Abstract
Abstract 4231
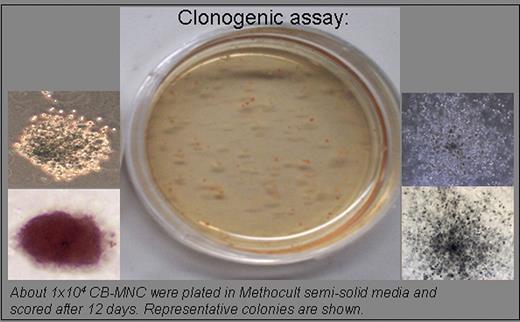
Cord blood (CB) is a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) with long-term repopulating activity necessary for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. CD34+ stem cells are considered sufficient for transplantation, however recent progress in stem cell biology indicates that cells with other surface markers such as CD133 or cells expressing high aldehyde dehydrogenase activity with low side scatter (ALDHhigh/SSClow) or a rare side population (SP) of cells that exclude the Hoechst 33342 vital dye via multi drug transporters have been shown to possess stem cell properties. We characterized CD34+, CD133+, ALDH+ and SP in mononuclear cells (MNC) isolated from human CB. While the SP cell population is rare and detectable in few CB-MNC examined, we found abundant CD34+ and CD133+ cells (1.0+/-0.5 and 0.8+/-0.4 per 100 CD45+ MNC cells, respectively) following the ISHAGE protocol. A distinct ALDH+ cell population (median of 0.26%; range of 0.1 to 0.5%) was also present in all of the CB-MNC analyzed. Over 90% of the ALDH+ cells were also CD34+ and CD133+. The ability of CB-MNC to form colonies in methocult semi-solid media supplemented with cytokines yielded myeloid, lymphoid and erythroid colonies. The clonogenic potential of CB-MNC ranged from 16-48%. We are assessing the colony forming ability of purified stem cell fractions using flow cytometry. The clonogenic efficiency of these individual putative stem cells will be discussed.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.