Abstract
Abstract 2660
Poster Board II-636
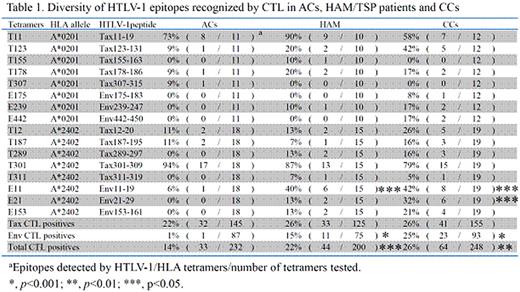
Human T-cell leukemia virus-1 (HTLV-1) causes adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) and HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) after long-term infection. A variety of collagen diseases such as Sjögren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus has been reported in HTLV-1-infected individuals, although the precise relationship between these disorders and HTLV-1 infection remains unknown. We have previously reported the decreased frequency and function of HTLV-1 Tax-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in ATL patients due to insufficient cytolytic effector molecules compared with asymptomatic carriers (ACs) (ASH annual meeting 2007). However, there is no report on the repertoire of HTLV-1-specific CTLs in HAM/TSP patients or carriers with collagen diseases (CCs), both of which are characterized by abnormal immune states. In order to characterize HTLV-1-specific CTLs in ACs, HAM/TSP patients and CCs, we examined the frequency and diversity of HTLV-1-specific CTLs using 16 distinct HTLV-1 Tax and Env HLA-A*0201 and HLA-A*2402 tetramers. There was no statistically significant difference in the proportion of patients having HTLV-1 Tax specific CTLs among ACs, HAM/TSP and CC patients, but a greater proportion of patients with HAM/TSP or collagen disease had HTLV-1 Env-specific CTLs compared with ACs (Env175-183, Env239-246, Env442-450 for HLA-A*0201 and Env11-19, Env21-29, Env153-161 for HLA-A*2402) (Table 1). Within CD8+ lymphocyte subsets, the percentage of cells binding either Tax11-19/HLA-A*0201 or Tax 301-309/HLA-A*2402 tetramer (Figure 1), was significantly higher for HAM/TSP patients compared to ACs, being lowest among CCs. Additionally, the number of epitope repertoires found on HTLV-1 Env-specific CD8+ cells in ACs was considerably lower than for HAM/TSP patients and CCs (ACs, 1/6; HAM/TSP, 4/6; CCs, 6/6). This study demonstrates the relatively greater importance of CTLs recognizing HTLV-1 envelope tetramers compared to HTLV-1 Tax tetramers, thereby suggesting that the diversity, frequency and repertoire of HTLV-1-specific CTL clones, especially Env-CTLs, may be related to the hyperimmune response in HAM/TSP and carriers with collagen diseases.
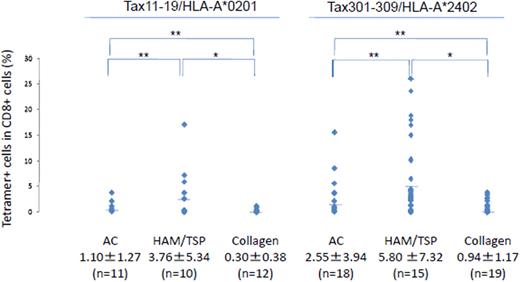
Frequency of Tax11-19/HLA-A*0201 or Tax301-309/HLA-A*0201 tetramer binding CD8+ T cells in ACs, HAM/TSP patients and CCs. The percentage of tetramer+ cells in CD8+ lymphocytes in ACs, HAM/TSP patients and CCs. Horizontal bars indicate the mean percentage of tetramer positive cells. The numbers below each subject indicate mean±S.D. *P<0.001; **P<0.05 (Significant differences by Mann-Whitney U test).
Frequency of Tax11-19/HLA-A*0201 or Tax301-309/HLA-A*0201 tetramer binding CD8+ T cells in ACs, HAM/TSP patients and CCs. The percentage of tetramer+ cells in CD8+ lymphocytes in ACs, HAM/TSP patients and CCs. Horizontal bars indicate the mean percentage of tetramer positive cells. The numbers below each subject indicate mean±S.D. *P<0.001; **P<0.05 (Significant differences by Mann-Whitney U test).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.