of Wnt10b in transgenic mice increases bone mass,12 and overexpression of Wnt7B and β-catenin in C3H10T1/2 osteoblastic precursor cells induces their differentiation into mature osteoblasts.13,14
Osteoclastogenesis is primarily regulated by receptor activator of the NF-κB ligand (RANKL) binding to RANK on the surface of osteoclast precursor cells. The ability of RANKL to bind RANK, and hence promote osteoclast development, is tightly regulated by the RANKL decoy receptor, osteoprotegerin (OPG).15,16 Remarkably, recent studies have shown that Wnt signaling in cells of the osteoblast lineage positively regulates the expression of OPG17,18 while negatively regulating RANKL.19 Taken together these studies suggest that Wnt signaling is likely to be a central regulator of bone remodeling through its direct effects on osteoblastogenesis and indirect effects on osteoclastogenesis.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignancy of antibody-secreting plasma cells that specifically accumulate in the bone marrow (BM) but not other organs. This bone tropism suggests that the BM provides a unique microenvironment of growth and survival signals for MM cells. MM, but not its benign precursor condition, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), is characterized by osteolytic bone disease, which can be traced to an uncoupling of bone remodeling as a result of increased osteoclast activity and decreased osteoblast activity.20-22 During the past 3 decades numerous experimental and clinical studies have focused on the role of osteoclast in the osteolytic phenotype, and numerous factors associated with increased osteoclast activity in MM have been identified.23
We recently found that MM tumor cells produce the Wnt signaling inhibitor Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) and that this plays a central role in MM-induced bone disease.24 DKK1 is the prototypical member of this family of secreted glycoproteins capable of inhibiting canonical Wnt signaling by binding to LRP5/6, causing it to be internalized and degraded.25 Wnt ligand interaction with its receptor is also regulated by secreted frizzled related proteins (sFRPs). As their name suggests, these factors are decoy receptors with frizzled domains capable of binding Wnts in solution.26 Interestingly, MM cells produce sFRP-227 and FRZB/sFRP-3,28,29 and these factors may also contribute to the suppression of Wnt signaling in the BM microenvironment.8
We have recently shown that MM cells express low-to-undetectable levels of canonical Wnt molecules.30,31 We also showed that treatment of preosteoblast cells with DKK1 protein can attenuate an endogenously produced Wnt3a-induced activation of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway in both mouse and human preosteoblast cells and that DKK1 from MM cells or MM serum inhibits BMP-2–induced osteoblast differentiation as evidenced by decreased ALP activity.32 Moreover, we have also shown that administration of a neutralizing antibody to DKK1 to myelomatous bones, presumably resulting in enhancement of Wnt signaling in the bone, prevented bone resorption and also tumor progression in vivo.33 Similarly, a recent study by Edwards et al34 showed that lithium chloride treatment activated Wnt signaling in osteoblasts, inhibited MM bone disease, and decreased tumor burden in bone in the murine 5TGM1 model of MM. We recently reported that MM-derived DKK1 can inhibit Wnt-induced OPG production while enhancing RANKL production by cells of the osteoblast lineage.35 The importance of DKK1 secretion in diseases associated with bone destruction is reinforced by a recent study showing that DKK1 mediates the bone destructive effects of rheumatoid arthritis and that a neutralizing antibody to DKK1 could inhibit the bone destructive process.36
Because Wnt signaling activation has been linked to several forms of cancer, including blood malignancies,37 the observation that neutralizing DKK1, and therefore enhancing Wnt signaling, has negative effects on MM tumor growth in bone might be considered counterintuitive. However, it is now well recognized that an interaction of tumors with their associated stroma can dramatically influence tumor behavior.38 Therefore, it is feasible that activation of the Wnt signaling pathway in the tumor-stroma milieu might override presumed proliferative effects of activating that signaling pathway in tumor cells when grown in a tissue culture environment. Moreover, recent studies have shown that, although Wnt signaling is primarily growth promoting or oncogenic in epithelial cells, suppression of Wnt signaling is growth promoting in cells of the mesenchymal lineage.39
Various clinical observations40 and experimental studies41-43 have linked the level of MM bone disease with tumor progression. The notion that bone disease drives MM progression, at least in the initial phases of the disease process, is supported by studies showing that osteoclasts alone can support long-term survival and proliferation of primary MM cells43,44 and that osteoblastic cultures impede growth of MM cells from a large subset of patients.33
To further study the effect of bone disease and in vivo MM progression, we tested and correlated the effect of Wnt3a on the growth of MM cells in in vitro cultures, extraosseous sites, and the BM where bone cells closely regulate MM progression. Because Wnt3a was shown to activate canonical Wnt signaling in MM cells30,31,45 and the consequences of Wnt activation on MM cell growth remain controversial,30,31,46 we expanded our previous work by performing a comprehensive analysis of the effect of Wnt3a on MM cell lines and primary MM plasma cells. Our studies showed that, although Wnt3a had no effect on MM growth in vitro or when tumors were grown subcutaneously in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice, it had anti-MM effects on MM cell lines and primary MM samples when growth was restricted to implanted human bones in SCID mice. Given that Wnt3a markedly activated bone formation was associated with reduced MM burden, these data suggest that the anti-MM effect of Wnt3a probably resulted from its indirect effects on the BM microenvironment.
Methods
Primary myeloma cells and cell lines
Primary MM cells were obtained from heparinized BM aspirates from patients with active myeloma during scheduled clinic visits. Signed informed consent forms approved by the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Institutional Review Board are kept on record. CD138-expressing MM cells were isolated as previously described.29
The human MM cell lines, EJM, H929, INA6, MM144, OPM-2, SKMM-1, and U226, were cultured in RPMI 1640 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS, and 4 mM l-glutamine as described previously.47,48 Mouse pluripotent mesenchymal precursor cell line C2C12 was purchased from ATCC (Manassas, VA) and Saos-2 were cultured in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (DMEM; Invitrogen) containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS, penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 mg/mL), and 4 mM l-glutamine. Cells were maintained at 37°C and humidified with 95% air and 5% CO2 for cell culture.
Preparation of conditioned medium
Wnt3a–conditioned medium (Wnt3a-CM) or control (Cont-CM) was prepared as preciously described.30 Briefly, Wnt3a-producing L cells (stably transfected with Wnt3a cDNA kindly provided by Dr Shinji Takata) or control L cells were cultured to become confluent in DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS after which the medium was replaced with serum-free DMEM. The culture supernatant was collected after 72 hours and was designated Wnt3a-CM and Con-CM, respectively. The concentration of Wnt3a in CM was evaluated by the ability to stabilize β-catenin using recombinant Wnt3a (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). The concentration in 100% CM equates to 150 to 200 ng/mL of recombinant Wnt3a to the stabilization of β-catenin.
Constructs and transfectants
The Wnt3a-expressing MM cell line was generated as previously described.31 Briefly, H929 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Wnt-3a cDNA or empty vector using Lipofectamine (Invitrogen) according to manufacturer's instructions. Clonal cell lines were generated by limited dilution in growth media containing 1 mg/mL G418. Positive clones were detected by anti-HA antibody.
Treatment and proliferation assay
Growth of the MM cells was determined by cell viability and a nonradioactive cell proliferation assay system (MTT assay).49 Briefly, H929, INA6, and OPM-2 cells and primary MM plasma cells (5 × 104/well) were cultured in serum-free medium with Wnt3a-CM or control-CM or with recombinant Wnt3a protein (100 ng/mL), IL-6 (10 ng/mL), or IGF-1 (100 ng/mL; PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ) in 96-well plates; at the indicated time points, 10 mL of 5 mg/mL MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolliumbromide] was added to each well and incubated for 4 hours at 37°C, followed by incubation in 100 mL of 10% sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) in 0.01 N HCl at 37°C overnight. The optical density of the plates was read on a Spectra MAX 340 Microplate Spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA) at 570 nm. Recombinant mouse Wnt3a was purchased from R&D Systems. Human recombinant IGF-1 and IL-6 were purchased from PeproTech (Rocky Hill, NJ).
Western blotting
Cells were incubated in Wnt3a-CM or control-CM for the indicated times and solubilized in lysis buffer as described.48 After incubation for 30 minutes at 4°C, cell debris and nuclei were removed by centrifugation at 15 000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C. Protein concentration was determined by BCA protein assay (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Proteins in lysate were separated with 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gels followed by electrophoretic transfer to Immobilon polyvinylidene diflouride membranes (Millipore, Bedford, MA). Membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat dried milk in Tris-buffered saline–Tween 20 and incubated for 1 or 2 hours with a specified monoclonal antibody. Detection was performed by a standard procedure with the use of 0.2 g/mL of a panel of secondary horseradish peroxidase–conjugated antibodies and chemiluminescence (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, United Kingdom). Anti–β-catenin antibody and horseradish peroxidase–conjugated anti–mouse antibodies were purchased from Transduction Laboratories (Lexington, KY).
GST–E-cadherin binding assay
The GST–E-cadherin binding assay was performed as described.50 Briefly, the β-catenin binding site of E-cadherin as a GST-fusion protein was purified using GST beads. GST–E-cadherin was used to precipitate uncomplexed β-catenin present in 500 mg cell lysate. Precipitated β-catenin was detected by immunoblotting using a β-catenin monoclonal antibody (Transduction Laboratories).
Myelomatous SCID-hu and SCID mice
SCID-hu mice were constructed as previously described.51 H929/W3A and H929/EV cells (0.5 × 106 cells/mouse) were each injected directly into the implanted bone (n = 6). Mice were bled weekly from the tail vein, and changes in levels of circulating human monoclonal light chain immunoglobulin (hIg) of the M-protein isotype were determined by enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay (ELISA) as described51,52 and used as an indicator of MM growth. Radiographs were taken with an AXR Minishot-100 beryllium source instrument (Associated X-Ray Imaging Corp, Haverhill, MA). Changes in bone mineral density (BMD) of the implanted human bone were determined with the use of a PIXImus dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA; GE Medical Systems LUNAR, Madison, WI).33 The experiment was ended after 11 weeks, at which time a large tumor was apparent on the outer surface of the implanted bone in control mice injected with H929/EV cells.
For testing subcutaneous growth, H929/W3A and H929/EV cells (5 × 106 cells/mouse) were each injected subcutaneously into SCID mice (n = 5), and the experiment was ended 9 weeks from cell injection. Subcutaneous tumors were visualized by x-ray radiographs, and myeloma burden was determined by measurements of κ light chain and tumor volume (length × width2 × ½).
To test the direct effect of Wnt3a on primary MM bone disease and tumor growth, SCID-hu mice were engrafted with MM cells from 5 patients. All patients were at stage III of disease and only 1 of the 5 patients was previously treated.
On establishment of MM growth as determined by increased level of hIg, myelomatous hosts were daily injected with Wnt3a-CM or Cont-CM (200 μL/injection) into the surrounding area of the implanted bone (patients 1 and 2) or treated with rWnt3a for 4 weeks using the Alzet pump (Durect, Cupertino, CA; 8 μg/100 μL/pump, 0.11 μL/h) directly connected to the open side of the implanted bone, allowing continual exposure of the myelomatous bone to rWnt3a (patients 3-5). Control hosts were similarly treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
Immunohistochemistry and histochemistry
Human bones were decalcified with 10% (wt/vol) ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, pH 7.0. The bones were embedded in paraffin for sectioning. Sections (5 μm) were deparaffinized in xylene, rehydrated with ethanol, rinsed in PBS, and underwent antigen retrieval using a microwave. After peroxidase quenching with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 minutes, sections were reacted with antibodies for osteocalcin (5 μg/mL; QED Bioscience, San Diego, CA).52 For β-catenin, we used 2 different antibodies, clone 8E7 (Millipore, Temecula CA; 15 μg/mL,) which detects the active form of β-catenin, and 14/β-Catenin (BD Transduction Laboratories, Sparks, MD; 5 μg/mL), which detects total β-catenin, as previously described.34 The assay was completed with the use of an immunoperoxidase kit (Dako North America, Carpinteria, CA). Sections were lightly counterstained with hematoxylin.43,53 Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining of deparaffinized bone sections was performed with an acid phosphatase kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO).43 Osteocalcin-expressing osteoblasts and TRAP-positive multinucleated osteoclasts in 4 nonoverlapping, millimeter-square areas were counted. Images were obtained using an Olympus BH2 microscope equipped with a 160×/0.17 numeric aperture objective (Olympus, Melville, NY). Original magnification, ×200. Images were acquired using a SPOT2 digital camera (Diagnostic Instruments, Sterling Heights, MI) and were processed using Adobe Photoshop version 10 (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA).
Statistical analysis
All values are expressed as means plus or minus SEM. Student t test was used to test the effect of treatment on BMD, MM burden, osteoblast and osteoclast numbers, and in vitro proliferation. Significant P values were less than .05 by the 2-tailed test.
Results
Wnt3a stabilizes β-catenin in MM cells
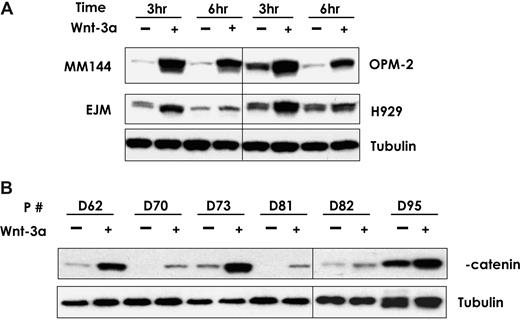
We have previously reported that Wnt3a signaling in myeloma cells causes morphologic changes and migration.30,31,45 Here, we examined the effect of Wnt3a on the stabilization of β-catenin in MM cell lines and primary MM plasma cells from 6 patients. Baseline levels of β-catenin varied between different MM cell lines and primary samples (Figure 1). Wnt3a-CM (50% vol/vol) increased the β-catenin protein level in a time-dependent manner in EJM, H929, MM144, and OPM-2 cells (Figure 1A). Similar results were found in SKMM-1, U266, INA6, and ANBL6 MM cell lines (data not shown). β-Catenin protein levels were highest at 3 hours after Wnt3a-CM treatment and decreased steadily during the subsequent 6 hours. Similar results were also seen in all 6 primary MM samples regardless of the baseline level of β-catenin (Figure 1B). These results indicate that Wnt3a consistently activates canonical Wnt signaling in MM cells.
Wnt3a stabilizes β-catenin in MM cell lines and primary MM plasma cells. The myeloma cells were treated with Wnt3a-CM or Cont-CM for the indicated time (A). Primary CD138-selected plasma cells from 6 patients with MM confirmed by flow cytometry analysis were treated with Wnt3a-CM or Cont-CM for 3 hours (B). Proteins isolated from the above-treated cells were subjected to Western blotting analysis as described in “Wnt3a stabilizes β-catenin in MM cells.” Total β-catenin was determined by using an antibody that recognized the protein. The vertical lines have been inserted to indicate different gels used.
Wnt3a stabilizes β-catenin in MM cell lines and primary MM plasma cells. The myeloma cells were treated with Wnt3a-CM or Cont-CM for the indicated time (A). Primary CD138-selected plasma cells from 6 patients with MM confirmed by flow cytometry analysis were treated with Wnt3a-CM or Cont-CM for 3 hours (B). Proteins isolated from the above-treated cells were subjected to Western blotting analysis as described in “Wnt3a stabilizes β-catenin in MM cells.” Total β-catenin was determined by using an antibody that recognized the protein. The vertical lines have been inserted to indicate different gels used.
Activation of Wnt signaling has no effect on MM cell growth in vitro
Because of conflicting data in the literature on the effects of canonical Wnt on MM growth,30,46 we next examined the consequences of Wnt signaling activation on MM cell growth in vitro. Exposure of H929, OPM-2, and the IL-6–dependent cell line INA6 to recombinant Wnt3a (rWnt3a) did not increase proliferation of the cells (Figure 2A). Moreover, Wnt3a had no additive or synergistic effects on MM cell growth when combined with IGF-1 and IL-6 (data not shown).
Wnt3a has no direct effect on growth of MM cell lines and primary MM cells. Cells from indicated MM cell lines were cultured in serum-free medium in the absence and presence of rWnt3a for the indicated times. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay as described in “Wnt3a does not promote MM growth.” (A) Protein isolated from H929/W3A or H929/EV was subjected to Western blotting analysis using anti-HA antibody to confirm Wnt3a expression (top) or using anti–β-catenin antibody (second panel from top). The same fractions were also blotted with antitubulin antibody as a control for protein loading (bottom). The proteins isolated from H929/W3a or H929/EV was subject to E-cadherin pull-down assay to measure the uncomplexed β-catenin (second panel from bottom). (B) H929/W3A and H929/EV cells were seeded in RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS for the indicated time, and proliferation was measured by MTT assay. (C) MM cell lines H929, INA6, and OPM-2 were incubated for 48 hours in the absence and presence of rWnts (100 ng/mL) and then subjected to MTT assay. (D) Primary CD138-selected plasma cells from 2 patients with MM (Pt no. 1 and Pt no. 2) were cultured in serum-free medium in the presence of Wnt3a-CM or Cont-CM or with rWnt3a protein for the indicated time. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. Results are expressed as means plus or minus SEM.
Wnt3a has no direct effect on growth of MM cell lines and primary MM cells. Cells from indicated MM cell lines were cultured in serum-free medium in the absence and presence of rWnt3a for the indicated times. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay as described in “Wnt3a does not promote MM growth.” (A) Protein isolated from H929/W3A or H929/EV was subjected to Western blotting analysis using anti-HA antibody to confirm Wnt3a expression (top) or using anti–β-catenin antibody (second panel from top). The same fractions were also blotted with antitubulin antibody as a control for protein loading (bottom). The proteins isolated from H929/W3a or H929/EV was subject to E-cadherin pull-down assay to measure the uncomplexed β-catenin (second panel from bottom). (B) H929/W3A and H929/EV cells were seeded in RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS for the indicated time, and proliferation was measured by MTT assay. (C) MM cell lines H929, INA6, and OPM-2 were incubated for 48 hours in the absence and presence of rWnts (100 ng/mL) and then subjected to MTT assay. (D) Primary CD138-selected plasma cells from 2 patients with MM (Pt no. 1 and Pt no. 2) were cultured in serum-free medium in the presence of Wnt3a-CM or Cont-CM or with rWnt3a protein for the indicated time. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. Results are expressed as means plus or minus SEM.
To determine whether MM growth in response to Wnt signaling is dependent on the maintenance of high Wnt3a concentration in cells, we stably transduced the MM cell line H929 with an expression construct containing a Wnt3a cDNA (henceforth referred to as H929/W3A) or empty vector (henceforth referred to as H929/EV). Because there are no commercial antibodies that recognize Wnt proteins, the Wnt3a gene was cloned as an HA (hemagglutinin) fusion protein. Western blot analysis with an anti-HA antibody showed clear recognition of an HA-positive band of the expected size in H929/W3a cells and not control H929/EV cells (Figure 2A). To determine whether H929/W3A cells produced a functional Wnt3a protein, we used the E-cadherin pull-down assay to detect uncomplexed β-catenin50 and performed Western blot analysis to detect the total level of β-catenin. Although H929/W3A, but not H929/EV, cells contained high levels of both forms of β-catenin (Figure 2A), there was no difference in their growth rate in vitro in the presence of serum (Figure 2B) or under serum-starved conditions (data not shown). We next determined whether Wnt3a acts as a growth factor in primary MM cells by using both Wnt3a-CM and rWnt3a. Similar to that observed in MM cell lines, neither Wnt3a-CM nor rWnt3a promoted proliferation of primary MM cells (Figure 2C,D), whereas the IGF-1 and IL-6 did promote proliferation of these cells (data not shown). Taken together, these results suggest that Wnt3a is not a growth factor necessary for MM cells to proliferate, have antiapoptotic effects, or synergizes with other MM growth factors such as IL-6 and IGF-1 in vitro.
Overexpression of Wnt3a in MM cells inhibits bone disease and tumor growth in SCID-hu mice
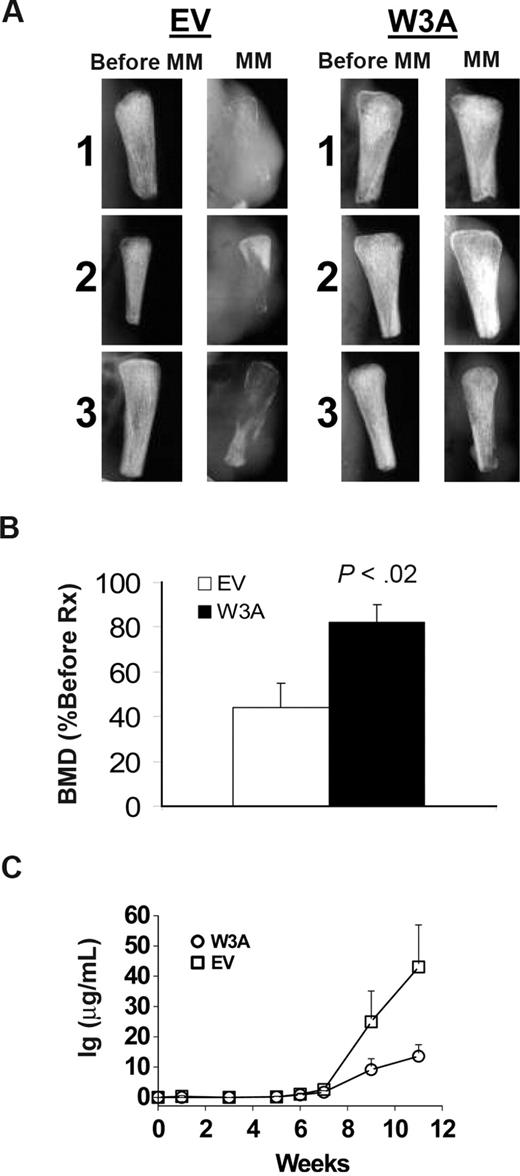
To determine the effect of a canonical Wnt signal on MM growth and bone disease characteristics in vivo, we transplanted the H929/W3A and H929/EV cells into implanted human bone in SCID mice. Growth of these cells was restricted to the implanted bone. Radiographic analysis of the bones showed that, as expected, bones injected with H929/EV control cells were severely resorbed and tumors spread to the outer surface of the implanted bone (Figure 3A). In contrast, the bones injected with H929/W3A cells were preserved even in cases where a small tumor was apparent on the bone surface (Figure 3A). Although BMD of bones injected with H929/EV cells was reduced by 56% plus or minus 11% from pretreatment levels, BMD in bones engrafted with H929/W3A cells was reduced by 18% plus or minus 9% from pretreatment level (P < .02, H929/EV vs H929/W3A groups; Figure 3B). Changes in the level of tumor burden was determined by periodic measurements of human immunoglobulin light chains secreted into the serum.51 To ensure the accuracy of using hIg as a marker of MM burden, we confirmed that H929/EV and H929/W3A cells secreted the same amount of Ig into culture media (15.5 ± 0.4 and 17.4 ± 0.9 μg/mL per 106 H929/EV and H929/W3A cells, respectively). Although equal numbers of cells were initially engrafted into each animal, in vivo circulating levels of hIg in sera of H929/W3A-bearing mice was significantly lower than in SCID-hu mice engrafted with H929/EV cells (P < .05; Figure 3C).
Wnt3a prevents bone loss and reduces tumor burden in myelomatous bones. SCID-hu mice were engrafted with H929/EV or H929/W3A cells. (A) X-ray radiographs of the implanted myelomatous bones taken from 3 representative mice in each group, before cell engraftment (Pre-MM) and at the experiment's end (MM). Note that, although EV-bearing bones were severely resorbed and tumors grew on the outer surface of the implanted bone, implanted bone mass from the H929/W3A-bearing hosts was preserved. (B) Changes in the level of BMD of implanted bones engrafted with H929/EV or H929/W3A cells. (C) Circulating human Ig level of SCID-hu mice engrafted with H929/EV or H929/W3A cells. Error bars represent SEM.
Wnt3a prevents bone loss and reduces tumor burden in myelomatous bones. SCID-hu mice were engrafted with H929/EV or H929/W3A cells. (A) X-ray radiographs of the implanted myelomatous bones taken from 3 representative mice in each group, before cell engraftment (Pre-MM) and at the experiment's end (MM). Note that, although EV-bearing bones were severely resorbed and tumors grew on the outer surface of the implanted bone, implanted bone mass from the H929/W3A-bearing hosts was preserved. (B) Changes in the level of BMD of implanted bones engrafted with H929/EV or H929/W3A cells. (C) Circulating human Ig level of SCID-hu mice engrafted with H929/EV or H929/W3A cells. Error bars represent SEM.
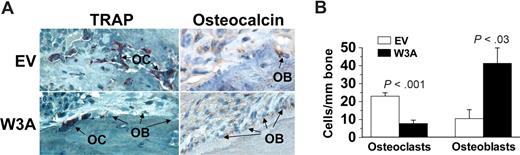
Because Wnt signaling is directly involved in the regulation of osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis, we evaluated the numbers of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bones engrafted with H929/EV- and H929/W3A-transfected cells. These histologic analyses showed significant differences in the cellular composition of the bone in the H929/W3A transfectants in comparison to the control. Bones engrafted with H929/W3A cells had more osteocalcin-expressing osteoblasts and reduced numbers of multinucleated TRAP-expressing osteoclasts on myelomatous bone surface than in the H929/EV group (Figure 4A,B). Taken together, these data indicate that Wnt3a (not normally expressed by MM cells) has a marked inhibitory effect on MM-induced osteolytic bone disease, an effect that indirectly resulted in attenuated MM growth.
Wnt3a increases osteoblastogenesis and reduces osteoclastogenesis in myelomatous bones. (A) Decalcified histologic bone sections of bones engrafted with H929/W3a or H929/EV cells stained for TRAP (red) and osteocalcin (brown). OB indicates osteoblast; OC, osteoclast. (B) Numbers of osteocalcin-expressing osteoblasts and TRAP-expressing multinucleated osteoclasts in implanted bones engrafted with H929/EV and H929/W3a cells. Error bars represent SEM.
Wnt3a increases osteoblastogenesis and reduces osteoclastogenesis in myelomatous bones. (A) Decalcified histologic bone sections of bones engrafted with H929/W3a or H929/EV cells stained for TRAP (red) and osteocalcin (brown). OB indicates osteoblast; OC, osteoclast. (B) Numbers of osteocalcin-expressing osteoblasts and TRAP-expressing multinucleated osteoclasts in implanted bones engrafted with H929/EV and H929/W3a cells. Error bars represent SEM.
Wnt3a has no effect on subcutaneous growth of H929 MM cells
To further evaluate whether overexpression of Wnt3a specifically affects MM growth in the BM microenvironment, H929/EV and H929/W3A cells were subcutaneously engrafted in SCID mice. Growth of MM cells, which was evaluated by circulating hIg and radiographic analysis of tumor volume, showed no differences in tumor progression over time (Figure 5A) and final tumor volume and size (Figure 5B,C). These data confirmed our in vitro results and suggest that Wnt3a has no direct stimulatory effect on growth of MM cells in vivo.
Wnt3a has no effect on subcutaneous MM growth in SCID mice. SCID mice were subcutaneously injected with H929/W3A or H929/EV cells. (A) Circulating human Ig levels were similarly increased in hosts engrafted with EV and W3a cells. (B) Subcutaneous tumor volume. Error bars represent SEM. (C) X-ray radiographs showing similar tumor size (white arrows) in hosts with H929/EV and H929/W3A cells.
Wnt3a has no effect on subcutaneous MM growth in SCID mice. SCID mice were subcutaneously injected with H929/W3A or H929/EV cells. (A) Circulating human Ig levels were similarly increased in hosts engrafted with EV and W3a cells. (B) Subcutaneous tumor volume. Error bars represent SEM. (C) X-ray radiographs showing similar tumor size (white arrows) in hosts with H929/EV and H929/W3A cells.
Wnt3a inhibits primary MM in SCID-hu mice
We also tested the direct effect of Wnt3a on primary MM bone disease and tumor growth. SCID-hu mice were engrafted with MM cells from 5 patients, and on establishment of MM growth mice were treated daily with Wnt3a-CM or Cont-CM31 (patients 1 and 2) or with continual direct infusion of recombinant Wnt3a into the myelomatous bone for 4 weeks (patients 3-5). As previously shown, growth of primary MM cells was restricted to the human BM microenvironment.51,52,54 In control myelomatous hosts, BMD of the implanted bone was reduced from pretreatment level in all 5 experiments (Figure 6B). In contrast, myelomatous BMD of hosts treated with Wnt3a increased from the pretreatment level in 3 experiments (patients 1, 2, and 4) and was reduced from the pretreatment level to a lesser extent than in controls in 2 experiments (patients 3 and 5; Figure 6B). Overall, in control hosts myelomatous BMD was reduced by 8.9% plus or minus 5.0%, whereas BMD of hosts treated with Wnt3a was increased by 12.1% plus or minus 8.0% from the pretreatment level (P < .02). Radiographic analysis further confirmed this prevention of osteolysis and increased bone mass afterWnt3a treatment and the increased osteolytic process in myelomatous bones of control hosts (Figure 6C,D). Wnt3a treatment was also associated with inhibition of MM progression in 4 of 5 experiments as analyzed by changes in hIg levels from pretreatment levels (Figure 6A). Overall, hIg was increased from the pretreatment level by 326% plus or minus 75% and 156% plus or minus 48% in control- and Wnt3a-treated hosts, respectively (P < .01). These data suggest that Wnt3a is capable of preventing bone loss and stimulating bone formation in primary myelomatous bones, an effect that is also associated with attenuated MM growth.
Wnt3A stimulates bone formation and attenuates primary MM growth in SCID-hu mice. SCID-hu mice engrafted with MM cells from 5 patients were daily injected with Cont-CM and Wnt3a-CM into the surrounding area of the implanted bones (patients 1 and 2) or treated with rWnt3a using Alzet pumps. (A,B) Changes in circulating human kappa Ig level (A) and in the BMD of the implanted bones (B) from pretreatment level. (C,D) X-ray radiographs showing changes in myelomatous bone mass of hosts treated with Cont-CM and Wnt3a-CM (C) and rWnt3a (D). Note that osteolytic lesions were evident before initiation of treatment (pre-Rx) and that, although in control hosts bone loss continued to increase (white arrows), Wnt3a treatment resulted in increased bone mass (white arrows).
Wnt3A stimulates bone formation and attenuates primary MM growth in SCID-hu mice. SCID-hu mice engrafted with MM cells from 5 patients were daily injected with Cont-CM and Wnt3a-CM into the surrounding area of the implanted bones (patients 1 and 2) or treated with rWnt3a using Alzet pumps. (A,B) Changes in circulating human kappa Ig level (A) and in the BMD of the implanted bones (B) from pretreatment level. (C,D) X-ray radiographs showing changes in myelomatous bone mass of hosts treated with Cont-CM and Wnt3a-CM (C) and rWnt3a (D). Note that osteolytic lesions were evident before initiation of treatment (pre-Rx) and that, although in control hosts bone loss continued to increase (white arrows), Wnt3a treatment resulted in increased bone mass (white arrows).
Wnt3a treatment activates canonical Wnt signaling in osteogenic cells on myelomatous bones
Finally, we performed immunohistochemical staining of myeloma-bearing bones to detect the presence of canonical Wnt signaling using the clone 8E7 antibody that detects the active form of β-catenin55 and total β-catenin.34 Similar to a recent report,56 we found that β-catenin was detectable in endothelial cells and osteogenic cells along the bone surface (Figure 7A,B). We observed similar results with the use of the antibody that recognizes total β-catenin (data not shown). MM cells also showed weak staining with both antibodies. Although immunohistochemistry is often hard to quantify, the immunohistochemical staining showed a marked increase in the expression of activated β-catenin in osteogenic cells along the bone surface of bones engrafted with H929/W3A cells compared with bones engrafted with H929/EV cells. Similarly, increased stabilized β-catenin was detected in osteoblasts along the bone surface of primary myelomatous bones treated with Wnt3A (Figure 7C,D). Taken together, these results indicate that Wnt3a activated canonical Wnt signaling in myelomatous bones and that this effect was associated with an increased number of osteocalcin-expressing, mature osteoblasts cells, resulting in prevention of MM bone disease.
Increased canonical Wnt signaling in osteogenic cells in myelomatous bones treated with Wnt3a. Myelomatous human bone sections were immunohistochemically stained with 8E7 antibody that reacts with the active form of β-catenin. (A,B) Bones were engrafted with H929/EV (A) and H929/W3A (B) MM cells. Note expression of active form of β-catenin in certain vascular endothelial cells (VECs) and in cellular components along the bone surface. Bones engrafted with H929/W3A had increased numbers of cells expressing the active form of β-catenin along the bone surface. (C,D) Primary myelomatous bones treated with Wnt3a had an increased number of osteoblastic (OB) cells expressing the active form of β-catenin. Osteoclasts (OCs) as well as MM cells expressed very low levels of β-catenin.
Increased canonical Wnt signaling in osteogenic cells in myelomatous bones treated with Wnt3a. Myelomatous human bone sections were immunohistochemically stained with 8E7 antibody that reacts with the active form of β-catenin. (A,B) Bones were engrafted with H929/EV (A) and H929/W3A (B) MM cells. Note expression of active form of β-catenin in certain vascular endothelial cells (VECs) and in cellular components along the bone surface. Bones engrafted with H929/W3A had increased numbers of cells expressing the active form of β-catenin along the bone surface. (C,D) Primary myelomatous bones treated with Wnt3a had an increased number of osteoblastic (OB) cells expressing the active form of β-catenin. Osteoclasts (OCs) as well as MM cells expressed very low levels of β-catenin.
Discussion
Canonical Wnt signaling is essential for osteoblastogenesis and normal bone metabolism, and secretion of Wnt signaling antagonists by MM cells is thought to contribute to the bone-destructive process as well as disease progression.24,27,57 MM plasma cells secrete the Wnt signaling inhibitor DKK1, and we have previously shown that treatment of myelomatous mice with a neutralizing antibody to DKK1 can inhibit bone destruction and tumor progression in a xenograft mouse model of human MM.58 Consistent with these findings, Edwards et al34 recently showed that treatment of MM-carrying mice with LiCl can inhibit bone destruction and MM growth in the bone. Because LiCl is known to inactivate GSKβ leading to stabilization of β-catenin, Edwards et al34 suggest that the antibone resorptive and antitumor effects of LiCl treatment are mediated by activation of Wnt signaling in bone marrow; however, these studies did not directly test the effects of Wnt ligands. In the current report we provide evidence that increasing Wnt signaling in the bone marrow, through direct administration of Wnt3a, can inhibit bone destruction and MM tumor growth in vivo.
Because activation of the Wnt pathway has been associated with tumorigenesis in certain cell types, it is noteworthy that we found no evidence that enhancing Wnt signaling promotes MM growth. This conclusion is supported by the following observations: (1) administration of rWnt3a or Wnt3a-CM had no effect on the growth of MM cell lines or primary MM cells in vitro and (2) overexpression of Wnt3a in MM cell lines did not confer a growth advantage in vitro or when grown subcutaneously in SCID mice. These findings confirm previous results showing that activation of canonical Wnt signaling by Wnt3a or by LiCl had no effect on the proliferation of MM cells nor conferred antiapoptotic signals.30,31 Furthermore, the present data provide evidence that Wnt3a does not synergize with IL-6 or IGF-1, which serve as 2 major proliferative and survival factors in MM cells.47,48 Moreover, we have shown that DKK1 has no effect on MM cell apoptosis, and its forced overexpression in MM cells did not inhibit cell growth or sensitize MM cells to apoptosis after treatment with thalidomide or lenalidomide.30,59
β-Catenin activity is tightly controlled by ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation after phosphorylation by GSK3β.60 Inhibition of proteasome activity was shown to promote osteoblast survival and differentiation by prevention of Runx2 degradation in osteoblast precursors.61 Bortezomib was shown to stimulate osteoblast activity62,63 and Runx2 transcriptional activity in the BM of MM patients.64 Interestingly, although bortezomib stimulated β-catenin stabilization and activation of TCF/LEF transcription in MM cells (Y-W.Q. and J.D.S., unpublished data, 2007), this compound clearly has clinical anti-MM effects and was shown to inhibit MM cell growth and to induce apoptosis in vitro at low nanomolar levels.65 Given that bortezomib induces stabilization of β-catenin in MM cells, these data also support the notion that activation of Wnt signaling is not likely to have a direct effect on MM cell growth.
In contrast to the lack of stimulation of MM growth by activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway described above, other studies reported that treatment of myeloma cells with sFRP1, a Wnt antagonist, or interfering TCF transcriptional activity with a chemical compound (PKF115-584) inhibited cell growth.46,66,67 Potential reasons for these seemingly divergent results might be attributable to the use of different cell lines and the techniques used to stimulate or block Wnt signaling pathways. Another possibility for this difference is that sFRP1, as a soluble decoy receptor, can bind and inhibit both canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling,68 which is unlike DKK1, which only inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway.69 Furthermore, sFRP1 can function as both an Wnt agonist or antagonist, depending on the concentration of the molecule with low concentrations stimulating stabilization of β-catenin and high concentrations inhibiting Wnt signaling.68 TCF transcriptional activity was also shown to be regulated by the Wnt–β-catenin independent pathway,70,71 which raises the possibility that anti-MM effects of PKF115-584 might be through inhibition of β-catenin–independent Wnt signaling. Further investigation is necessary to distinguish between these possibilities.
In their recent study Edwards et al34 suggested that activation of Wnt signaling by LiCl decreased 5TGM1 MM cell growth and osteolysis but increased extraosseous tumor growth. In the current study we did not observe that Wnt signaling increased tumor growth of human MM cells when grown subcutaneously. These conflicting results deserve comment. The differences might be attributable to intrinsic differences between the mouse and human MM. Alternatively, although we directly tested the effect of Wnt3a on MM, Edwards et al34 used LiCl, which, although capable of mimicking Wnt signaling by inhibiting GSK3β leading to subsequent increased β-catenin stabilization, GSK3β has broad biologic effects.72 Thus, there is the possibility that the LiCl-induced subcutaneous growth of 5TGM1 may be independent of β-catenin stabilization. Nevertheless, both studies support the concept that increased Wnt signaling in the BM microenvironment prevents bone disease and attenuates MM tumor growth.
Remarkably, we found that, although increasing Wnt signaling in MM tumors had no effect on cell growth in vitro or when cells were grown in subcutaneous locations, tumor growth was attenuated when grown in bone. This reduction in tumor growth correlated with reduced bone destruction, suggesting that Wnt-3a–induced alteration of the bone marrow microenvironment has antimyeloma effects, a result that is consistent with our previous studies showing that neutralization of DKK1, which is thought to enhance Wnt signaling, attenuates bone destruction and tumor growth. Activation of Wnt signaling in the bone appears to exert its antitumor activity by promoting mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts and subsequent suppression of osteoclastogenesis. These results are in line with previous studies showing the negative effect of osteoclast inhibition42,54,73 and increased bone formation58 on MM progression.
Treatment of myeloma bone disease has focused on the use bisphosphonates (BPs), which function by blocking osteoclastogenesis. Although BPs have proven effective in preventing the lytic process, it is now recognized that their long-term use can reduce osteoblasts as well as increase the risk of osteonecrosis.74,75 Moreover, although BPs effectively blunt or halt the lytic process, lytic lesions fail to heal,76 indicating that bone anabolic treatment strategies are required.
It was shown more than 80 years ago that PTH has anabolic effects on bone,77 and clinical trials have shown that intermittent exposure of bone to PTH can increase bone formation and bone mass in humans.78 PTH is now approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of osteoporosis. Recombinant human BMP2 is used clinically to mediate spinal fusions, and BMP7 is used for the treatment of nonunion of long-bone fractures that occurs secondary to trauma. Although there is no evidence of suppression of PTH or BMP signaling in MM bone disease, given that Wnts and PTH stimulate bone formation by complementary pathways79 and that BMP2 synergizes with canonical Wnts to promote osteoblast differentiation,32,80,81 it is possible that combining these compounds with Wnt agonists may prove to be effective anabolic strategies for treating MM bone disease.
Our study confirmed a previous report showing that β-catenin is stabilized in certain vascular endothelial cells, osteogenic cells, and MM cells in myelomatous bone specimens.56 Although we detected β-catenin in control myelomatous bone with severe bone disease, bones engrafted with H929/W3A cells had a significant increase in β-catenin stabilization along the bone surface. Because immunohistochemical staining showed an increased number of osteocalcin-expressing osteogenic cells in the H929/WA3 group (Figure 4), our study suggests that Wnt3a-stimulated canonical signaling in bone significantly enhances osteoblastogenesis in myelomatous bones.
In summary, our data indicate that overexpression of Wnt3a in bone has marked inhibitory effect on MM-induced osteolytic bone lesions and tumor growth in bone marrow microenvironment, whereas the activation of Wnt signaling has no effect on growth of MM cells in vitro or when grown subcutaneously. Further studies are needed to completely elucidate the mechanism by which Wnt signaling suppresses tumor growth in vivo.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of the Lambert Laboratory of Myeloma Genetics; Yu Chen, David R. Williams, Austin Porter III, Rachel Flinchum, and Yan Xaio, as well as Wen Ling, Rinku Saha, and Paul Perkins from Dr Yaccoby's laboratory. We also thank the faculty, staff, and patients of the Myeloma Institute for Research and Therapy for their support.
This work was supported by National Cancer Institute grants CA93897 (S.Y.), CA55819 (J.S.), and CA97513 (J.S.); Senior and Translational Research Awards from the Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation (S.Y. and Y.W.Q.); the Lebow Fund to Cure Myeloma; and the Nancy and Stephen Grand Philanthropic Fund.
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: Y-W.Q. and S.Y. designed the research, designed and performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the results, and wrote the paper; J.D.S. conceptualized and designed the research, analyzed and interpreted the results, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: John D. Shaughnessy Jr, Myeloma Institute for Research and Therapy, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, 4301 W Markham, Little Rock, AR 72205; e-mail: shaughnessyjohn@uams.edu.