Abstract
Viperin (virus inhibitory protein, endoplasmic reticulum [ER]–associated, interferon-inducible) has been identified as a highly inducible ER protein that has antiviral activity. Here, we characterized the phenotype of mice deficient in viperin and examined the biological function of viperin in peripheral T-cell activation and differentiation. Splenic CD4+ T cells deficient in viperin exhibited normal anti–T-cell receptor (TCR)–induced proliferation and IL-2 production, but produced significantly less T helper 2 (Th2) cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, in association with impaired GATA3 activation, after stimulation with anti-CD3 antibody, which was not restored upon costimulation with anti-CD28. Th2 differentiation of viperin-deficient naive T cells was also impaired in the presence of strong TCR signaling and minimum IL-4, but not under optimal Th2-skewed conditions. In parallel, viperin-deficient T cells showed decreases in NF-κB1/p50 and AP-1/JunB DNA binding activities after TCR engagement. Thus, viperin facilitates TCR-mediated GATA-3 activation and optimal Th2 cytokine production by modulating NF-κB and AP-1 activities.
Introduction
Viperin (virus inhibitory protein, endoplasmic reticulum–associated, interferon-inducible) was first cloned from interferon-treated human macrophages,1 and identified as an antiviral protein that is protective against human cytomegalovirus and influenza A virus.1,2 In the following studies using oligonucleotide microarray chip assays, viperin has been recognized as a highly inducible candidate gene in response to a wide range of viruses and microbial products such as LPS and double-stranded RNA,3,4 implying that viperin is an important component of innate immunity to diverse pathogens. Viperin induction upon stimulation has been reported in human fetal astrocytes,5 fibroblasts, Huh-7 and HepG2 cells6,7 in vitro, and in disease conditions such as vascular cells of atherosclerosis8 and liver tissue of patients with chronic hepatitis C.3 Nevertheless, the cell types that are capable of producing viperin are still enigmatic, and the functions of viperin other than its antiviral activity have remained unexplored
In order to delineate the physiologic role of viperin in the immune system, a mouse model defective in viperin was generated by gene targeting. We assessed here whether viperin deficiency affects T-cell development and function. T-cell responses are intimately dependent upon survival-promoting signals induced by T-cell receptors (TCRs), the costimulatory molecule CD28, and cytokine receptors. Several transcription factors have been shown to contribute to these processes, including those belonging to NFAT, AP-1, NF-κB, and STAT families.9 We found that viperin−/− CD4+ T cells produced a normal amount of IL-2 and were able to respond to polarizing cytokines for T helper 2 (Th2) differentiation. However, there was reduced Th2 cytokine production (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13) in association with impaired GATA-3 induction in viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells after stimulation with anti-CD3 in the presence or absence of anti-CD28 antibodies. In addition, viperin−/− T cells showed decreased DNA binding activities of NF-κB1/p50 and JunB in response to TCR ligation in gel-shift assays. These data suggest that viperin induction is required for TCR-mediated NF-κB and AP-1 activities, GATA-3 activation, and subsequent Th2 cell development for optimal Th2 response.
Methods
Generation of viperin-deficient mice
Mice deficient in viperin was generated using standard procedures. The viperin targeting vector consisted of a 1.8-kb short fragment in putative promoter region, a neomycin resistance gene cassette that replaced exons 1 and 2 as well as an upstream 2.2-kb putative promoter, and a 5.4-kb-long genomic fragment containing exons 3 and 4 (Figure 1A). One embryonic stem cell clone derived from 129/Sv mice, with a targeted viperin allele detected by Southern blot, was injected into C57BL/6 blastocysts to produce chimeric mice, and germline transmission of the mutation was verified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of tail DNA. Reverse transcription (RT)–PCR with primers spanning exons 2 and 3 in enriched splenic CD4+ cells and immunofluorescence staining in TCR-primed T cells as well as in frozen sections of murine spleens using a rabbit polyclonal antibody against the C-terminal peptide of viperin1 were also performed to confirm the disruption of the viperin gene at mRNA and protein levels. Heterozygous mutant mice were backcrossed into C57BL/6J mice 7 times before use in experiments. Age- and sex-matched littermate wild-type mice were used as controls. All mice were used at 6 to 12 weeks of age and were maintained in pathogen-free facilities in accordance with the guidelines of the Committee on Animal Care and Use of National University of Singapore.
Cell isolation and stimulation
CD4+ T cells from splenocytes were isolated by using the mouse CD4 negative selection kit and autoMACS system according to the manufacturer's instructions (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany). Purified CD4+ T cells (purity greater than 92%) were suspended in RPMI 1640 glutamax medium (Gibco-BRL [now Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA]), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Hyclone, Logan, UT), 25 mM HEPES, 100 U penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 5 μM 2-mercaptoethanol, and cultured at 4 to 5 × 105 cells/well in 24-well plates coated with anti-CD3 mAb (10 μg/mL; clone 145–2C11) in the presence or absence of anti-CD28 mAb (5 μg/mL; clone 37.51) for 72 hours at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. For T-cell proliferation assays, 5 × 104 cells were cultured with or without immobilized anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in triplicate in 96-well microtiter plates. Proliferation of T cells was determined by incorporation of BrdU for the last 8 to 12 hours of the culture, and assayed using a Cell Proliferation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit for BrdU (Roche, Indianapolis, IN) after 3 days of culture according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Naive T helper cells were isolated from mouse spleens by use of the CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit II and an AutoMACS separator (Miltenyi Biotec). The purity of the naive CD4+CD62Lhigh T cells was greater than 92%. For in vitro differentiation, naive splenic CD4+ T cells were stimulated with 1 to 5 μg/mL of immobilized anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in the presence of 30 U/mL recombinant human IL-2 under various T-cell–polarizing conditions. In typical T-cell differentiation cultures, Th2 cell–skewed (IL-4, 10 ng/mL; anti–IL-12, 10 μg/mL; and anti–IFN-γ, 10 μg/mL) and nonskewed (IL-2 with or without anti–IL-4, anti–IL-12, and anti–IFN-γ mAbs) conditions were used. After 4 to 5 days, the cells were split with fresh medium supplemented with IL-2 and IL-4, and left to rest for 2 to 3 days before restimulation. On days 7 and 14, the cells were washed, counted, and restimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 for various time periods, and the cytokine production was measured with intracellular cytokine staining and ELISA. Brefeldin A (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) was added for the final 2-hour restimulation before proceeding with intracellular staining using Cytofix/Cytoperm (BD Pharmingen, San Diego, CA). The stained cells were analyzed with FACSCalibur and CellQuest analysis software (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). Live events, based on the forward- and side-scatter pattern and the absence of ethidium monoazide bromide (EMA; Molecular Probes [now Invitrogen]) fluorescence, were collected for analysis. The polarizing cytokines and blocking antibodies used in the study were from BD Pharmingen.
Immunoblotting
Whole-cell extracts were lyzed in lysis buffer consisting of 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 0.5 M NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1.25% Nonidet P-40, 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 50 mM NaF, and protease inhibitor cocktail tablet (Roche). Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were prepared using NE-PER Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Extraction Reagent (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Protein concentrations were determined by Bradford method-based assay (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). Antibodies against GATA-3 (HG3–31), T-bet (4B10), JunB (C-11), NFATc-1 (NFATc, 7A6), NFATc-2 (NFATp, 4G6-G5), c-Maf (M-153), p65 (C-20), p50 (C-19), and α-tubulin (B-7) were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). Polyclonal anti–c-Rel and monoclonal anti-STAT6 antibodies were products from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). Mouse monoclonal anti–β-actin was from Chemicon (Temecula, CA). The protein levels were visualized by SuperSignal West Pico chemiluminescent substrate (Pierce).
EMSAs
Oligonucleotides (Sigma-Aldrich) labeled with biotin at the 5′ termini of sense strands were annealed with reverse strands in annealing buffer and purified with an agarose gel DNA extraction kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA). Nuclear extracts that contained equal amounts of protein were incubated in reaction buffer, which contained 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 60 mM KCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 4% glycerol, 1 μg poly(dI)·poly(dC) (Amersham Biosciences [now GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, United Kingdom]), and 200 μg/mL bovine serum albumin with biotin-labeled probe. For supershift assays, antibodies against p50 (Upstate, Charlottesville, VA), c-Rel (R&D Systems), p65 (F-6), Jun B (C-11), and c-Fos (K-25; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) were preincubated with lysates before addition of biotin-labeled probe. The binding reaction mixtures were subjected to electrophoresis on prerun 6% native polyacrylamide gel (0.5 × TBE; acrylamide/bisacrylamide, 29:1), and the binding signal was detected with LightShift Chemiluminescent Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) kit (Pierce).
Results
Characterization of viperin-deficient mice
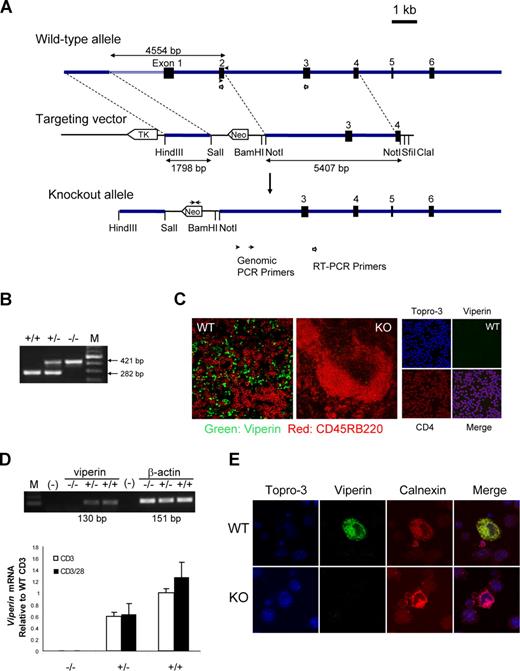
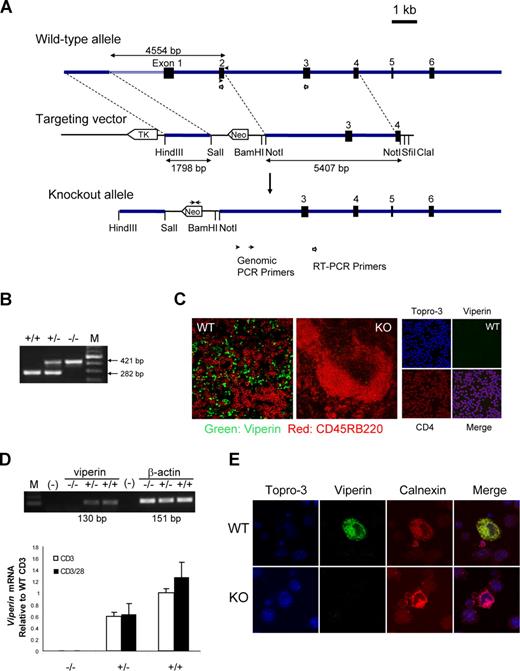
To investigate the biological functions of viperin in vivo, we constructed a gene-targeting vector with a neomycin resistance gene cassette to replace exons 1 and 2 of the mouse viperin gene, which encodes 166 amino acids of viperin protein sequence known to be critical for its endoplasmic reticulum (ER) localization and antiviral activity (Figure 1A,B and K.-C.C., unpublished data, September 2003). The null mutation of viperin in viperin−/− mice was confirmed by the absence of viperin protein in spleens by immunofluorescence staining (Figure 1C), whereas the presence of viperin was largely confined to spleens, but not in thymi and peripheral lymph nodes, of wild-type littermates (Figure 1C). The elimination of viperin mRNA and protein production was also validated in isolated peripheral CD4+ T cells, in contrast with the induction of viperin in wild-type T cells in response to TCR/CD28 ligation as examined by RT-PCR and immunofluorescence staining (Figure 1D,E). Unexpectedly, the mRNA level of viperin in freshly isolated splenic CD4+ T cells was relatively high (Figure S1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article), whereas the viperin protein by CD4+ cells was rarely detectable in both spleen tissue section from naive mice and unstimulated CD4+ cells (Figure 1C; data not shown).
Generation of viperin-deficient mice. (A) Diagram shows the wild-type allele (WT), the targeting vector, and the mutated allele. ■ represents exons 1 through 6. Neomycin (neo) and thymidine kinase (tk) are shown as open arrows that indicate the direction of transcription. (B) PCR genotyping of a litter born to a viperin heterozygous intercross is shown. M indicates 100-bp DNA ladder. (C) Immunofluoresence staining for viperin (green) with CD45RB220 (red) in spleens of wild-type (WT) and knockout (KO) mice, and with CD4 (red) in freshly isolated CD4+ T cells. (D) RT-PCR analysis in enriched splenic CD4+ T cells after treatment with anti-CD3 with or without anti-CD28 for 72 hours. Results are represented as transcript abundance relative to anti-CD3–treated wild-type T cells. The data shown are representative of 5 independent experiments, and error bars are the SD of transcript values. (E) Detection of viperin induction (green) with immunofluorescence staining in stimulated CD4+ T cells, which was costained with anti-calnexin (red) for ER localization and counterstained with Topro-3 (purple). Images in panels C and E were captured with an LSM 510 Meta confocal microscope (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) equipped with 40×/0.75 NA and 100×/1.3 NA oil Plan-Neoflour objective lenses.
Generation of viperin-deficient mice. (A) Diagram shows the wild-type allele (WT), the targeting vector, and the mutated allele. ■ represents exons 1 through 6. Neomycin (neo) and thymidine kinase (tk) are shown as open arrows that indicate the direction of transcription. (B) PCR genotyping of a litter born to a viperin heterozygous intercross is shown. M indicates 100-bp DNA ladder. (C) Immunofluoresence staining for viperin (green) with CD45RB220 (red) in spleens of wild-type (WT) and knockout (KO) mice, and with CD4 (red) in freshly isolated CD4+ T cells. (D) RT-PCR analysis in enriched splenic CD4+ T cells after treatment with anti-CD3 with or without anti-CD28 for 72 hours. Results are represented as transcript abundance relative to anti-CD3–treated wild-type T cells. The data shown are representative of 5 independent experiments, and error bars are the SD of transcript values. (E) Detection of viperin induction (green) with immunofluorescence staining in stimulated CD4+ T cells, which was costained with anti-calnexin (red) for ER localization and counterstained with Topro-3 (purple). Images in panels C and E were captured with an LSM 510 Meta confocal microscope (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) equipped with 40×/0.75 NA and 100×/1.3 NA oil Plan-Neoflour objective lenses.
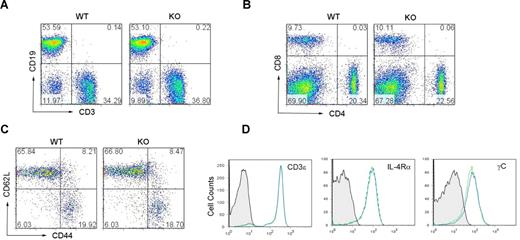
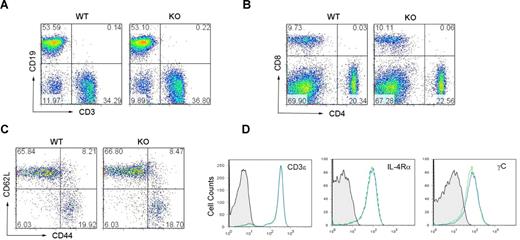
Viperin−/− mice were healthy and fertile, and exhibited no overt tissue phenotypic changes by histologic examination. Wild-type and viperin−/− mice had similar numbers of thymocytes and a comparable ratio of CD4+ to CD8+ thymocytes (Figure S2). Analysis of spleens from 6-week-old viperin−/− mice with a C57BL/6 background revealed a slightly higher number of splenocytes (94.42 ± 27.01 × 106) compared with wild-type (70.08 ± 12 × 106), which were still within the normal range. The percentage of CD3+ T cells or CD19+ B cells and the cell populations of CD4+ or CD8+ T lymphocytes in the spleens of viperin−/− mice were similar to that of wild-type littermate controls (Figure 2A,B). The cell surface expressions of CD3, IL-2R (CD25), CD69, IL-4Rα, common-γC (γC), CD44, and CD62L on the splenic CD4+ or CD8+ T cells were found to be comparable with those of controls (Figures 2C,D and S3; data not shown). Thus, no obvious defect in the phenotype of viperin−/− CD4+ T cells was noted and viperin appears not to be required for T-cell development.
Phenotypic characterization of viperin−/− mice. (A,B) Representative CD3/CD19 (A) and CD4/CD8 (B) profiles in splenocytes from 6-week-old wild-type and viperin−/− mice. The numbers in quadrants indicate the percentage of each quadrant. (C,D) Surface expression of CD44, CD62L, CD3, IL-4Rα, and common γc was analyzed on the splenic CD4+ T-cell population from viperin−/− mice (solid line) and its wild-type controls (dotted line). Background staining is shown as hatched areas. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Phenotypic characterization of viperin−/− mice. (A,B) Representative CD3/CD19 (A) and CD4/CD8 (B) profiles in splenocytes from 6-week-old wild-type and viperin−/− mice. The numbers in quadrants indicate the percentage of each quadrant. (C,D) Surface expression of CD44, CD62L, CD3, IL-4Rα, and common γc was analyzed on the splenic CD4+ T-cell population from viperin−/− mice (solid line) and its wild-type controls (dotted line). Background staining is shown as hatched areas. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Decreased OVA-specific IgG1 in viperin−/− mice
To assess the effect of the viperin depletion on Th1/Th2 development in vivo, serum levels of basal and antigen-specific immunoglobulins (Igs) were assessed in viperin-deficient mice. As shown in Figure S4A, the mean basal concentrations of serum IgG1, IgG2a, and IgE were comparable between viperin−/− and wild-type mice. However, when viperin-deficient mice and their heterozygous and wild-type littermates were challenged with ovalbumin (OVA) emulsified in complete and/or incomplete Freund adjuvant (CFA and/or IFA), there was a significantly reduced production of OVA-specific IgG1 in viperin-deficient mice at 2 weeks after second immunization, with a mean concentration of approximately 2-fold less than that in the wild-type mice (P = .014; Figure S4B). In contrast, OVA-specific IgE and OVA-specific IgG2a were not markedly affected (data not shown). The observation of decreased OVA-specific IgG1 in this mixed Th1/Th2 response model suggests the likelihood of viperin involvement in regulating the Th2 response.
Impaired Th2 cytokine production in viperin−/− CD4+ T cells mediated by anti-TCR stimulation
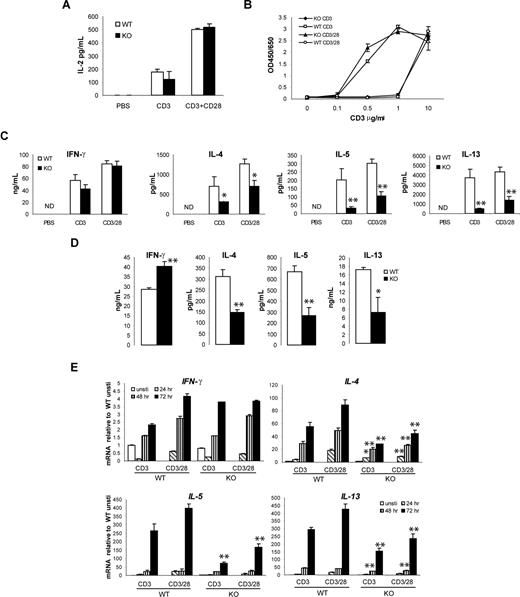
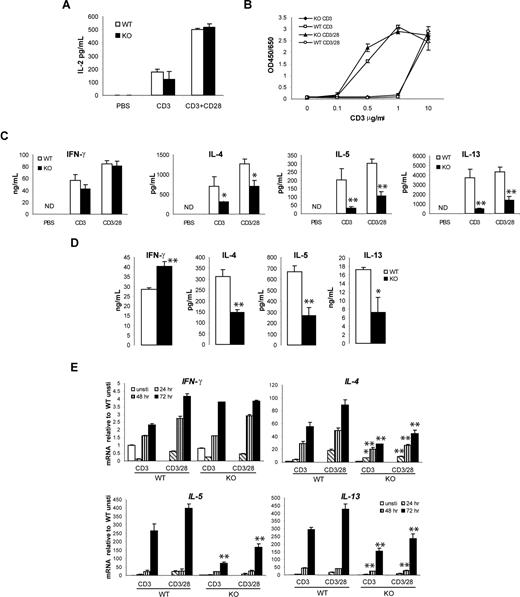
To understand the biological function of viperin in T-cell immune response regulation, we then examined T-cell activation in splenocytes from viperin−/− mice compared with their wild-type littermates. Freshly prepared splenic CD4+ T cells from viperin−/− and wild-type mice were stimulated in vitro with immobilized anti-CD3 mAb alone or in combination with immobilized anti-CD28 for various time periods, and the amounts of cytokines secreted into the culture supernatant were determined by ELISA. Analysis of IL-2 production in 24-hour culture supernatant did not reveal significant differences between viperin−/− and wild-type T-cell cultures after stimulation with anti-CD3 with or without anti-CD28 antibodies (Figure 3A). In parallel, anti-CD3/CD28–induced proliferative responses were indistinguishable between viperin+/+ and viperin−/− CD4+ T cells (Figure 3B). By contrast, the production of Th2 cytokines IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 by viperin−/− T cells was remarkably reduced after stimulation with anti-CD3 for 72 hours at both mRNA and protein levels. This was not rescued by addition of anti-CD28 antibody, although costimulation with anti-CD28 modestly enhanced the Th2 cytokine products in both viperin-deficient and wild-type cultures (Figure 3C,E). IFN-γ production by viperin−/− T cells, on the other hand, was equivalent to viperin+/+ T cells. Similar cytokine production profiles were obtained in cultures stimulated with phorbol-12- myristate-13-acetate (PMA) plus calcium ionophore ionomycin (Figure 3D). Notably, a differential induction pattern for Th2 cytokine gene expression was detected, with IL-4 induced earlier at 48 hours, followed by IL-13 at 72 hours and IL-5 at 90 hours (data not shown). Thus, the impaired production of multiple Th2 cytokines might possibly reflect a global Th2 defect in viperin-deficient T cells in response to TCR ligation, and viperin deficiency appears to be associated with a deficit in Th2 cytokine production in mature T cells.
Decreased production of Th2 cytokines by viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells. (A) IL-2 production from CD4+ T cells after stimulation with anti-CD3 with or without anti-CD28 Abs for 24 hours. (B) BrdU incoporation assay for T cells primed with a serial concentration of anti-CD3 mAb or in conjunction with anti-CD28 (5 μg/mL). (C) Th1 and Th2 cytokine production in supernatants were analyzed after stimulation for 72 hours. The data shown are representative of more than 10 independent experiments, each using different mice. ND indicates not detectable. (D) Amount of IFN-γ and IL-4 was measured in culture supernatants of CD4+ T cells following stimulation with 5 ng/mL PMA plus 500 ng/mL ionomycin for 4 days. IL-5 and IL-13 production was determined after a 5-day culture. A representative of 5 independent experiments is shown. *P < .05; **P < .01, WT versus knockout (KO). (E) RNA expression of cytokines in stimulated T cells was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. A representative of 3 independent experiments is shown. All data are expressed as the mean value of duplicate-triplicate determinations plus or minus SD. *P < .05; **P < .01 WT versus KO at most of the time points for IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 determined by Student t test.
Decreased production of Th2 cytokines by viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells. (A) IL-2 production from CD4+ T cells after stimulation with anti-CD3 with or without anti-CD28 Abs for 24 hours. (B) BrdU incoporation assay for T cells primed with a serial concentration of anti-CD3 mAb or in conjunction with anti-CD28 (5 μg/mL). (C) Th1 and Th2 cytokine production in supernatants were analyzed after stimulation for 72 hours. The data shown are representative of more than 10 independent experiments, each using different mice. ND indicates not detectable. (D) Amount of IFN-γ and IL-4 was measured in culture supernatants of CD4+ T cells following stimulation with 5 ng/mL PMA plus 500 ng/mL ionomycin for 4 days. IL-5 and IL-13 production was determined after a 5-day culture. A representative of 5 independent experiments is shown. *P < .05; **P < .01, WT versus knockout (KO). (E) RNA expression of cytokines in stimulated T cells was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. A representative of 3 independent experiments is shown. All data are expressed as the mean value of duplicate-triplicate determinations plus or minus SD. *P < .05; **P < .01 WT versus KO at most of the time points for IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 determined by Student t test.
Defects in Th2 cytokines in strong TCR-mediated suboptimal Th2 polarization
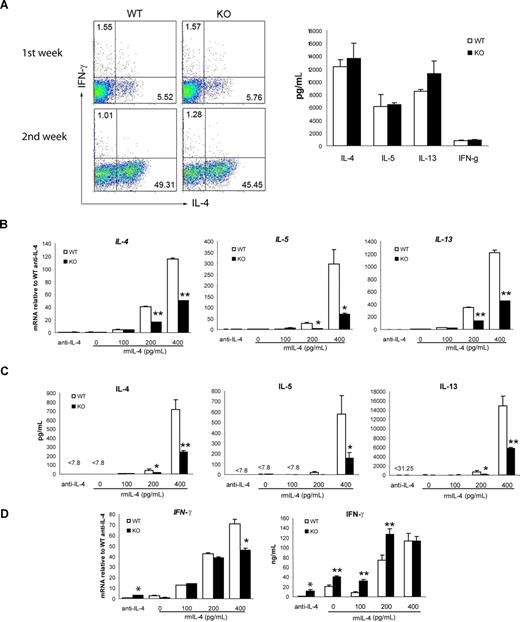
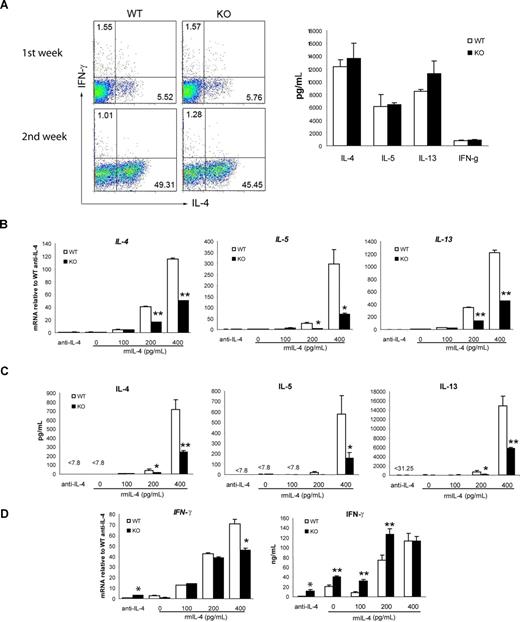
To further identify the CD4+ T-cell subset that is defective in Th2 cytokine production, we next determined whether the loss of viperin would affect the secretion of Th2 cytokines by naive (CD62LhighCD44low) CD4+ T cells under conditions promoting Th2 polarization. T helper cell differentiation is influenced by signals from both the TCR and cytokines themselves. To assess whether viperin-deficient cells have defective responses to cytokines, naive CD4+ T cells from viperin-deficient and wild-type mice were stimulated with anti-CD3 (1 μg/mL) and anti-CD28 (5 μg/mL) in the presence of exogenous IL-2, excess IL-4 (10 ng/mL), and neutralizing antibodies against IL-12 and IFN-γ. As shown in Figure 4A, the percentages of IL-4–producing cells in viperin−/− Th2 differentiation cultures were essentially equivalent to those in wild-type naive cell cultures after a 2-week polarization, and the amounts of Th1 and Th2 cytokine secreted by naive viperin-deficient T cells were indistinguishable from naive wild-type counterparts. Thus, viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells have retained the ability to respond to extrinsic IL-4 signals and can differentiate into the appropriate Th2 cell lineages in vitro.
Impaired Th2 response in viperin−/− naive CD4+ T cells cultured under suboptimal Th2 conditions. (A) Naive CD4+ T cells were stimulated under optimal Th2-skewed conditions for 2 weeks. Differentiated cells were restimulated with 5 μg/mL plate-bound CD3/CD28 for 6 hours for intracellular production of IL-4 and IFN-γ (left panel), or for 24 hours for the amount of cytokines secreted into the supernatants (right panel; data shown is a restimulated culture after 1 week of differentiation). Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. The numbers in quadrants indicate the percentage of each quadrant. (B) Naive T cells were cultured with 5 μg/mL anti-CD3 and 1 μg/mL anti-CD28 in the presence of 30 U/mL IL-2 and a graded dose of IL-4 for 5 days. RNA expression of Th2 cytokines was measured with real-time RT-PCR. (C) Naive T cells were stimulated as in panel B for 5 days, washed, counted, and then restimulated with 10 μg/mL anti-CD3 for 48 hours. The culture supernatants were then assayed for cytokine production measurement. (D) IFN-γ production cultured as in panels B and C was analyzed. Data shown in panels B-D are representative of 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as the mean value of triplicate determinations plus or minus SD. *P < .05; **P < .01, WT versus KO.
Impaired Th2 response in viperin−/− naive CD4+ T cells cultured under suboptimal Th2 conditions. (A) Naive CD4+ T cells were stimulated under optimal Th2-skewed conditions for 2 weeks. Differentiated cells were restimulated with 5 μg/mL plate-bound CD3/CD28 for 6 hours for intracellular production of IL-4 and IFN-γ (left panel), or for 24 hours for the amount of cytokines secreted into the supernatants (right panel; data shown is a restimulated culture after 1 week of differentiation). Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. The numbers in quadrants indicate the percentage of each quadrant. (B) Naive T cells were cultured with 5 μg/mL anti-CD3 and 1 μg/mL anti-CD28 in the presence of 30 U/mL IL-2 and a graded dose of IL-4 for 5 days. RNA expression of Th2 cytokines was measured with real-time RT-PCR. (C) Naive T cells were stimulated as in panel B for 5 days, washed, counted, and then restimulated with 10 μg/mL anti-CD3 for 48 hours. The culture supernatants were then assayed for cytokine production measurement. (D) IFN-γ production cultured as in panels B and C was analyzed. Data shown in panels B-D are representative of 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as the mean value of triplicate determinations plus or minus SD. *P < .05; **P < .01, WT versus KO.
Current evidence supports that the strength of TCR signaling influences Th2 differentiation by differential induction of GATA-3 rather than T-bet.10,11 To examine whether the TCR stimulation (CD3, 1 μg/mL) we used in optimal Th2 polarization conditions would be not appropriate enough to demonstrate the defects in viperin-deficient naive T cells, we varied the plate-bound concentrations of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies, and compared their effects on Th2 differentiation under nonskewed and neutralizing conditions in the absence of exogenous IL-4. However, the Th2 defect in viperin−/− naive T cells was not detected when stimulated with a low strength of TCR signaling (data not shown), which is known to favor Th2 polarization, whereas the Th2 cytokine production in both wild-type and viperin-deficient naive cell cultures was too low to be detectable when activated with a high dose of anti-CD3 mAb (5 μg/mL; Figure 4B), despite the moderate increase in IFN-γ production by viperin-lacking naive CD4+ T cells compared with wild-type cells (Figure 4D). We then sought to determine whether the addition of minimal amount of exogenous IL-4 into the culture medium would enhance Th2 products, taking into account that abundant IL-4 would act through IL-4R/STAT6 signaling to compensate the Th2 defects mediated by TCR signaling. As expected, the production of Th2 cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13, was enhanced in a dose-dependent manner by exogenous IL-4 in wild-type T-cell cultures at both mRNA and protein levels; whereas both the secreted amounts and transcripts of Th2 cytokines by viperin-/- naive T cells were significantly decreased under these suboptimal Th2-skewed conditions (Figure 4B,C). The ability of viperin-/- naive CD4 T cells to differentiate into Th2 cells may be significantly compromised in a defined niche and T cells deficient in viperin have a TCR-specific defect in Th2 cytokine induction.
Impaired GATA-3 Activation in viperin−/− CD4+ T cells upon TCR stimulation
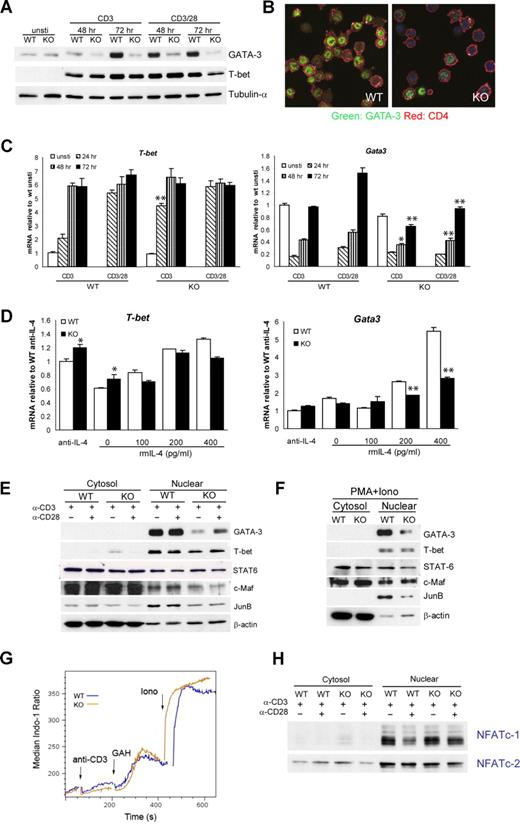
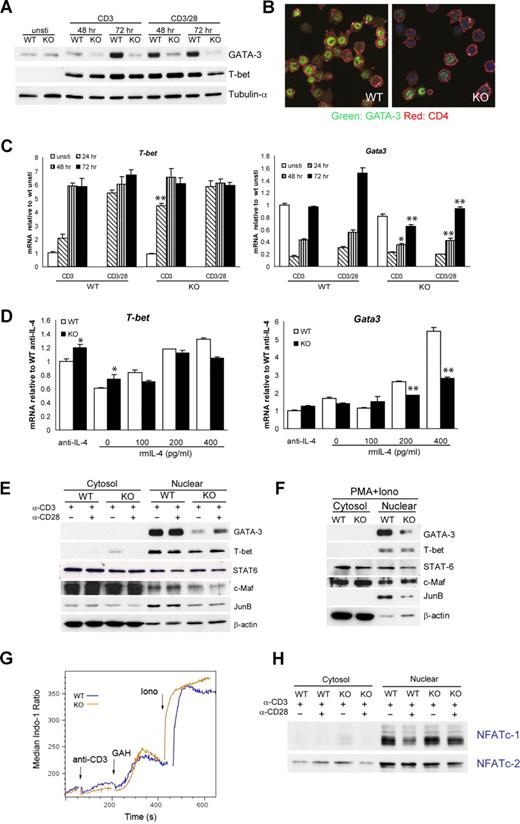
To address the molecular mechanisms that account for the impaired Th2 cytokine expression by viperin−/− CD4+ T cells after TCR cross-linking, we used real-time RT-PCR as well as immunoblotting to analyze the expression of T-bet and GATA-3, the 2 master regulators of Th1 and Th2 differentiation, respectively. The basal levels of GATA-3 in freshly isolated wild-type and viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells were similar at both mRNA and protein levels, and no detectable T-bet was observed in both cells before stimulation. Following activation with anti-CD3, wild-type CD4 T cells had gradually increased induction of GATA-3 protein from 48 hours to 72 hours, while viperin-deficient T cells showed a marked defect in the induction of GATA-3 protein (Figure 5A,B). The defect in the Gata3 transcript paralleled the defect in protein products, and the peak difference was notable at 72 hours after stimulation, with an average of 0.65 plus or minus 0.15 relative to wild-type controls (P < .001; Figure 5C). By contrast, T-bet induction remained largely intact, despite a modest increase in T-bet transcripts in viperin-deficient T cells at 24 hours. Naive T cells from viperin−/− mice exhibited a similar Gata3 defect in suboptimal Th2 differentiation cultures, with a 2-fold reduction in cultures supplemented with 400 pg/mL IL-4 compared with wild-type cells (Figure 5D). The expression of T-bet mRNA by viperin−/− naive T cells was unaffected. Thus, our results suggest that GATA-3 induction is significantly impaired in viperin−/− CD4+ T cells upon TCR ligation. This defect was also observed when adding anti–IL-4 antibody during the culture for neutralization (Figure S5).
Viperin is required for optimal GATA3 induction. (A) Total-cell lysates were prepared from activated CD4+ T cells and blotted with anti–GATA-3 and anti–T-bet. Tubulin-α was used as a loading control. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of GATA-3 (green) and CD4 (red) in stimulated T cells, counterstained with Topro-3 (purple). (C) T-bet and Gata3 mRNA expression by CD4+ T cells in response to stimulation at indicated times. (D) RT-PCR analyses of naive CD4+ T cells cultured under suboptimal Th2-skewed conditions consisted of immobilized 5 μg/mL anti-CD3 and 1 μg/mL anti-CD28, exogenous IL-2, and the indicated amount of IL-4 for 5 days. Data (C,D) are expressed as the mean value of triplicate determinations plus or minus SD, and the data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05; **P < .01, WT versus KO. (E,F) Cytosolic and nuclear extracts prepared from CD4+ T cells stimulated as indicated for 72 hours (E) or for 4 days (F) were processed for immunoblotting. β-actin was used as a control for equal protein loading. A total of 4 (E) or 3 (F) independent experiments were performed with similar results. (G) Indo-1–loaded CD4+ T cells were subjected to challenge with anti-CD3 (5 μg/mL), goat–anti-hamster IgG (40 μg/mL; GAH), and ionomycin (500 ng/mL; iono) sequentially. Histogram data are presented as median ratio of calcium mobilization as measured by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS). Experiments were repeated twice with similar results. (H) Nuclear translocation of NFATc-1 and NFATc-2 was analyzed with extracts prepared from T cells stimulated for 72 hours. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Viperin is required for optimal GATA3 induction. (A) Total-cell lysates were prepared from activated CD4+ T cells and blotted with anti–GATA-3 and anti–T-bet. Tubulin-α was used as a loading control. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of GATA-3 (green) and CD4 (red) in stimulated T cells, counterstained with Topro-3 (purple). (C) T-bet and Gata3 mRNA expression by CD4+ T cells in response to stimulation at indicated times. (D) RT-PCR analyses of naive CD4+ T cells cultured under suboptimal Th2-skewed conditions consisted of immobilized 5 μg/mL anti-CD3 and 1 μg/mL anti-CD28, exogenous IL-2, and the indicated amount of IL-4 for 5 days. Data (C,D) are expressed as the mean value of triplicate determinations plus or minus SD, and the data shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05; **P < .01, WT versus KO. (E,F) Cytosolic and nuclear extracts prepared from CD4+ T cells stimulated as indicated for 72 hours (E) or for 4 days (F) were processed for immunoblotting. β-actin was used as a control for equal protein loading. A total of 4 (E) or 3 (F) independent experiments were performed with similar results. (G) Indo-1–loaded CD4+ T cells were subjected to challenge with anti-CD3 (5 μg/mL), goat–anti-hamster IgG (40 μg/mL; GAH), and ionomycin (500 ng/mL; iono) sequentially. Histogram data are presented as median ratio of calcium mobilization as measured by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS). Experiments were repeated twice with similar results. (H) Nuclear translocation of NFATc-1 and NFATc-2 was analyzed with extracts prepared from T cells stimulated for 72 hours. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
To assess the possible involvement of any other transcription factors that may also regulate Th2 cell differentiation, we also examined the expression of STAT6, c-Maf, JunB, NFATc-1, and NFATc-2 in viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells after TCR activation. Consistent with the intact ability of viperin−/− T cells to respond to IL-4 signaling, the STAT6 protein level in either total lysates or cytosolic and nuclear lysates was similar to that in controls (Figure 5F; data not shown). c-Maf, a Th2 molecule that is specific for transactivation of IL-4, was also found to be mostly unaffected after stimulation with anti-CD3 with or without anti-CD28 or with PMA plus ionomycin. Unexpectedly, there was a slight but consistent decrease in JunB protein by viperin−/− T cells in response to anti-CD3 and PMA/ionomycin stimulation, suggesting its potential implication in TCR-mediated Th2 cytokine defects by viperin-deficient T cells. The levels of both calcium responses induced by TCR cross-linking were essentially equivalent between viperin+/+ and viperin−/− CD4 T cells (Figure 5G). In line with the normal IL-2 production and proliferative responses by viperin−/− T cells, the intracellular calcium fluxes and nuclear translocation of NFATc-1 and NFATc-2 following TCR cross-linking in viperin−/− CD4 T cells remained intact (Figure 5H).
Combined defects in NF-κB and AP-1 activities in viperin−/− CD4+ T cells regulated by TCR signals
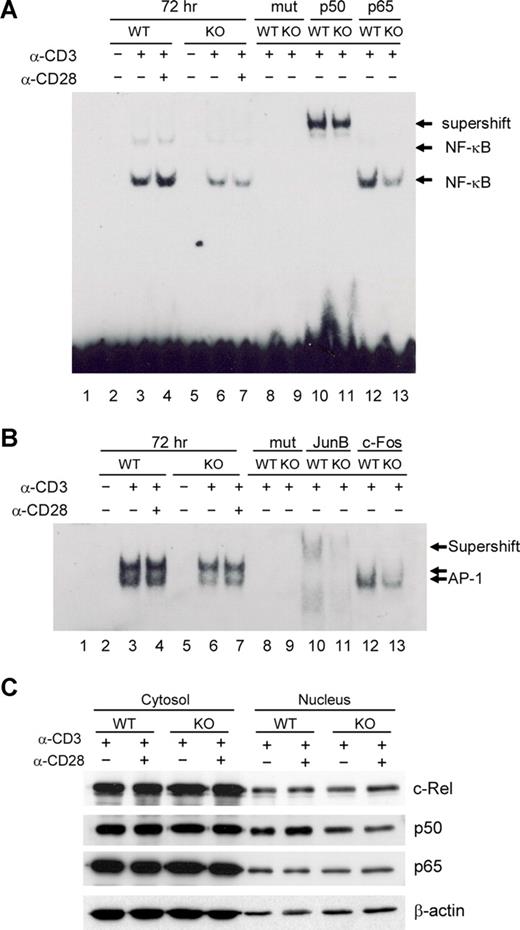
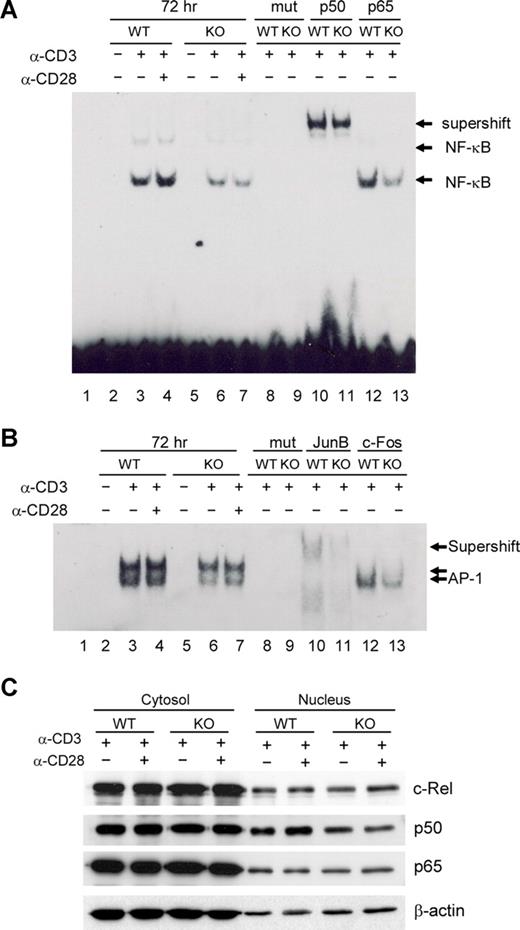
Several reports have suggested that NF-κB activation via TCR plus CD28 signaling is a crucial event in the induction of GATA-3 transcription, but has no bearing on T-bet or IFN-γ expression.12,13 To investigate molecular mechanisms underlying the observed Th2 defects in viperin-deficient T cells, we examined NF-κB activity in viperin−/− T cells by EMSAs. Little DNA binding activity of NF-κB was detected in unstimulated splenic CD4 T cells isolated from wild-type and viperin-deficient mice. Upon TCR/CD28 engagement, there was a gradual increase in the formation of NF-κB DNA binding complexes from 24 hours onwards in wild-type T cells, suggesting an enhanced and sustained NF-κB activity after prolonged activation. In contrast, the formation of NF-κB DNA binding complexes was greatly reduced in viperin-deficient T cells, which was particularly evident at 72 hours after stimulation, indicating an impaired NF-κB DNA binding activity in peripheral CD4+ T cells deficient in viperin (Figure 6A; data not shown). Challenge with anti-p50 lead to a substantial mobility shift of NF-κB DNA probe containing complexes in both wild-type and viperin-deficient T cells (Figure 6A lanes 10-11), suggesting a predominance of p50 subunit in these binding complexes in TCR-primed T cells. We were unable to detect any supershift with several other NF-κB antibodies against p65 and c-Rel (Figure 6A lanes 12-13; data not shown), implying the possibly insignificant contribution of p65 and c-Rel activity in TCR-mediated NF-κB activation. Unexpectedly, the nuclear level of p50 protein was only modestly reduced in contrast with the unaffected expression of p65 and p75 (c-Rel) in nuclear fractions from viperin−/− T cells. Thus, the nuclear translocation of the NF-κB p50, p65, and p75 subunits remains largely intact in T cells with viperin deletion (Figure 6C).
Defects in NF-κB and AP-1 activity in viperin−/− CD4+ T cells. (A,B) EMSA analysis of NF-κB (A) and AP-1 (B) activity in nuclear extracts from unstimulated or stimulated CD4+ T cells for 72 hours. The supershift assays were performed with indicated antibodies. Lane 1 was probe-only control without lysates. Lanes 8 and 9: mutant probes (mut) were used to replace specific probes in binding reactions to verify the specificity of probes. (C) Immunoblotting analysis for NF-κB subunits in CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 for 72 hours. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Defects in NF-κB and AP-1 activity in viperin−/− CD4+ T cells. (A,B) EMSA analysis of NF-κB (A) and AP-1 (B) activity in nuclear extracts from unstimulated or stimulated CD4+ T cells for 72 hours. The supershift assays were performed with indicated antibodies. Lane 1 was probe-only control without lysates. Lanes 8 and 9: mutant probes (mut) were used to replace specific probes in binding reactions to verify the specificity of probes. (C) Immunoblotting analysis for NF-κB subunits in CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 for 72 hours. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Due to the observed JunB deficit in nuclear extracts from viperin-deficient T cells after TCR stimulation, we sought to determine whether AP-1 contributes to the TCR-mediated Th2 defects in the absence of viperin as well. Similar to NF-κB activity, the AP-1 DNA binding complexes were found to be gradually enhanced after stimulation with anti-CD3 alone or with anti-CD28 in wild-type CD4+ T cells during a 3-day culture, which was remarkably reduced in viperin-deficient T cells (Figure 6B; data not shown). The decrease in AP-1 DNA binding activity was maximized after 72 hours of stimulation compared with wild-type control cells, suggesting the implication of AP-1 activity in mediating Th2 defects in viperin-deficient T cells. Supershift with several AP-1 antibodies revealed the composition of JunB, c-Fos, and c-Jun, but not JunD, in these binding complexes (Figure 6B lanes 10-13; data not shown), indicating the complexity of AP-1 DNA binding complexes for its transcriptional activity. Moreover, incubation with anti-JunB antibody was shown not only to supershift the 2 AP-1 DNA binding complexes, but also to reduce their formation, leading to several binding complexes of weaker band intensity and faster mobility. Therefore, the impaired AP-1 activity upon TCR/CD28 stimulation might reflect, at least, the decreased nuclear expression of Jun B protein by viperin−/− T cells.
Discussion
We report here the first study in viperin-deficiency mice that examined the biological function of viperin in peripheral T helper lymphocytes. Viperin appears to modulate the NF-κB and AP-1 activities in response to TCR engagement, and subsequent induction of GATA-3 and Th2 cytokines in early developing Th2 cells.
It was demonstrated in this study that there was a marked impaired Th2 cytokine production by viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells in association with a decrease in GATA-3 induction after stimulation with anti-CD3/CD28, which was not restored by exogenous IL-2, while the production of Th1 cytokine IFN-γ was not appreciably affected. These Th2 defects in viperin−/− splenic CD4+ T cells became only evident at 72 hours after TCR activation, but not at the early stage of TCR ligation, implying that viperin is not involved in the proximal events of TCR signaling. This was confirmed by the intact responses in viperin−/− T cells when assessed with IL-2 production, cell proliferation, expression of early T-cell markers (CD25 and CD69), and calcium flux. The notable Th2 defects in viperin−/− T cells after prolonged stimulation paralleled the kinetics of viperin mRNA expression in CD4+ T cells after TCR cross-linking, where induction was evident at day 3 (Figure S1). Moreover, observation of the Th2 defects in cultures with both TCR and PMA/ionomycin stimulation suggests that viperin may participate in distal T-cell signaling events, occurring after activation of the presumed targets of PMA plus ionomycin (ie, protein kinase Cs [PKCs] and calcium fluxes),14,15 but before triggering of Th2 regulator GATA-3.
In line with the Th2 defects observed in viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells in vitro, we demonstrated a deficit in OVA-specific IgG1 in viperin knockout mice on a C57BL/6 genetic background after immunization with OVA. Notably, the maximally significant reduction in OVA-specific IgG1 by viperin-deficient mice was noted only at 2 weeks after the second immunization, whereas our in vitro observation suggests that the Th2 defects were linked with naive T cells but not memory T-cell types (Figure S6). The findings that antigen priming in CFA favors the production of Th1 cytokines, whereas priming with IFA favors a Th2 response,16 might possibly provide a rationale for our observations in this viperin-deficiency mouse model, as well as account for the discrepancies between our in vivo and in vitro observations. Indeed, viperin expression was clustered in T cell–rich red pulp, particularly in the paracortical region, in spleens of naive wild-type mice (Figure 1C; data not shown), where high endothelial venules reside and active interaction between CD4+ T cells and antigen-presenting dendritic cells occurs. This specific but unique localization of viperin prompts us to speculate a physiologic role for viperin in the modulation of proper immune cell function and appropriate responses to antigens and infectious agents.
Optimal GATA-3 induction in naive CD4+ T cells requires integration of both TCR-mediated and IL-4R–mediated signals. In this study, we demonstrated a TCR-specific Th2 defect in association with impaired GATA-3 activation, while the IL-4/STAT6 signaling pathway remained intact in viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells. The reduction in Th2 cytokine products by viperin−/− T cells upon TCR ligation possibly occurs through the attenuation of GATA-3 activation in an IL-4/STAT6-independent manner.17 The indispensable role of IL-4–independent GATA-3 up-regulation in early IL-4 production has been highlighted in a recent study with conditional Gata3 knockout mice.18 GATA-3 plays a key role in the initiation of chromatin remodeling in the Th2 cytokine gene cluster and can drive expression of Th2 cytokines.19,20 GATA-3 is also shown to inhibit Th1 response as well as augmenting its own expression by a positive feedback loop to stabilize the Th2 phenotype.20,21
Nevertheless, how signals downstream of TCR ligation connect to transcriptional activation of the Gata3 gene remains largely unknown. The prevalent view holds that GATA-3 expression and function is under tight control by both positive and negative regulatory mechanisms. Such representative molecules as mel-18, SAP, Runx1, and Notch1 have been identified recently for their positive and negative regulation of Gata3 expression, respectively.15,22–24 Studies from 2 separate groups have reported the requirement of NF-κB1/p50 for optimal GATA-3 induction in T cells, based on the fact that GATA-3 expression and Th2 differentiation were specifically abrogated in p50−/− T cells and in SAP−/− cells where nuclear translocation of NF-κB was inhibited.12,15 Mice deficient in NF-κB1 showed impairment in Th2 development in murine models of allergic asthma and Trichuris muris infection,12,25 indicating the critical role of NF-κB activity in mediating Th2 immune responses. Consistent with these studies, we demonstrated a defect in p50 DNA binding activity in association with impaired GATA-3 induction in viperin-deficient CD4+ T cells following T-cell activation, which was not overcome by anti-CD28 costimulation. The GATA-3 promoter region contains several consensus-potential NF-κB binding sites,12,15 and direct binding of NF-κB subunits may control the transcriptional activation of Gata3 and thereafter the Th2 lineage development. Unlike the elimination or attenuation of nuclear p50 levels in p50−/− and SAP−/− T cells, the nuclear retention of p50 was only modestly affected in viperin−/− T cells. This distinguishes viperin from other molecules such as SAP that affect the DNA binding affinity of p50 heterodimers and/or homodimers, and suggests possible posttranslational interactions. This is supported by a study with murine Schnurri-2−/− (Shn-2−/−) mice, in which Shn-2 was shown to compete with p50 for binding to a consensus NF-κB motif and inhibit NF-κB–driven promoter activity without perturbing nuclear p50 protein levels, leading to the subsequent control of Th2 cell differentiation.26
In parallel to the NF-κB1/p50 defect, we observed a defect in AP-1 activity in terms of reduction in JunB protein level and the formation of JunB-containing DNA binding complexes in viperin−/− T cells after TCR/CD28 stimulation. The association between JunB and Th2 differentiation has been demonstrated previously. JunB-deficient mice showed decreased IL-4 and IL-5 levels and impaired allergen-induced airway inflammation.27 In primary T cells, the accumulated AP-1–containing complexes in the gel-shift assay were only observed using activated Th2 extracts, which were composed of some c-Fos and high levels of JunB.28,29 However, there is no direct evidence linking JunB to GATA-3 activation. In Itch−/− T cells, remarkably elevated nuclear JunB protein levels and augmented Th2 cytokine expression in the presence of an unperturbed GATA-3 expression was observed after stimulation with anti-CD3 with or without anti-CD28.30 A number of experiments have indicated that GATA sites in conjunction with an AP-1 site constitute an active promoter.31,32 It is highly likely that JunB acts synergistically with GATA-3 to promote Th2 cytokine production and enhance Th2 differentiation.
It appears that viperin is involved in the sustained activation of both NF-κB and AP-1 after TCR engagement, which in turn mediates induction of GATA-3 and Th2 cytokines. The precise mechanism that connects viperin, an ER-localized protein, to the modulation of NF-κB and AP-1 nuclear activity remains to be identified. Indeed, most of the molecules involved in NF-κB activation following antigen receptor stimulation, such as Vav1, Carma1, RIP2, and PKC-θ, also play an important role in AP-1 activation.33–35 PKC-θ expression is largely restricted to mature T cells, and PKC-θ−/− T cells are deficient in both NF-κB and AP-1 activation.36 The T-cell activation–induced translocation of PKC-θ to lipid rafts and immunologic synapse is crucial for its function in T-cell activation.37 Coincidentally, an antiviral inhibitory mechanism by viperin has been revealed recently that viperin is capable of perturbing plasma membrane fluidity by affecting the formation of lipid rafts.2 These studies highlight the potential involvement of lipid raft in mediating PKC-θ activity by viperin, whose deficiency may contribute to the attenuation in both NF-κB and AP-1 activities downstream of TCR signaling as observed in this study. However, PKC-θ mediates critical signals required for T-cell proliferation and IL-2 production as well, which were not affected in viperin−/− CD4+ T cells. Thus, it remains uncertain whether there is an alternative PKC isoenzyme in the lipid raft that accounts for the combined deficiency in NF-κB and AP-1 activity in the presence of normal amounts of IL-2 production, or whether the defect arises from downstream signaling molecules after PKC-θ activation, but before divergence between these 2 pathways.
In addition, viperin may involve in several steps of posttranslational modifications, such as formation of disulfide bonds, folding, specific proteolytic cleavages, and assembly into multimeric proteins, which take place exclusively in the rough ER. Possible posttranslational modifications, such as acetylation, ubiquitination, and phosphorylation, may alter the DNA-binding activities of NF-κB subunits, including p50 and JunB as well.30,38,39 This speculation is supported by the observed time-frame of 3 days required to observe the effect of viperin in primary murine T cells after TCR engagement; the function might be downstream of de novo synthesis of its targeted molecules.
We provide evidence here for a crucial role of viperin in CD4+ T-cell activation and differentiation. Though viperin was shown to be required for NF-kB1/p50 and AP-1 activity in optimal Th2 immune response, the 2 key regulators of inflammatory and immune response genes, the precise physiologic function of viperin in the immune system has not been fully elucidated. It still remains largely unknown whether defects in NF-κB and AP-1 activity in the absence of viperin are specific to TCR signaling or a general response to stimuli, and whether the in vitro Th2 defects will be recapitulated in in vivo Th2-associated disease models.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Joyce Jing Yi Wong and Calvin Sum for administrative and technical assistance.
Authorship
Contribution: L.-Q.Q. performed the experiments, interpreted results, and contributed to writing the manuscript; P.C. provided guidance for the original generation of viperin−/− mice and edited the manuscript; and K.-C.C. established the viperin−/− mice, edited the manuscript, and supervised the project.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Keh-Chuang Chin, Singapore Immunology Network, Biomedical Sciences Institute, 8A Biomedical Grove, No. 04-06 Immunos, Singapore 138648; e-mail: kehchuang_chin@immunol.a-star.edu.sg.