Abstract
A comprehensive understanding of the genes and pathways regulating hematopoiesis is needed to identify genes causally related to bone marrow failure syndromes, myelodysplastic syndromes, and hematopoietic neoplasms. To identify novel genes involved in hematopoiesis, we performed an ethyl-nitrosourea mutagenesis screen in zebrafish (Danio rerio) to search for mutants with defective definitive hematopoiesis. We report the recovery and analysis of the grechetto mutant, which harbors an inactivating mutation in cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 1 (cpsf1), a gene ubiquitously expressed and required for 3′ untranslated region processing of a subset of pre-mRNAs. grechetto mutants undergo normal primitive hematopoiesis and specify appropriate numbers of definitive HSCs at 36 hours postfertilization. However, when HSCs migrate to the caudal hematopoietic tissue at 3 days postfertilization, their numbers start decreasing as a result of apoptotic cell death. Consistent with Cpsf1 function, c-myb:EGFP+ cells in grechetto mutants also show defective polyadenylation of snrnp70, a gene required for HSC development. By 5 days postfertilization, definitive hematopoiesis is compromised and severely decreased blood cell numbers are observed across the myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid cell lineages. These studies show that cpsf1 is essential for HSC survival and differentiation in caudal hematopoietic tissue.
Introduction
Hematopoiesis is a complex developmental process that results in the production of mature blood cells from HSCs and depends on the highly regulated activation of specific genetic programs.1 Analysis of critical genetic regulators of normal hematopoiesis has identified that constitutional or acquired inactivating mutations of such genes may contribute to bone marrow failure syndromes, myelodysplastic syndromes, and/or hematopoietic neoplasms.2-4 Despite advances in whole-genome analysis, the underlying genetic events that contribute to many hematopoietic disorders remain unclear, and innovative gene-discovery approaches are needed to deepen our understanding of hematopoietic development in order to design more effective and specific therapeutic approaches to treating hematopoietic diseases.
In recent years, the zebrafish (Danio rerio) has emerged as an excellent animal model system for studying the genetic pathways of vertebrate development.5 The combined genetic and embryologic advantages of the zebrafish are ideal for studying organogenesis and, in particular, hematopoiesis.6 Zebrafish and mammalian hematopoiesis are very comparable with respect to all cell lineages, and key genetic regulators have been conserved through evolution.7 The sequential waves of zebrafish hematopoietic cell development correspond well with the distinct waves of blood cell generation observed during mammalian embryogenesis.7 Embryonic hematopoiesis in the zebrafish is divided into 2 major waves that differ in the specific blood cell lineages that are formed. Primitive hematopoiesis is characterized by the generation of embryonic erythrocytes in the intermediate cell mass8 and a distinct population of primitive macrophages that arise from the anterior lateral plate mesoderm between 14 and 16 hours postfertilization (hpf).9 Studies in mutants lacking definitive hematopoiesis indicate that most primitive hematopoietic cells are gradually lost between 8 and 12 days postfertilization (dpf).10 Definitive hematopoiesis occurs in 2 phases: initially, transient erythromyeloid progenitors form in the caudal hematopoietic tissue (CHT) starting around 24 hpf,11 and by 30 hpf HSCs begin to form in the ventral wall of the dorsal aorta, a region corresponding to the mammalian aorta-gonad-mesonephros region.12 These HSCs then migrate to the CHT, and from there colonize the kidney—the adult hematopoietic organ—and the thymus.12 HSCs are the only cells capable of producing myeloid, erythroid, thrombocytic, and lymphoid cells,12 and it is believed that they are responsible for sustaining hematopoiesis throughout the adult life of the fish from the kidney marrow.
The zebrafish model system has many attributes that contribute to its utility in identifying genes required for hematopoiesis. A combination of small size, rapid embryonic development, fecundity, external fertilization, and optical transparency permit the conduct of large-scale, forward-genetic screens.13 The forward-genetic capacity of the zebrafish allows the unbiased identification of mutations based on abnormal hematopoietic phenotypes.13 Indeed, ethyl-nitrosourea (ENU) mutagenesis screens have thus far successfully identified a large number of zebrafish lines containing a wide range of mutations that affect different stages and cell lineages of embryonic hematopoiesis.14 The identification and characterization of the affected genes from such screens has led to their validation regarding conserved function in human hematopoiesis, as well as to the elucidation of novel processes and pathways involved in hematopoietic disease.15
In this report, we have used ENU-mutated zebrafish lines to screen for mutations that inactivate genes required for definitive hematopoiesis and report the analysis of the grechetto mutant phenotype, caused by an inactivating mutation of the cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 1 (cpsf1) gene.
Methods
Zebrafish maintenance and breeding
Wild-type (WT) AB and WIK stocks of D rerio; the transgenic lines Tg(pu.1:EGFP),16 Tg(c-myb:EGFP),17 Tg(gata1:DsRED),18 and Tg(cd41:EGFP)19 ; and the mutant line tp53zdf1/zdf1 (tp53M214K/M214K, referred in the text as p53m/m)20 were raised and kept under standard laboratory conditions at 28.5°C.21 Embryos were staged by somite number and fixed at specific hpf or dpf, as described by Kimmel et al.22 To better visualize internal structures in some experiments, embryos were incubated with 0.2mM 1-phenyl-2-thiourea (Sigma-Aldrich) to inhibit pigment formation.21 All animal protocols were approved by the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Animal Care and Use Committee.
Mutagenesis and screen design
Male zebrafish of the AB background were mutagenized and crossed with WT AB females. The efficiency of ENU mutagenesis was estimated by noncomplementation of the pigment-deficient indicator golden locus. Eggs were obtained by squeezing F1 heterozygous females and fertilized with UV-inactivated sperm. Second meiotic division was inhibited by the application of 562 kg/cm2 80 seconds after fertilization, as described previously.23 Pressure was maintained for 240 seconds and then slowly released.23 The resulting gynogenetic diploid embryos were then grown for 5 days and subjected to whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) using the pan-leukocyte peroxidase mpx probe. Positive hits were defined as embryos showing no mpx staining in the CHT and greater than 2-fold reduction in mpx-positive cells overall compared with their WT siblings. Positive F1 heterozygous females were then raised and out-crossed to AB WT. The resulting F2 progeny was then in-crossed to derive the recessive mutations to homozygosity and confirm the phenotype.
Mapping and molecular analysis of zdfl8a12
The zdfl8a12 (AB background) allele was mapped by out-crossing heterozygous AB fish into the polymorphic WT strain WIK, followed by in-breeding of the heterozygous progeny. We scanned the genome for linked simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) markers by bulk segregant analysis using standard methods.24,25 Once the mutation was placed between 2 flanking SSLP markers, fine-resolution mapping was achieved by testing other SSLP and then single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers (from 3′ untranslated regions [UTRs] or intronic gene regions) in 1590 individual mutant embryos. cDNA from candidate genes was then sequenced from pooled mutant RNA, and the candidate zdfl8a12 mutation was then confirmed by sequencing genomic DNA from the entire panel of recombinants. All primers used for the analysis are provided in supplemental Table 1 (available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). Genotyping data from all recombinants are provided in supplemental Table 2.
Morpholinos, microinjections, WISH, and cartilage staining
Morpholinos targeting cpsf1 5′UTR/ATG or the splice donor site of exon 9 and a control morpholino (a 5-bp mismatch ATG morpholino) were designed by Gene Tools. Sequences are provided in supplemental Table 3. The Cpsf1 e9i9 morpholino dose was titrated to the lowest dose resulting in 100% cpsf1 knock-down, and injected into 1-cell-stage embryos using a gas-driven microinjection apparatus through a glass micropipette. Efficacy of the cpsf1 e9i9 morpholino was evaluated using RT-PCR (primer sequences are provided in supplemental Table 4). Cpsf1 5′UTR/ATG morpholinos were injected at the highest tolerated dose, and their efficacy was evaluated at 5 dpf looking for a phenocopy of the grechetto phenotype.
Fluorescence analysis of zebrafish embryos and imaging
Whole-mount acridine orange staining, anti–green fluorescent protein (anti-GFP), and anti–activated caspase3 immunostaining were performed as described previously.28 Embryos were mounted in 1% low-melt agarose in coverslip-bottom dishes (MatTek). Confocal images were captured on a spinning disk confocal microscope (Yokogawa) using an Andor iXon DU-897 EM-CCD camera with a 20× Plan-Apo DIC NA 0.75 objective. Images were analyzed using Volocity software Version 5 (Perkin-Elmer).
For terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) analysis, zebrafish embryos were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in 5% sucrose/2% agar, sunk in 30% sucrose at 4°C, and cryo-sectioned at a 14-μm thickness. The TUNEL assay on cryosectioned samples was performed using the ApopTag Red In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit (Millipore) following the manufacturer's instructions. Rhodamine-conjugated anti-digoxigenin antibody was added to visualize TUNEL-positive cells.
Analysis and sorting of zebrafish cells by flow cytometry
For FACS analysis, the bodies and tails of Tg(c-myb:EGFP) embryos were dissociated in Liberase Blendzyme 3 (Roche) for 45 minutes at 32°C. The resulting cell suspension was passed through a 40μM filter, and washed 3 times in cold PBS before FACS analysis. c-myb:EGFP–positive cells were either analyzed or sorted from the 25% top Forward Scatter population, as described previously,12 using a FACSCanto II or a FACSAria sorter (BD Biosciences), respectively. The DNA content of sorted c-myb:EGFP cells was determined by hypotonic propidium iodide staining. Data were analyzed using FlowJo software Version 8.8.6 (TreeStar).
qRT-PCR assays
For quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR), total RNA from whole embryos was extracted with TRIzol (Invitrogen). cDNA was prepared with the SuperScript III First Strand Synthesis System for RT-PCR (Invitrogen) using oligo-dT primers. qRT-PCR was performed using the SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems). Gene expression changes were quantified as linear ratio to β-actin or as log2 ratio to ef1a. Oligonucleotide sequences are provided in supplemental Table 4.
Poly(A) tail assay
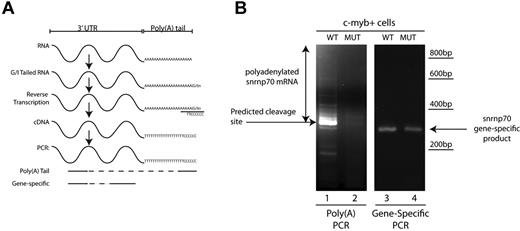
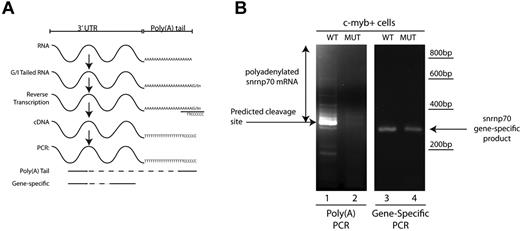
Analysis of poly(A) tail length was performed using the Poly(A) Tail-Length Assay Kit (USB Products/Affymetrix) following manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, 500 ng of total RNA was used in a G/I tailing reaction in which poly(A) polymerase adds a limited number of guanosine and inosine residues to the 3′ end of poly(A)–containing RNAs. After reverse transcription using the newly added G/I sites as priming sites, cDNAs of interest were probed with a gene-specific forward primer designed upstream of the polyadenylation site and a universal reverse primer that includes the poly(A) tail of the gene of interest (Figure 7A; primer sequences are provided in supplemental Table 4). To control for the presence of the transcript of interest, gene-specific primers were used in a one-step RT-PCT reaction (primer sequences are provided in supplemental Table 4).
Results
grechetto mutant isolation and characterization
To identify genes required for definitive hematopoiesis, we performed an early-pressure ENU-mutagenesis screen in which gynogenetic diploid offspring of heterozygous F1 females were assayed at 5 dpf. Embryos were analyzed with an antisense mpx WISH probe to detect abnormalities in myelopoiesis.
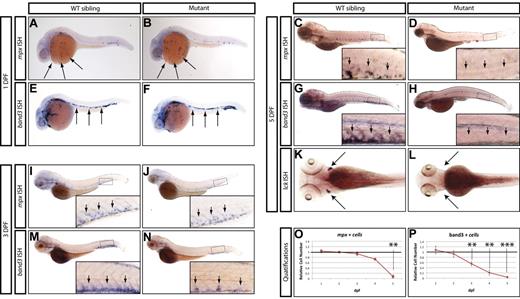
From this screen, we identified a mutant allele (zdfl8a12) in which mpx-positive cells were markedly reduced in the CHT at 5 dpf compared with their WT siblings (Figure 1C-D inset arrows), but normal in the anterior lateral plate mesoderm at 1 dpf (Figure 1A-B arrows). Similarly, erythroid cells stained by the band3 probe at 1 dpf were normally represented in the intermediate cell mass of mutants compared with their WT siblings (Figure 1E-F arrows), but markedly reduced by 5 dpf in the mutant CHT (Figure 1G-H inset arrows, quantified in 1O-P). At 3 dpf, an intermediate phenotype was observed in mutant CHT, which showed a reduced number of band3-positive cells relative to that of WT siblings, whereas mpx-positive cells still appeared normal (Figure 1 M-N and I-J, respectively, inset arrows). To assess whether lymphoid development was also affected, we examined the expression of the T-lymphocyte marker lck and found that the mutants lacked thymocytes at 5 dpf (Figure 1K-L arrows). We also extended our analysis to include other markers of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid differentiation, and found that at 5 dpf, mutants also lacked expression of the myeloid markers l-plastin and lysozyme-C (supplemental Figure 1A-D), the erythroid marker gata1 (supplemental Figure 1E-F), and the lymphoid marker rag1 (supplemental Figure 1G-H). These observations indicate that whereas this mutant exhibited normal primitive hematopoietic development, definitive hematopoiesis was severely affected and mutant embryos did not express markers of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid differentiation at 5 dpf. This recessive lethal mutation exhibited normal Mendelian inheritance and the phenotype was 100% penetrant in all backgrounds tested (AB and WIK). Because the mutation affects white blood cells in addition to RBCs, we followed the unofficial convention used to name zebrafish blood mutants and called this mutant grechetto, after an Italian white wine.
Hematopoietic phenotype of grechetto mutants. (A-D,I-J) WISH for mpx: lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. mpx expression is normal in the anterior lateral plate mesoderm of 1 dpf embryos (A-B arrows) and in the CHT of 3 dpf (I-J; CHT magnified in the inset and highlighted by arrows), but almost absent in the CHT of 5 dpf (C-D; CHT magnified in the inset and highlighted by arrows) grechetto mutants. (E-H,M-N) WISH for band3: lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. band3 expression is normal in the intermediate cell mass of 1 dpf embryos (E-F arrows), reduced in the CHT of 3 dpf (M-N; CHT magnified in the inset and highlighted by arrows), and almost absent in the CHT of 5 dpf (G-H; CHT magnified in the inset and highlighted by arrows) grechetto mutants. (K-L) WISH for lck: ventral view, anterior to the left. lck expression is lost in 5 dpf grechetto mutants (L). The bilateral zebrafish thymic region is indicated with arrows. (O-P) Quantification of the number of mpx-expressing cells (O) and band3-expressing cells (P), as counted in 15 WISH-stained embryos per condition. Cells were counted from the anterior lateral plate mesoderm (mpx) or intermediate cell mass (band3) of 1 and 2 dpf animals and from the CHT of 3, 4, and 5 dpf animals (1 and 2 dpf embryos were genotyped after counting to identify mutants). The number of cells in mutants was plotted as a ratio to the number of cells in WT siblings at the same stage normalized to 1. Error bars represent SEM. **P ≤ .005; ***P ≤ .0005 by Student t test.
Hematopoietic phenotype of grechetto mutants. (A-D,I-J) WISH for mpx: lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. mpx expression is normal in the anterior lateral plate mesoderm of 1 dpf embryos (A-B arrows) and in the CHT of 3 dpf (I-J; CHT magnified in the inset and highlighted by arrows), but almost absent in the CHT of 5 dpf (C-D; CHT magnified in the inset and highlighted by arrows) grechetto mutants. (E-H,M-N) WISH for band3: lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. band3 expression is normal in the intermediate cell mass of 1 dpf embryos (E-F arrows), reduced in the CHT of 3 dpf (M-N; CHT magnified in the inset and highlighted by arrows), and almost absent in the CHT of 5 dpf (G-H; CHT magnified in the inset and highlighted by arrows) grechetto mutants. (K-L) WISH for lck: ventral view, anterior to the left. lck expression is lost in 5 dpf grechetto mutants (L). The bilateral zebrafish thymic region is indicated with arrows. (O-P) Quantification of the number of mpx-expressing cells (O) and band3-expressing cells (P), as counted in 15 WISH-stained embryos per condition. Cells were counted from the anterior lateral plate mesoderm (mpx) or intermediate cell mass (band3) of 1 and 2 dpf animals and from the CHT of 3, 4, and 5 dpf animals (1 and 2 dpf embryos were genotyped after counting to identify mutants). The number of cells in mutants was plotted as a ratio to the number of cells in WT siblings at the same stage normalized to 1. Error bars represent SEM. **P ≤ .005; ***P ≤ .0005 by Student t test.
grechetto mutants exhibit a severe abnormal morphology by 5 dpf
grechetto mutants initially developed with normal circulating blood and were morphologically indistinguishable from WT siblings through 48 hpf. By 3 dpf, mutant animals had a slightly smaller head and lacked a protruding jaw. By 5 dpf, most mutants had curved bodies, cardiac edema, lacked an inflated swim bladder, and had significantly smaller heads and eyes relative to WT siblings (Figure 2A-B). grechetto mutants also showed smaller lateral fins (Figure 2C-D arrows) and pigment abnormalities, including reduced melanophores in the lateral stripe (Figure 2A-B) and aberrant melanophores in the dorsal stripe (Figure 2C-D, insets). Iridophore cell numbers were markedly decreased along the trunk and tail of the mutants (Figure 2E-F), whereas xanthophores appeared to develop normally. Alcian Blue staining at 5 dpf showed severe jaw defects in grechetto mutants (Figure 2G-J): the posterior ceratohyal and ceratobranchial cartilages failed to properly develop, whereas the more anterior ethmoidal, Meckel, and palatoquadrate cartilages were normal. Because of the severe heart edema observed in grechetto mutants, we examined the expression of the myocardial marker gata6 by WISH at 5 dpf and found it to be normal (supplemental Figure 1I-J arrows). Furthermore, the heart continued to beat normally at this time and circulation persisted. At the same time point, gata6 expression in the guts of grechetto mutants was reduced (supplemental Figure 1I-J asterisk), along with the expression of pdx1 in the same region (supplemental Figure 1K-L asterisk). However, pdx1 expression in the endocrine pancreas was normal in the mutants at 5 dpf (supplemental Figure 1K-L arrows), suggesting that the zdfl8a12 allele selectively affects specific tissues rather than causing global developmental defects. All grechetto mutants died by 6 dpf.
General developmental defects of grechetto mutants. (A-B) Live bright-field image of a 5 dpf WT sibling (A) and of a grechetto mutant (B). Lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. The mutant shows a curved body, cardiac edema, lack of an inflated swim bladder, smaller head and eyes, and reduced melanophores in the lateral stripes compared with the WT sibling. (C-F) Dorsal view, anterior to the left, of a 5 dpf WT sibling (C,E) and of a grechetto mutant (D,F) shown in transmitted light (C-D) or epi-illumination (E-F). grechetto mutants show smaller lateral fins (D arrows), aberrant melanophores (D insets), and markedly reduced iridophore cell numbers in the dorsal stripe (F) compared with their WT siblings. (G-J) Alcian Blue staining of the jaw cartilages of a 5 dpf WT sibling (G,I) and of a grechetto mutant (H,J) shown in lateral (G-H) or ventral (I-J) views. ch indicates ceratohyal; cb, ceratobranchial; eth, ethmoidal; Mk, Meckel; and qu, palatoquadrate. grechetto mutants show abnormal development of the posterior ceratohyal and ceratobranchial cartilages.
General developmental defects of grechetto mutants. (A-B) Live bright-field image of a 5 dpf WT sibling (A) and of a grechetto mutant (B). Lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. The mutant shows a curved body, cardiac edema, lack of an inflated swim bladder, smaller head and eyes, and reduced melanophores in the lateral stripes compared with the WT sibling. (C-F) Dorsal view, anterior to the left, of a 5 dpf WT sibling (C,E) and of a grechetto mutant (D,F) shown in transmitted light (C-D) or epi-illumination (E-F). grechetto mutants show smaller lateral fins (D arrows), aberrant melanophores (D insets), and markedly reduced iridophore cell numbers in the dorsal stripe (F) compared with their WT siblings. (G-J) Alcian Blue staining of the jaw cartilages of a 5 dpf WT sibling (G,I) and of a grechetto mutant (H,J) shown in lateral (G-H) or ventral (I-J) views. ch indicates ceratohyal; cb, ceratobranchial; eth, ethmoidal; Mk, Meckel; and qu, palatoquadrate. grechetto mutants show abnormal development of the posterior ceratohyal and ceratobranchial cartilages.
The zdfl8a12 mutation disrupts the cpsf1 gene
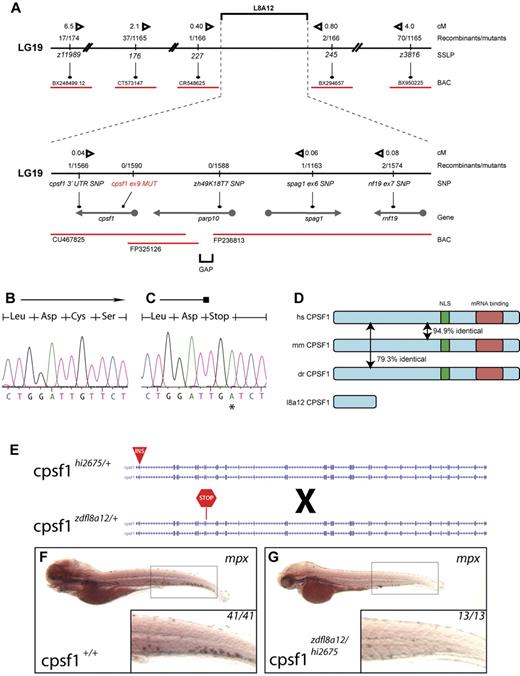
We identified the affected gene disrupted in grechetto by genetic mapping and molecular analysis of the zdfl8a12 mutation. Genetic mapping by bulk segregant analysis indicated that the zfdfl8a12 mutation was located on linkage group 19 between z11989 and z3816 (Figure 3A top). We established a fine map of the region by scoring other SSLP and SNP markers (from 3′UTRs and intronic gene regions) in the 1590 mutant embryo panel that we generated. Using this approach, we identified 2 linked SNP markers, one in parp10 (intron 1) and one in cpsf1 (3′UTR), for which we had 0 and 1 recombinants, respectively, in the mutant embryo panel (Figure 3A bottom). We analyzed these candidate genes by complete sequencing of their cDNA isolated by RT-PCR from WT and mutant 5 dpf zdfl8a12 animals. In mutant embryos, the parp10 cDNA contained no mutations, whereas the cpsf1 cDNA had a T → A base substitution at position 1140, leading to a premature stop of the protein sequence at codon 324 (Figure 3B-C). This result was substantiated by sequencing PCR products from genomic DNA derived from all recombinants in the original panel. All mutants carried the same mutation in exon 9 of the cpsf1 gene (Gene ID: 432372), whereas all homozygous WT siblings lacked this base change (supplemental Table 2).
Positional cloning of the zdfl8a12 allele. (A) Genetic map of the grechetto region on LG 19. Top panel shows low- and intermediate-resolution mapping carried out with SSLPs. Bottom panel shows fine mapping obtained by sequencing of intronic and 3′UTR SNPs. Solid black line indicates chromosome 19 (not in scale); red lines, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC); arrows, genes. The distance in centimorgans (cM) between markers was calculated assuming 1.5 recombination events per meiosis. (B-C) Chromatograms from cpsf1 cDNA sequencing of genotypic WT and mutant grechetto siblings, respectively, showing a T → A mutation in the latter resulting in a premature stop codon. (D) Identity at the protein level between the human (hs), mouse (mm), and zebrafish (dr) CPSF1 protein. The nuclear localization signal (NLS) is schematically represented by a green box and the putative RNA-binding domain by a red box. (E-G) Complementation experiment performed by crossing a cpsf1hi2675 heterozygous fish (carrying a viral insertion in exon 2 of the cpsf1 gene) with a cpsf1zdfl8a12 heterozygous fish (carrying a premature stop codon in exon 9 of the cpsf1 gene) depicted schematically in panel E. (F-G) WISH for mpx. All lateral views, anterior to the left, and dorsal upward, showed that the compound cpsf1zdfl8a12/hi2675 heterozygote offspring lacked myelopoiesis in the CHT at 5 dpf (compare the inset in panel G to a WT sibling in panel F), a typical feature of the grechetto phenotype.
Positional cloning of the zdfl8a12 allele. (A) Genetic map of the grechetto region on LG 19. Top panel shows low- and intermediate-resolution mapping carried out with SSLPs. Bottom panel shows fine mapping obtained by sequencing of intronic and 3′UTR SNPs. Solid black line indicates chromosome 19 (not in scale); red lines, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BAC); arrows, genes. The distance in centimorgans (cM) between markers was calculated assuming 1.5 recombination events per meiosis. (B-C) Chromatograms from cpsf1 cDNA sequencing of genotypic WT and mutant grechetto siblings, respectively, showing a T → A mutation in the latter resulting in a premature stop codon. (D) Identity at the protein level between the human (hs), mouse (mm), and zebrafish (dr) CPSF1 protein. The nuclear localization signal (NLS) is schematically represented by a green box and the putative RNA-binding domain by a red box. (E-G) Complementation experiment performed by crossing a cpsf1hi2675 heterozygous fish (carrying a viral insertion in exon 2 of the cpsf1 gene) with a cpsf1zdfl8a12 heterozygous fish (carrying a premature stop codon in exon 9 of the cpsf1 gene) depicted schematically in panel E. (F-G) WISH for mpx. All lateral views, anterior to the left, and dorsal upward, showed that the compound cpsf1zdfl8a12/hi2675 heterozygote offspring lacked myelopoiesis in the CHT at 5 dpf (compare the inset in panel G to a WT sibling in panel F), a typical feature of the grechetto phenotype.
The cpsf1 gene encodes a 1449–amino acid, 160-kD protein that is the largest component of the CPSF complex.29,30 As part of the CPSF complex, cpsf1 plays an essential role in determining the specificity and efficiency of the 3′-end processing of a subset of pre-mRNAs.29,30 Cpsf1 recognizes the canonical polyadenylation signal AAUAAA (or, less frequently, AUUAAA) and, by interacting with CstF-77, PAP, and RNA Pol II-CTD, facilitates both mRNA 3′UTR endonucleolytic cleavage and subsequent poly(A) tail addition.29,30 In zebrafish, the Cpsf1 protein is highly conserved with humans, sharing 79.3% amino acid identity (Figure 3D). Because the predicted Cpsf1 protein produced in the cpsf1zdfl8a12 mutants encodes a premature stop codon after amino acid 323, each of the known functional domains in the protein is predicted to be missing, including a bipartite nuclear localization signal (residues 891-912)30 and the putative RNA binding site at the C-terminus (Figure 3D; http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/IEntry?ac = IPR004871), indicating that cpsf1zdfl8a12 most likely represents a null allele of cpsf1.
Disruption of cpsf1 is responsible for the grechetto phenotype
To determine whether the disruption of the cpsf1 gene was responsible for the grechetto phenotype, we performed a complementation analysis by breeding cpsf1zdfl8a12 heterozygous fish with cpsf1hi2675 heterozygous fish (Figure 3E), which represent a known mutant cpsf1 zebrafish line that carries a viral insertion in cpsf1 exon 2 and thus is most likely a functional null (a kind gift from N. Hopkins and A. Amsterdam).31 The compound cpsf1zdfl8a12/hi2675 heterozygote offspring had a similar phenotype to grechetto mutants at 5 dpf and lacked mpx expression in the CHT, as shown by WISH staining (Figure 3F-G), as well as the same characteristic developmental defects seen in grechetto mutants: curved bodies, a smaller head and eyes, cardiac edema, no swim bladder, abnormal jaws (supplemental Figure 2A), and defects in pigment and iridophore development (supplemental Figure 2B-C, quantified in D-E). The lack of complementation of the grechetto phenotype with the cpsf1hi2675 allele therefore suggests that it results from the homozygous disruption of the cpsf1 gene.
To provide additional evidence that inactivating mutations in the cpsf1 gene specifically cause the grechetto phenotype, we injected one-cell-stage embryos with a splice-blocking morpholino directed against the splice donor site of cpsf1 exon 9, which is where the zdfl8a12 mutation was mapped. To obviate nonspecific p53-dependent morpholino toxicity, we injected p53m/m embryos.32 To assess morpholino function, we performed RT-PCR using primers that amplify over the splice site and observed an aberrant cpsf1 transcript that contained an early stop codon encoded by the retained intron 9 (supplemental Figure 2F). Injection of the morpholino resulted in a loss of mpx expression at 5 dpf in cpsf1 morphants compared with control morpholino-injected embryos (supplemental Figure 2G-H). Moreover, cpsf1 morphants showed all of the same morphologic defects seen in grechetto mutants (supplemental Figure 2I-P) compared with control morpholino-injected embryos, indicating that the grechetto phenotype is p53 independent. In conclusion, data from the complementation experiment and from the morpholino-mediated knock-down show that cpsf1 inactivation can recapitulate all of the features of the grechetto phenotype. This strongly suggests that the cpsf1 exon 9 mutation is responsible for the grechetto phenotype.
cpsf1 is expressed throughout embryonic development
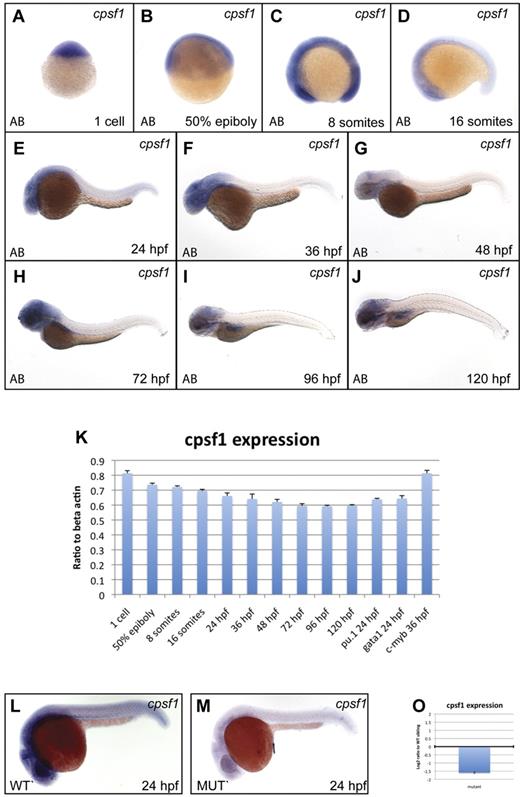
To assess normal cpsf1 expression in embryos, we performed qRT-PCR and WISH experiments (primers are provided in supplemental Table 4). Cpsf1 was maternally provided in 1-cell-stage embryos (Figure 4A and 4K) and was ubiquitously expressed through the 16-somite stage (Figure 4B-D). Subsequently, cpsf1 expression was reduced in the trunk and tail tissue, but remained relatively high in the more anterior parts of the embryo. By 24 hpf, cpsf1 expression was strongest in the developing brain, eye, and anterior nervous system (Figure 4E). This pattern of cpsf1 expression persisted through 36-48 hpf (Figure 4F-G), except that it became more clearly visible in the developing lateral fin buds. Between 72 and 120 hpf, cpsf1 expression remained strongest in the brain, the pharyngeal arches of the jaw, and the developing gut (Figure 4H-J). We also confirmed the expression of cpsf1 in developing hematopoietic tissue by qRT-PCR on isolated primitive myeloid and erythroid cells and definitive HSCs that were FACS-sorted from the hematopoietic lineage-specific fluorescent reporter transgenic lines Tg(pu.1:EGFP), Tg (gata1:DsRed), and Tg(c-myb:EGFP), respectively (Figure 4K).
cpsf1 expression in normal embryos and grechetto mutants. (A-J) Lateral views of normal AB zebrafish embryos stained with a cpsf1 WISH probe at the 1-cell stage (A), 50% epiboly (B), 8 somites (C), 16 somites (D), 24 hpf (E), 36 hpf (F), 48 hpf (G), 72 hpf (H), 96 hpf (I), and 120 hpf (J). (K) qRT-PCR in cDNA from embryos at the same stages as in panels A through J showing expression levels of cpsf1 as a linear ratio to β-actin expression at each stage. In the 3 right columns, cpsf1 expression was probed in pu.1:EGFP- and gata1:DsRed–sorted cells from 24 hpf embryos and in c-myb:EGFP cells sorted at 36 hpf, demonstrating expression in the developing primitive and definitive hematopoietic system. Bars represent the average of triplicate runs and error bars represent SEM. (L-M) Lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal upward of WISH staining for cpsf1 in 24 hpf genotyped grechetto mutants (M) and WT siblings (L) showing decreased expression in the former. (O) qRT-PCR for cpsf1 expression in mutants compared with their WT siblings at 72 hpf is shown in a log2 y-axis normalized for ef1a expression.
cpsf1 expression in normal embryos and grechetto mutants. (A-J) Lateral views of normal AB zebrafish embryos stained with a cpsf1 WISH probe at the 1-cell stage (A), 50% epiboly (B), 8 somites (C), 16 somites (D), 24 hpf (E), 36 hpf (F), 48 hpf (G), 72 hpf (H), 96 hpf (I), and 120 hpf (J). (K) qRT-PCR in cDNA from embryos at the same stages as in panels A through J showing expression levels of cpsf1 as a linear ratio to β-actin expression at each stage. In the 3 right columns, cpsf1 expression was probed in pu.1:EGFP- and gata1:DsRed–sorted cells from 24 hpf embryos and in c-myb:EGFP cells sorted at 36 hpf, demonstrating expression in the developing primitive and definitive hematopoietic system. Bars represent the average of triplicate runs and error bars represent SEM. (L-M) Lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal upward of WISH staining for cpsf1 in 24 hpf genotyped grechetto mutants (M) and WT siblings (L) showing decreased expression in the former. (O) qRT-PCR for cpsf1 expression in mutants compared with their WT siblings at 72 hpf is shown in a log2 y-axis normalized for ef1a expression.
To determine whether the zdfl8a12 mutation affects its own mRNA expression, we performed WISH in 24 hpf genotyped grechetto mutants and WT siblings with an cpsf1 antisense probe (Figure 4L-M). We found that cpsf1 mRNA levels were severely decreased in grechetto mutants, likely because of missense-mediated RNA decay, and that maternally provided cpsf1 mRNA was no longer present in grechetto embryos by 24 hpf. Furthermore, we investigated cpsf1 expression levels by qRT-PCR in grechetto mutants relative to WT siblings at 3 dpf, when the mutant embryos first become morphologically distinguishable. Again, cpsf1 RNA levels were markedly reduced in mutants compared with their WT siblings (Figure 4O).
Neural crest development and survival are affected in grechetto mutants
Because many of the affected tissues in grechetto mutants at 5 dpf are derived or receive cellular contributions from the neural crest, we analyzed the effects of cpsf1 loss on neural crest development in grechetto mutants using WISH. Analysis of foxd3 expression at the 3-, 10-, and 13-somite stage indicated that neural crest induction occurred normally in grechetto mutants (supplemental Figure 3C-D and data not shown).33 sox10 expression, which is required for specification of pigment cells and other nonectomesenchymal neural crest derivatives,34 was slightly reduced at the 13-somite stage (supplemental Figure 3A-B arrows). In addition, dlx2 expression35 was slightly reduced in the migrating neural crest cells that contribute to the pharyngeal arches at 36 hpf (supplemental Figure 3G-H arrows). Expression of other neural crest genes, such as the pan-neural crest marker crestin at 24 hpf36 (supplemental Figure 3E-F) or pax9a at 48 hpf,37 appeared normal (supplemental Figure 3I-J). These results suggest that cpsf1 loss only causes mild defects in neural crest specification and migration. We then assayed for cell death by staining grechetto mutants and WT siblings with acridine orange. Starting at 3 dpf, grechetto mutants showed increased numbers of acridine-orange–positive cells in the developing jaw (supplemental Figure 3K-L arrows), which peaked at 4 dpf (supplemental Figure 3M-N arrows) and were still visible at 5 dpf (supplemental Figure 3O-P arrows). We next asked whether the observed cell death could be ascribed to apoptosis, and therefore stained 4 dpf embryos for activated caspase3. Single-slice confocal images of ventral views of the head of 4 dpf grechetto mutants showed the presence of apoptotic cells in the jaw region that were not found in their WT siblings (supplemental Figure 4A,C), and lateral views of the head not only confirmed apoptosis in the jaw region, but also showed apoptosis in the brain and in the eyes (supplemental Figures 4B,D arrow, star, and arrowhead, respectively). We then analyzed the extent of apoptosis in the whole embryo. Epifluorescence pictures of lateral (supplemental Figure 4E-F), ventral (supplemental Figure 4E-F insets), and dorsal (supplemental Figure 4G-H) views of whole embryos confirmed the apoptotic phenotype in the head, and also unveiled apoptosis in the gut (supplemental Figures 4F,H arrows) of grechetto mutants. These data show that the defects observed in neural crest–derived tissues in grechetto mutants do not result from aberrant specification, migration, or differentiation of neural crest cell progenitors, but rather from apoptotic cell death in several tissues that receive cellular contributions from the neural crest.
cpsf1 is required for HSC survival
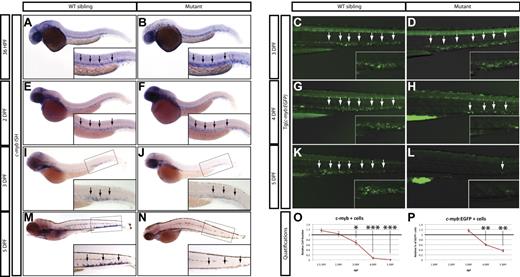
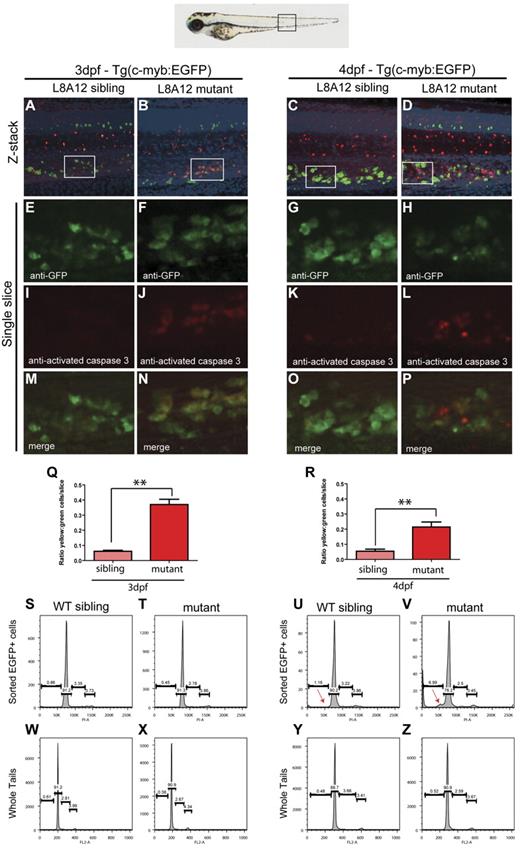
Because the expression of myeloid, erythroid, and lymphoid markers is lost in grechetto mutants at 5 dpf, we investigated whether definitive HSCs form by assaying c-myb expression. At 36 hpf, c-myb–positive HSCs were properly specified and correctly localized in the ventral wall of the aortas of grechetto mutants (Figure 5A-B arrows, quantified in 5O). Their numbers were still normal at 48 hpf compared with their WT siblings (arrows in Figure 5E-F, quantified in 5O). However, by 3 dpf, on migration to the CHT, the number of HSCs was decreased in the mutants (Figure 5 I-J arrows, quantified in 5O). At 5 dpf, virtually no c-myb–positive cells were detectable in the mutants (Figure 5M-N arrows, quantified in 5O) by WISH analysis. To confirm these observations, we crossed the cpsf1zdfl8a12 mutant with the reporter lines Tg(cd41:EGFP) and Tg(c-myb:EGFP) to visualize HSCs in vivo by their expression of enhanced GFP (EGFP). In Tg(cd41:EGFP) embryos, low levels of GFP in the CHT identifies hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.12 At 3 dpf, the number of stationary GFPlow cells in the CHT of grechetto mutants was lower than WT siblings (supplemental Figure 5A-B arrows, quantified in G), and this difference increased at 4 and 5 dpf, when virtually no GFPlow cells were visible in the mutants (supplemental Figure 5C-F arrows, quantified in G). We next turned our attention to the Tg(c-myb:EGFP) line. At 3 dpf, the number of EGFP+ cells was normal in mutants compared with their WT siblings (Figure 5C-D arrows); however, decreased numbers of HSCs were observed starting at 4 dpf (Figure 5G-H and 5K-L arrows, quantified in 5P). Therefore, to investigate the fate of HSCs on cpsf1 loss and to determine whether properly formed HSCs undergo apoptosis similarly to neural-crest–derived tissues, we used the Tg(c-myb:EGFP);cpsf1zdfl8a12 line. Whole-mount double immunostainings using anti-GFP (in green) and anti–activated caspase3 (in red) were performed to assay for apoptotic c-myb–positive HSCs. At 3 dpf, grechetto mutants showed normal numbers of c-myb:EGFP+ HSCs in the CHT compared with their WT siblings (Figure 6A-B and 6E-F). However, more than one-third of these cells also expressed cleaved caspase3, exhibiting a 6-fold increase in apoptotic HSCs relative to their WT siblings (Figure 6I-J and 6M-N, quantified in 6Q). We also examined cross-sections of Tg(c-myb:EGFP);cpsf1zdfl8a12 animals and stained for TUNEL to confirm that grechetto mutants did indeed possess increased numbers of TUNEL+/EGFP+ HSCs compared with their WT siblings (supplemental Figure 6A-H). By 4 dpf, grechetto mutants expressed fewer EGFP+ cells compared with their WT siblings (Figure 6C-D and 6G-H). Nonetheless, apoptotic HSCs expressing activated caspase3 were again more prevalent in mutants relative to their WT siblings (Figure 6K-L and 6O-P, quantified in 6R). At 4 dpf, many cells were positive for activated caspase3 but not for EGFP (Figure 6P). These cells may represent HSCs at a more advanced stage of apoptosis, when the degradation of cellular proteins could result in the loss of EGFP expression. This hypothesis is supported by the observed increase in nuclear versus cytoplasmically localized activated caspase3 and pyknotic nuclei in HSCs at 4 dpf (Figure 6L).38 Cell-cycle analysis of sorted c-myb:EGFP cells confirmed these findings by revealing the presence of a sub-G1 apoptotic peak in the cell-cycle profiles of HSCs sorted from 4 dpf (Figure 6U-V arrow). Interestingly, propidium iodide cell-cycle analysis at 3 dpf in sorted c-myb:EGFP cells (Figure 6S-T) and in 3 or 4 dpf whole tails (Figure 6W-Z) from grechetto mutants and WT siblings showed no alterations in the cell-cycle profile.
Loss of HSCs in grechetto mutants. (A-B,E-F,I-J,M-N) WISH for c-myb in 36 hpf (A-B), 2 dpf (E-F), 3 dpf (I-J), 5 dpf (M-N) grechetto mutants (B,F,J,N), and their WT siblings (A,E,I,M). Lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. grechetto mutants specify normal numbers of c-myb–positive HSCs at 36 and 2 dpf (B,F), but this number decreases by 3 dpf (J), and c-myb–positive cells were almost undetectable at 5 dpf (N) compared with their WT siblings. Arrows in panels A and B and E and F indicate the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region. Arrows in panels I and J and M and N indicate the CHT. (C-D,G-H,K-L) Anti-GFP whole-mount immunostaining of the body region (CHT magnified in the inset) of cpsf1zdfl8a12;Tg(c-myb:EGFP) embryos at 3 dpf (C-D) and 4 dpf (G-H), and 5 dpf (K-L) grechetto mutants (D,H,L) and their WT siblings (C,G,K). Lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. EGFP+ cells are normally represented at 3 dpf (D) but decrease at 4 dpf (H) and are almost undetectable at 5 dpf (L) compared with their WT siblings. (O-P) quantifications of the experiments in panels A through N. (O) c-myb–positive cells as counted in 15 WT and mutant WISH-stained embryos. Cells were counted from the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region of 36 and 2 dpf animals and from the CHT of 3, 4, and 5 dpf animals (36 and 2 dpf embryos were genotyped after counting to identify mutants). The number of cells in mutants was plotted as a ratio to the number of cells in WT siblings at the same stage normalized to 1. (P) Percentage of GFP+ cells in single-cell suspensions from the dissected tails of cpsf1zdfl8a12;Tg(c-myb:EGFP) embryos at 3, 4, and 5 dpf plotted as a ratio to the percentage of cells in WT siblings at the same stage normalized to 1. Error bars represent SEM. *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .005; ***P ≤ .0005 by Student t test.
Loss of HSCs in grechetto mutants. (A-B,E-F,I-J,M-N) WISH for c-myb in 36 hpf (A-B), 2 dpf (E-F), 3 dpf (I-J), 5 dpf (M-N) grechetto mutants (B,F,J,N), and their WT siblings (A,E,I,M). Lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. grechetto mutants specify normal numbers of c-myb–positive HSCs at 36 and 2 dpf (B,F), but this number decreases by 3 dpf (J), and c-myb–positive cells were almost undetectable at 5 dpf (N) compared with their WT siblings. Arrows in panels A and B and E and F indicate the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region. Arrows in panels I and J and M and N indicate the CHT. (C-D,G-H,K-L) Anti-GFP whole-mount immunostaining of the body region (CHT magnified in the inset) of cpsf1zdfl8a12;Tg(c-myb:EGFP) embryos at 3 dpf (C-D) and 4 dpf (G-H), and 5 dpf (K-L) grechetto mutants (D,H,L) and their WT siblings (C,G,K). Lateral view, anterior to the left, dorsal upward. EGFP+ cells are normally represented at 3 dpf (D) but decrease at 4 dpf (H) and are almost undetectable at 5 dpf (L) compared with their WT siblings. (O-P) quantifications of the experiments in panels A through N. (O) c-myb–positive cells as counted in 15 WT and mutant WISH-stained embryos. Cells were counted from the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region of 36 and 2 dpf animals and from the CHT of 3, 4, and 5 dpf animals (36 and 2 dpf embryos were genotyped after counting to identify mutants). The number of cells in mutants was plotted as a ratio to the number of cells in WT siblings at the same stage normalized to 1. (P) Percentage of GFP+ cells in single-cell suspensions from the dissected tails of cpsf1zdfl8a12;Tg(c-myb:EGFP) embryos at 3, 4, and 5 dpf plotted as a ratio to the percentage of cells in WT siblings at the same stage normalized to 1. Error bars represent SEM. *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .005; ***P ≤ .0005 by Student t test.
HSCs undergo apoptotic cell death in grechetto mutants. (A-P) Confocal microscope images of anti-GFP (in green) and anti–activated caspase3 (in red) double whole-mount immunostaining of the CHT in 3 dpf (A-B,E-F,I-J,M-N) and 4 dpf (C-D,G-H,K-L,O-P) WT siblings (A,E,I,M,C,G,K,O) or grechetto mutant (B,F,J,N,D,H,L,P) cpsf1zdfl8a12;Tg(c-myb:EGFP) embryos. (A-D) Merged green/red/4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, dihydrochloride/bright-field extended focus images (20×). (E-H) Single-slice images of cells expressing EGFP under the control of the c-myb promoter: grechetto mutants show a normal number of EGFP+ cells at 3 dpf (F) compared with their WT siblings (E), but reduced numbers at 4 dpf (G-H). (I-L) Single-slice images of cells expressing activated caspase3, labeled in red, showing increased numbers in grechetto mutants compared with their WT siblings both at 3 dpf (J) and 4 dpf (L). (M-P) Merged single-slice images of cells expressing EGFP and activated caspase3 show that more EGFP+ cells undergo apoptosis in grechetto mutants compared with their WT siblings both at 3 dpf (N) and 4 dpf (P). (Q-R) Quantification of the experiments in panels A through P performed by plotting the ratio of EGFP+ cells that express activated caspase3 to the total number of EGFP+ cells at 3 dpf (Q) and 4 (R) dpf. Error bars represent SEM. **P ≤ .005 by Student t test. Cells were counted from 4 single slices from 3 embryos per condition. (S-Z) Propidium iodide cell-cycle analysis of sorted EGFP+ cells (S-V) or whole tails (W-Z) in 3 dpf (S-T,W-X) or 4 dpf (U-V,Y-Z) cpsf1zdfl8a12;Tg(c-myb:EGFP), WT (S,W,U,Y), or mutant (T,X,V,Z) embryos. Whereas the cell-cycle profile of sorted EGFP+ cells at 3 dpf is not different between WT siblings and mutant embryos (S-T), grechetto mutants at 4 dpf show a sub-G1 apoptotic peak not present in WT siblings (red arrows in U-V). The cell-cycle profile of whole tails shows no difference between mutants and WT siblings at 3 dpf (W-X) and 4 dpf (Y-Z).
HSCs undergo apoptotic cell death in grechetto mutants. (A-P) Confocal microscope images of anti-GFP (in green) and anti–activated caspase3 (in red) double whole-mount immunostaining of the CHT in 3 dpf (A-B,E-F,I-J,M-N) and 4 dpf (C-D,G-H,K-L,O-P) WT siblings (A,E,I,M,C,G,K,O) or grechetto mutant (B,F,J,N,D,H,L,P) cpsf1zdfl8a12;Tg(c-myb:EGFP) embryos. (A-D) Merged green/red/4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, dihydrochloride/bright-field extended focus images (20×). (E-H) Single-slice images of cells expressing EGFP under the control of the c-myb promoter: grechetto mutants show a normal number of EGFP+ cells at 3 dpf (F) compared with their WT siblings (E), but reduced numbers at 4 dpf (G-H). (I-L) Single-slice images of cells expressing activated caspase3, labeled in red, showing increased numbers in grechetto mutants compared with their WT siblings both at 3 dpf (J) and 4 dpf (L). (M-P) Merged single-slice images of cells expressing EGFP and activated caspase3 show that more EGFP+ cells undergo apoptosis in grechetto mutants compared with their WT siblings both at 3 dpf (N) and 4 dpf (P). (Q-R) Quantification of the experiments in panels A through P performed by plotting the ratio of EGFP+ cells that express activated caspase3 to the total number of EGFP+ cells at 3 dpf (Q) and 4 (R) dpf. Error bars represent SEM. **P ≤ .005 by Student t test. Cells were counted from 4 single slices from 3 embryos per condition. (S-Z) Propidium iodide cell-cycle analysis of sorted EGFP+ cells (S-V) or whole tails (W-Z) in 3 dpf (S-T,W-X) or 4 dpf (U-V,Y-Z) cpsf1zdfl8a12;Tg(c-myb:EGFP), WT (S,W,U,Y), or mutant (T,X,V,Z) embryos. Whereas the cell-cycle profile of sorted EGFP+ cells at 3 dpf is not different between WT siblings and mutant embryos (S-T), grechetto mutants at 4 dpf show a sub-G1 apoptotic peak not present in WT siblings (red arrows in U-V). The cell-cycle profile of whole tails shows no difference between mutants and WT siblings at 3 dpf (W-X) and 4 dpf (Y-Z).
c-myb:EGFP+ cells show defective polyadenylation of snrnp70 in grechetto mutants
Because Cpsf1 loss is likely to disrupt the polyadenylation of a subset of RNAs in grechetto mutants, we investigated the effectiveness of polyadenylation of mature RNA transcripts of snrnp70 (also known as the U1 small ribonuclear protein), a gene that contains the canonical polyadenylation signal in the 3′ UTR and is known to be required for the control of HSC development.39 Using mRNA from sorted 3 dpf c-myb:EGFP+ cells, we investigated whether we could show a defective poly(A) tail in snrnp70 mRNA using a poly(A) tail-length assay, which is illustrated diagrammatically in Figure 7A. Interestingly, we found that snrnp70 showed an almost complete loss of its poly(A) tail in RNA from cpsf1 mutants compared with WT embryos (Figure 7B compare lanes 1 and 2). As a control, gene-specific primers confirmed the presence of snrnp70 RNA in c-myb:EGFP+ cells from both grechetto animals and their WT siblings (Figure 7B compare lanes 3 and 4). Therefore, the lack of a snrnp70 poly(A) tail in HSCs provides a readout of functional consequences of the cpsf1 mutation in grechetto mutants.
c-myb:EGFP+ cells show defective polyadenylation of snrnp70 in grechetto mutants. (A) Schematic representation of the poly(A) length assay, described in “Poly(A) tail assay.” (B) Poly(A) length assay for snrnp70 in c-myb:EGFP+–sorted cells from grechetto mutants (lane 2) or WT siblings (lane 1) shows defective polyadenylation of the transcript in the mutants. Control gene-specific RT-PCR showed the presence of the snrnp70 transcript in both grechetto mutants (lane 4) and WT siblings (lane 3).
c-myb:EGFP+ cells show defective polyadenylation of snrnp70 in grechetto mutants. (A) Schematic representation of the poly(A) length assay, described in “Poly(A) tail assay.” (B) Poly(A) length assay for snrnp70 in c-myb:EGFP+–sorted cells from grechetto mutants (lane 2) or WT siblings (lane 1) shows defective polyadenylation of the transcript in the mutants. Control gene-specific RT-PCR showed the presence of the snrnp70 transcript in both grechetto mutants (lane 4) and WT siblings (lane 3).
Discussion
In the present study, we describe a grechetto mutant derived from an early-pressure ENU mutagenesis screen in zebrafish that inactivates the cpsf1 gene, and show that this gene is required for HSC survival.
Cpsf1 is a protein involved in the 3′UTR processing of a subset of pre-mRNAs, where it binds to the polyadenylation signal and mediates 3′UTR cleavage and poly(A) tail addition.29,30 We show here that primitive hematopoiesis and the specification of definitive HSCs in the ventral wall of the aorta are normal in grechetto mutants. The grechetto mutant phenotype, including craniofacial abnormalities and the loss of HSCs in the CHT, appears first at 3 dpf and progresses until the death of the embryo at 5-6 dpf. This is somewhat surprising given the ubiquitous expression of Cpsf1 and its role in cleavage and polyadenylation of the 3′UTR of a large subset of the RNAs that are transcribed.29,30 We cannot conclude, however, that Cpsf1 is dispensable for primitive hematopoiesis or for the specification of definitive HSCs, because it is possible that maternally provided Cpsf1 protein could support development in grechetto mutants up to 3 dpf. Unfortunately, we were unable to obtain antibodies that recognize zebrafish Cpsf1 or to identify 5′UTR/ATG morpholinos that showed specific activity, so we were not able to exclude this possibility.
Activation of caspase3 and TUNEL positivity imply apoptosis as the cause of HSC loss in grechetto mutants at 3 dpf. Interestingly, other studies have shown apoptotic death of hematopoietic cells depleted of proteins involved in pre-mRNA processing40 or transcription,41 suggesting that cell death pathways are activated when RNA maturation/transcription is impaired. Furthermore, evidence that inactivation of a ubiquitous protein can produce defects in hematopoietic cells has been previously reported: loss of the ubiquitous mitochondrial protein Hspa9b results in ineffective hematopoiesis and apoptosis of HSCs in zebrafish,42 and morpholino knock-down of the ubiquitous ribosomal protein Rps19 result in selective loss of RBCs.43 Moreover, a recent report has shown that the inactivation of Tif1γ, a ubiquitous protein involved in mRNA transcription, causes specific defects in erythropoiesis through its interaction with hematopoietic-specific transcription complexes.44 In grechetto mutants, several possibilities could underlie the causal relationship between ubiquitous loss of cpsf1 and the rather specific requirement for Cpsf1 to promote HSC survival. First, HSCs and other differentiating tissues could require higher levels of Cpsf1, and thus the consequences of its loss could be more marked in such tissues. Second, redundancy for a role of CPSF1 in polyadenylation could exist in some tissues, but could be absent in HSC. Third, cpsf1 cofactors or targets with tissue-restricted expression could determine this phenotype. In Figure 7, we show that polyadenylation of snrnp70, a splicing factor required for HSC development, was defective in HSCs from grechetto mutants but not in those from their WT siblings, providing a functional readout for the loss of Cpsf1 activity in HSCs and suggesting that the loss of functional Snrnp70 may be one of the factors that explains HSC apoptosis in mutant animals. grechetto mutants therefore provide additional evidence that pre-mRNA processing is a key process in HSC specification and survival, because HSCs are exquisitely sensitive to its disruption. Consistent with this idea, defects of mRNA processing are found to be implicated in an increasing number of human hematopoietic diseases.45
Despite exhibiting a distinct hematopoietic phenotype, grechetto mutants suffer from other developmental defects that also arise starting at 3 dpf and together result in embryonic lethality by 6 dpf. Intriguingly, most of such developmental defects observed in grechetto mutants represent defects in tissues derived from the neural crest. In grechetto mutants, neural crest cells that give rise to the branchial arches exhibit normal specification, migration, and initial differentiation before undergoing apoptosis at later stages, paralleling the effects seen in HSCs. Therefore, our analysis of the cellular pathways impaired by cpsf1 inactivation implicate this gene in the maintenance and survival of key cell lineages, including normal HSCs and a subset of the diverse neural crest–derived lineages.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We thank Adam Amsterdam and Nancy Hopkins for kindly providing the hi2675 zebrafish line.
This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health (grant R01 CA93152 to A.T.L.); by a Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Special Fellow Award (to N.B.); by Leukaemia & Lymphoma Research, United Kingdom (to E.M.P.); and by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health (award R00 NS058608 to R.A.S.).
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: N.B. designed the project, planned and performed experiments, and wrote the paper; E.M.P. and R.A.S. planned and performed experiments; J.R. designed the project and planned and performed experiments; E.G., A.B.J., F.G., J.-S.L., and A.T.C. performed experiments; and J.P.K., Y.Z., L.I.Z., and A.T.L. designed and supervised the project.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: L.I.Z. is a founder and stock holder of Fate Inc and a scientific advisor for Stemgent. The remaining authors declare no other competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Niccolò Bolli or A. Thomas Look, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Mayer Bldg, Rm M630, 450 Brookline Ave, Boston MA 02115; e-mail niccolo_bolli@dfci.harvard.edu or thomas_look@dfci.harvard.edu.