Abstract
Pleiotrophin (Ptn) is strongly expressed by stromal cells which maintain HSCs. However, in vivo, Ptn deficiency does not alter steady-state hematopoiesis. However, knockdown of Ptn (PtnKD) in stromal cells increases production of hematopoietic progenitors as well as HSC activity in cocultures, suggesting that Ptn may have a role in HSC activation. Indeed, transplantations of wild-type (Ptn+/+) HSCs into Ptn−/− mice show increased donor cell production in serial transplantations and dominant myeloid regeneration caused by Ptn-dependent regulation of HSC repopulation behavior. This regulation of Lin−Kit+Sca1+ function is associated with increased proliferation and, on a molecular level, with up-regulated expression of cyclin D1 (Ccnd1) and C/EBPα (Cepba), but reduced of PPARγ. The known HSC regulator β-catenin is, however, not altered in the absence of Ptn. In conclusion, our results point to different Ptn-mediated regulatory mechanisms in normal hemostasis and in hematopoietic regeneration and in maintaining the balance of myeloid and lymphoid regeneration. Moreover, our results support the idea that microenvironmental Ptn regulates hematopoietic regeneration through β-catenin–independent regulation of Ccnd1 and Cebpa.
Introduction
All mature blood cells derive from HSCs. These HSCs have been shown to reside mainly in specialized microenvironments, referred to as niches. It is thought that the niche regulates HSC quiescence (dormancy), self-renewal, and differentiation by expression of surface molecules and secretion of soluble factors. Which signals are provided by the niche and how exactly these signals affect HSCs still remains uncertain.1
We have established a number of stromal cell clones from mid gestation embryonic sources, of which we identified 2 cell lines (EL08-1D2 and UG26-1B6) which maintain fetal as well as adult HSCs, even though they had no direct contact with the hematopoietic cells (noncontact cocultures).2,3 In gene expression studies, we observed that, in comparison to a number of nonsupporting stromal cell lines, those 2 cell lines both expressed larger amounts of mRNA corresponding to a number of secreted molecules. We recently described that one of these factors, secreted frizzled-related protein 1, is required for sustained self-renewal of HSCs in vivo and that this was because of extrinsic regulation of HSCs by the microenvironment, most probably, through regulating β-catenin (Ctnnb1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (Pparg), both mediators of the Wnt signaling pathways.4 One other overrepresented factor was the pleiotrophic cytokine pleiotrophin (Ptn).3 Ptn was also found to be overexpressed by other HSC supportive cells, such as human brain endothelial cells5,6 or the stromal cell line AFT024,7 suggesting that high expression of Ptn may be a common feature among HSC-supportive stromal cells.
Ptn, because of its pleiotrophic activities, is known under many alternative names, including heparin-binding growth-associated molecule and osteoblast-stimulating factor. Ptn is a highly conserved 17-kDa cytokine,8 which, together with Midkine, forms a small family of low molecular weight factors.9 Several receptors are known to bind Ptn as a ligand: receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase β/ζ (Rptpz1),10 nucleolin,11 and N-syndecan.12 It was recently shown that Rptpz1 is expressed on BM-derived lineage− Ly6a+ Kit+ (LSK) cells.6 Binding of Ptn to RPTPβ/ζ inactivates the phosphatase domain through dimerization of the receptor. This leads to an increasing phosphorylation status of the numerous targets of RPTPβ/ζ, including β-catenin, ALK, β-adducin, CD81, c-Fyn, and others.10,13 The effects of Ptn on proliferation and differentiation appear to converge in β-catenin and its downstream factor Dlk1.10,14 Interestingly, Dlk1 has previously been identified to be overrepresented in the Ptn-overexpressing HSC-maintaining cell line AFT024 and to promote cobblestone area formation by HSC-derived progeny.15 Because it was shown that Rptpz1 is expressed on BM-derived LSK cells,6 these pathways may well be relevant in HSC regulation.
Ptn is known to play important roles in proliferation and differentiation in various cell types. It was shown that Ptn is mitogenic for fibroblasts, epithelial, and endothelial cells.16 Ptn leads to an increased expansion and differentiation of human osteoprogenitor cells.17 A similar effect was found in murine osteoprogenitors, but only with low concentrations of Ptn; higher concentrations showed no effect.18 In human embryonic stem cells, the addition of Ptn induces increased clonal growth, without differentiation.19 In neural stem cells, however, Ptn lead to an decreased proliferation and an increase of differentiation of these cells.20 Recently, it was shown that Ptn also affects cellular proliferation of HSCs. Although Ptn by itself does not affect proliferation, it enhances proliferation of HSCs stimulated in vitro with the use of a 3-growth factor cocktail. Interestingly, Ptn-enhanced proliferation does not lead to HSC loss, but Ptn also increases absolute HSC number, suggesting Ptn increases HSC self-renewal in vitro.6
Thus, Ptn can have opposing effects, probably depending on the Ptn dose and the expression of its different receptors. In this article, we studied the effect of HSCs in vivo. In particular, we were interested in how the absence of Ptn in microenvironmental stromal cells would affect early hematopoiesis, and we here report a differential role for Ptn in the myeloid and lymphoid engraftment response of HSCs.
Methods
Mice
Ptn deficient (Ptn−/−) mice21 were backcrossed to (129S2 × C57BL/6.J)F1 (129B6) mouse strains. For experiments, C57BL/6. B6.SJL-Ptprca Pep3b/BoyJ (Ly5.1) were used as wild-type (WT) donor cells, whereas littermates of (129S2 × C57BL/6.J) F2 background (129.B6 Ptn+/+, Ptn−/−) were used as recipients. In transplantations of 129.B6 Ptn+/+ or Ptn−/− donor cells, WT (129S2 × Ly5.1)F1 (129.Ly5.1; Ly5.1 × Ly5.2) mice were used as recipients.
Stromal cells and cell lines
Primary stromal cells were prepared from aorta-gonad-mesonephros regions of genotyped Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− embryo (E11.5) as previously described.2 The stromal cell lines EL08-1D2, UG26-1B6, UG15-1B7, EL28-1B3, and AM30-3F4 were cultured as described previously.2,3 Lentiviral shRNAmir in pLKO.1 vector (OpenBiosystems) was used for stable knockdown of Ptn (PtnKD) in the stromal cell lines as described previously.4 As a control (pLKO.1) stromal cells transformed with empty vector were used. Infected cells were selected by 5 μg/mL puromycin in the medium for 3 days after infection or thawing.
Flow cytometry
Surface markers were stained with antibodies from eBioscience (Natutec), except for CD150-PE, which was obtained from BioLegend (Biozol). For intracellular staining, cells were fixed and permeabilized with Cytofix/Cytoperm Buffer (BD Biosciences) and stained with anti-Ccnd1, 92G2 (Cell Signaling). FACS analyses were performed on a Coulter EPICS XL (Beckman Coulter) or CyAn ADP Lx P8 (Coulter-Cytomation). Data were analyzed with FlowJo software (TreeStar Inc). Sorting of cell populations was done with a BD FACSAria IIlu (Becton Dickinson).
Short-term colony assay
The number of colony-forming cells was determined with culture in growth factor–supplemented methylcellulose medium as described by the manufacturer (MethoCult GF M3434; StemCell Technologies). BM cells (2.5 × 104) or, after culturing on stroma, 1000 Lin− (see “Stromal cell cocultures”) input equivalent cells were seeded per 3-cm dish.
Stromal cell cocultures
For all cocultures, lineage-depleted BM cells (Lin−) were cocultured with confluent and irradiated stromal cells (30 Gy for cells lines and 15 Gy for primary cells). Lin− cells were negatively selected from flushed BM (Lineage depletion kit; Miltenyi Biotec). Lin− cells (n = 5000) were plated on stromal cells in a 3-cm dish. For long-term cocultures, cells were cultured in long-term culture medium (M5300; Stem Cell Technologies). Each week, half of the supernatant was replaced with fresh medium.
In vivo engraftment
In all experiments, recipient mice were lethally irradiated with 9 Gy (KD2 Mevatron; Siemens). Three types of experiments were performed. First, BM cells from Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− mice were serially transplanted into tail vein of WT (129.Ly5.1) recipients. Alternatively, WT Ly5.1 cells were transplanted into either Ptn−/− or their Ptn+/+ littermates. First-degree transplants were injected with 2 × 105, second-degree with 1 × 106, third-degree with 2 × 106, and finally fourth-degree with 5 × 106 total BM cells isolated from previous recipient, respectively. In the second set of experiments, Lin− cells from the BM of Ly5.1 mice were first cocultured with pLKO.1 and PtnKD stroma for 3 weeks. The input equivalent of 2500 cocultured Lin− cells were transplanted into WT B6.Ly5.2 recipients. For secondary transplants, 5 × 106 BM cells were transplanted into the recipients with the same background. In the third set of experiments, Lin−Kit+ cells were sorted from primary Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− recipients of 2 × 105 WT (Ly5.1) BM cells, 16 weeks after initial transplantation. The equivalent of 1000 LSK cells was then transplanted into lethally irradiated secondary B6.Ly5.2 recipients, together with 2 × 105 recipient-type competitor cells.
In the first 5 weeks after transplantation, all recipients received 1 mg/mL neomycin sulfate (Sigma-Aldrich) and 500 U/mL Polymyxin B (Sigma-Aldrich) with the drinking water. Peripheral blood was analyzed 5 and 10 weeks after transplantation by flow cytometry. Sixteen weeks after transplantation mice were killed; BM, spleen, and peripheral blood (PB) were analyzed by flow cytometry. BM cells were also used as donor cells for further transplantations. Donor and recipient cells were identified because of differential expression of Cd45 (Ly5) gene (Ly5.1 and Ly5.2 alleles). Mice were counted positive with ≥ 1% myeloid and 1% lymphoid donor engraftment.
High-resolution tracking of cell division
Lin− cells were depleted from the WT BM, labeled with CFSE (Invitrogen) and cultured overnight in long-term culture medium (M5300; Stem Cell Technologies). The next day, cells were stained with antibodies, and a tight peak of CFSE+ LSK and multipotent myeloid progenitor (MMP) cells was sorted to facilitate detection of single divisions, as described earlier.22 Cocultures were set up with MMP cells and karyomax (Invitrogen) to enable detection of undivided cells. LSK cells were then cocultured on primary WT or Ptn−/− stroma for 3 days and analyzed for the presence of Lin−, Kit+, and Ly6a+ cells in combination with different cell divisions.
Real-time PCR
cDNA was generated with Dynabeads mRNA DIRECT micro kit (Invitrogen) and Quantitect RT kit (QIAGEN). For the real-time PCR reaction Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) was used, and samples were run in an Applied Biosystems 7900HT. All primers used in this study are shown in supplemental Table 1 (available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).
Immunocytofluorescence staining
Single-cell staining assays were performed as modified from our previously described protocol.4 In brief, 500 cells were spotted on poly-L-lysine–coated slides. Spotted cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and blocked with 10% FCS and 0.1% Triton-X in PBS. Cells were stained with anti-Ctnnb1 (L54E2 Alexa Fluor 488–conjugated mouse antibody; Cell Signaling), rabbit anti-Ccnd1 (92G2; Cell Signaling), or anti-Cebpa (2295; Cell Signaling). As a secondary antibody we used anti–rabbit, Alexa Fluor 488–conjugated antibody (4412; Cell Signaling). All stains were counterstained with DAPI (4,6-diamino-2-phenylindole, dihydrochloride; Invitrogen). A Leica DM RBE fluorescent microscope (Leica) was used for detection. Fluorescence intensities of stained cells were quantified in total pixels with the use of ImageJ (NIH). Each stain included a negative Ig control, the detected pixels of which were deducted from the total pictures as background. Nuclear and cytoplasmic regions were differentially defined on the basis of the boundaries of the DAPI staining, and the ratio of total pixels within the nuclear region and the cytoplasm was determined as described previously.4
Western blotting
For Ptn expression analysis, 15 μL of supernatant from confluent cultures (10 mL of total medium) was denaturated with 3 μL of 5X Lämli buffer and loaded on 18% reducing polyacrylamide gels. After blotting the proteins on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Millipore), 2% horse serum in PBS with 0.1% Tween-20 was used for blocking and dilution of anti-Ptn antibody (ab14025; Abcam). Primary antibody was detected with an anti–rabbit horseradish peroxidase–conjugated secondary antibody (Pierce) and developed with the use of Super Signal chemoluminescent substrates (Pierce).
Statistics
For statistical analysis, unpaired Welsh-corrected and paired Student t tests were used where appropriate (InStat, GraphPad Software). Stem cell frequencies in cocultures were estimated from single cell doses with the use of the L-Calc software (StemCell Technologies).
Results
Loss of Ptn alters hematopoiesis in vitro
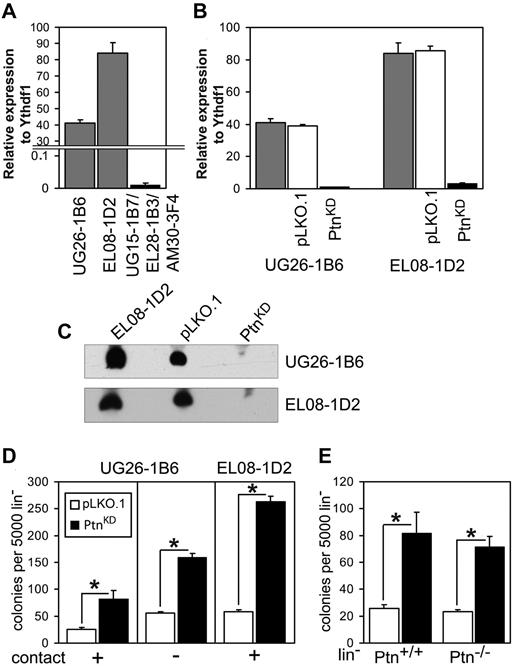
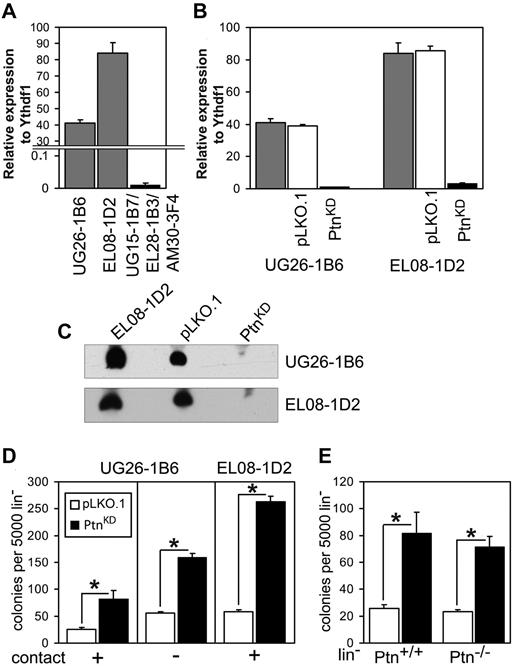
We previously demonstrated that Ptn is overrepresented in the cell lines EL08-1D2 and UG26-1B6,which support maintenance of HSCs in culture.3 Here, we confirmed this finding with the use of real-time PCR (Figure 1A). To study the importance of Ptn for stem cell maintenance, we stably knocked-down expression of Ptn (PtnKD) in both cell lines (Figure 1B-C). Cocultures of WT Lin− cells on PtnKD stromal cells displayed increased production of committed progenitors (Figure 1D) compared with the control (pLKO.1) cells. To ascertain that a soluble factor was responsible for this increase in colony formation, we also performed cocultures in which Lin− cells and UG26-1B6 were separated by a membrane. In these noncontact cocultures we found a similar increase in colony-forming cells (CFCs) as in the contact cocultures (Figure 1D). These results indicate that the knockdown of Ptn affects CFC production in an extrinsic manner. To rule out intrinsic effects of the Ptn loss, we used Lin− cells from Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− mice21 for cocultures on pLKO.1 and PtnKD UG26-1B6 cells. Here, we observed a same effect independently from the genotype of cocultured Lin− cells. (Figure 1E).
Loss of Ptn affects hematopoiesis in vitro. (A) Expression of Ptn in UG26-1B6 and EL08-1D2 cell lines compared with a mixture of nonsupportive stromal cell lines (UG15-1B7, EL28-1B3, and AM30-3F4) as detected by real-time PCR. Shown is expression relative to housekeeping gene Ythdf1. (B) Knockdown of Ptn in supportive stromal cell lines as measured by real-time PCR. Shown is expression relative to Ythdf1. Gray bars represent the unmanipulated parental stromal cells, white bars represent the stromal cells transduced with empty pLKO.1 vector (pLKO.1), and shPtn-transduced cells (PtnKD) are shown in black bars. (C) Western blot analysis of Ptn expression, using supernatant of confluent monolayer of stromal cell lines. (D) Colony number of WT Lin− after 2 weeks of coculture on PtnKD and pLKO.1 stromal cell lines (n = 10, (UG26-1B6 contact; n = 4, UG26-1B6 noncontact; n = 3, EL08-1D2 contact). (E) The colony number of Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− Lin− cells after 2 week of coculture on PtnKD and pLKO.1 UG26-1B6 (n = 4). All values are mean ± SEM; *P < .05.
Loss of Ptn affects hematopoiesis in vitro. (A) Expression of Ptn in UG26-1B6 and EL08-1D2 cell lines compared with a mixture of nonsupportive stromal cell lines (UG15-1B7, EL28-1B3, and AM30-3F4) as detected by real-time PCR. Shown is expression relative to housekeeping gene Ythdf1. (B) Knockdown of Ptn in supportive stromal cell lines as measured by real-time PCR. Shown is expression relative to Ythdf1. Gray bars represent the unmanipulated parental stromal cells, white bars represent the stromal cells transduced with empty pLKO.1 vector (pLKO.1), and shPtn-transduced cells (PtnKD) are shown in black bars. (C) Western blot analysis of Ptn expression, using supernatant of confluent monolayer of stromal cell lines. (D) Colony number of WT Lin− after 2 weeks of coculture on PtnKD and pLKO.1 stromal cell lines (n = 10, (UG26-1B6 contact; n = 4, UG26-1B6 noncontact; n = 3, EL08-1D2 contact). (E) The colony number of Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− Lin− cells after 2 week of coculture on PtnKD and pLKO.1 UG26-1B6 (n = 4). All values are mean ± SEM; *P < .05.
Ptn-deficient mice show normal steady-state hematopoiesis
These in vitro results show that in the absence of Ptn, maintenance of hematopoietic cell subsets in culture is altered, resulting in increased CFC production. Thus, we studied hematopoiesis in Ptn−/− mice in more detail. In general, mature hematopoietic populations were unaltered in Ptn−/− animals compared with their Ptn+/+ littermates, except for an increase in myeloid cells in the PB of Ptn−/− animals (supplemental Figure 1). Characterization of early hematopoietic progenitors and stem cells in the Ptn−/− mice indicates that steady-state hematopoiesis in these mice is similar to that of Ptn+/+ littermates (supplemental Figure 1). To find out whether knockout of Ptn expression in HSCs would affect their ability to engraft and regenerate lethally irradiated recipients, we transplanted Ptn−/− and Ptn+/+ BM cells into WT recipients. In these experiments, we observed that Ptn−/− HSCs show normal myeloid and lymphoid engraftment behavior in primary (first-degree) as well as secondary (second-degree) recipients (supplemental Figure 2). However, it is notable that 5 weeks after the initial transplantation of Ptn−/− cells into second-degree recipients, myeloid engraftment is slightly lower. Because at 16 weeks after transplantation this altered engraftment pattern was not found anymore, the finding suggests that the loss of the Ptn gene may have “primed” this short-term repopulation behavior of Ptn−/− cells. It seems unlikely that this “priming” is the result of an intrinsic expression of Ptn in stem and progenitors, because in real-time PCR analyses of Ptn in LSK and MMP cells from Ptn−/− and their Ptn+/+ littermates, we failed to detect Ptn mRNA (supplemental Figure 3).
Loss of microenvironmental Ptn leads to enhanced stem cell maintenance in vivo
The results of the cocultures of Lin− cells with PtnKD stromal cells are reminiscent of similar experiments we previously performed to study Sfrp1.4 Because stromal cell cocultures model recapitulate a regenerative response rather than steady-state hematopoiesis, we also investigated hematopoietic regeneration. For this purpose, WT Ly5.1 BM cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated Ptn−/− mice and Ptn+/+ littermates. These mice were analyzed 16 weeks after transplantation and showed an increased donor cell compartment in BM and PB compared with Ptn+/+ recipient mice (Figure 2B-C). In addition, we found an increased amount of donor-derived myeloid progenitors (common myeloid progenitor [CMP] and granulocyte macrophage progenitor [GMP]) in the BM of these first-degree recipients (supplemental Figure 4B).
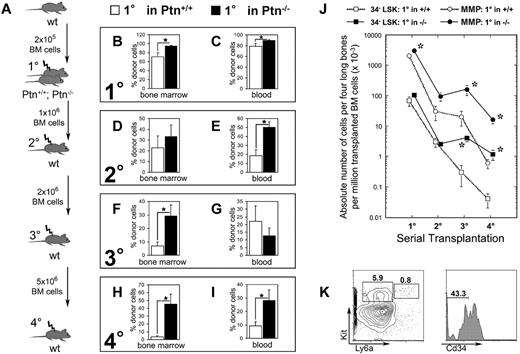
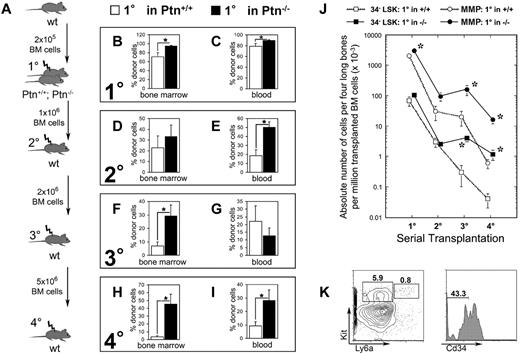
Loss of microenvironmental Ptn leads to enhanced stem cell maintenance in vivo. (A) Experimental design of serial transplantation experiments. WT Ly5.1 BM cells (2 × 105) were transplanted into Ptn−/− and Ptn+/+ littermate (Ly-5.2+) recipients irradiated with 9 Gy. Sixteen weeks after transplantation, recipients were killed, and 1 × 106 BM cells were serially transplanted into WT secondary recipients. Again, mice were killed 16 weeks after transplantation, and 2 × 106 BM cells were serially transplanted into tertiary irradiated WT mice. Finally, 5 × 106 BM cells of these tertiary recipients were again transplanted into irradiated quaternary WT recipients. (B) Engraftment levels as percentage of Ly-5.1+ donor cells in BM of first-degree recipients, n = 5 (+/+), n = 10 (−/−). (C) Primary transplantation, engraftment levels in PB 16 weeks after transplantation. (D) Secondary transplantation, engraftment levels in BM 16 weeks after transplantation, percentage of donor cells in total cell count of 4 long bones, n = 10 (Ptn+/+), n = 8 (Ptn−/−). (E) Secondary transplantation, engraftment levels in PB 16 weeks after transplantation. (F) Tertiary transplantation, engraftment levels in BM 16 weeks after transplantation as percentage of donor cells; n = 7 (Ptn+/+), n = 5 (Ptn−/−). (G) Tertiary transplantation, engraftment levels in PB 16 weeks after transplantation. (H) Quaternary transplantation, engraftment levels in BM 16 weeks after transplantation, as percentage of donor cells; n = 5 (Ptn+/+), n = 6 (Ptn−/−). (I) Quaternary transplantation, engraftment levels in PB 16 weeks after transplantation. (J) Calculated absolute numbers of Cd34−LSK and MMP cells per 4 long bones in the serial transplantations, based on the number of transplanted BM cells. (K) Flow cytometric analysis of BM of quaternary transplants. LSK and MMP are gated in Lin− cells, Cd34−LSKs were gated in the LSK cells. All values are mean ± SEM; *P < .05.
Loss of microenvironmental Ptn leads to enhanced stem cell maintenance in vivo. (A) Experimental design of serial transplantation experiments. WT Ly5.1 BM cells (2 × 105) were transplanted into Ptn−/− and Ptn+/+ littermate (Ly-5.2+) recipients irradiated with 9 Gy. Sixteen weeks after transplantation, recipients were killed, and 1 × 106 BM cells were serially transplanted into WT secondary recipients. Again, mice were killed 16 weeks after transplantation, and 2 × 106 BM cells were serially transplanted into tertiary irradiated WT mice. Finally, 5 × 106 BM cells of these tertiary recipients were again transplanted into irradiated quaternary WT recipients. (B) Engraftment levels as percentage of Ly-5.1+ donor cells in BM of first-degree recipients, n = 5 (+/+), n = 10 (−/−). (C) Primary transplantation, engraftment levels in PB 16 weeks after transplantation. (D) Secondary transplantation, engraftment levels in BM 16 weeks after transplantation, percentage of donor cells in total cell count of 4 long bones, n = 10 (Ptn+/+), n = 8 (Ptn−/−). (E) Secondary transplantation, engraftment levels in PB 16 weeks after transplantation. (F) Tertiary transplantation, engraftment levels in BM 16 weeks after transplantation as percentage of donor cells; n = 7 (Ptn+/+), n = 5 (Ptn−/−). (G) Tertiary transplantation, engraftment levels in PB 16 weeks after transplantation. (H) Quaternary transplantation, engraftment levels in BM 16 weeks after transplantation, as percentage of donor cells; n = 5 (Ptn+/+), n = 6 (Ptn−/−). (I) Quaternary transplantation, engraftment levels in PB 16 weeks after transplantation. (J) Calculated absolute numbers of Cd34−LSK and MMP cells per 4 long bones in the serial transplantations, based on the number of transplanted BM cells. (K) Flow cytometric analysis of BM of quaternary transplants. LSK and MMP are gated in Lin− cells, Cd34−LSKs were gated in the LSK cells. All values are mean ± SEM; *P < .05.
To investigate whether increased primary engraftment reflects overactivation (reduced self-renewal) or increased HSC maintenance (increased self-renewal), BM of these first-degree mice was used for transplantation into lethally irradiated second-degree WT recipient mice. In contrast to our results in primary Sfrp1−/− knockout recipients we published earlier,4 analysis of these second-degree recipients of cells from the primary Ptn−/− environment 16 weeks after injection showed a clear increase in donor cell regeneration in the PB (Figure 2E; supplemental Figure 4D-F), indicating that loss of Ptn in the primary environment does not impair HSC self-renewal.
Further serial transplantations showed that the apparent increase in self-renewal in first-degree recipients resulted in a long-lasting increase in engraftment, which is even more outspoken in tertiary (third-degree) transplants. Analysis of third-degree recipients suggest a 4-fold increase of donor engraftment in BM (Figure 2F), accompanied by a 10.3-fold increase in Cd34− LSK (Lin− Ly6a+ Kit+) and a 6.8-fold increase in MMP populations (Figure 2J). This effect is still more outspoken in quaternary (fourth-degree) recipients, whereby we found an increase in engraftment levels of both BM (14.3-fold increase) and blood (3.5-fold increase) in donor engraftment (Figure 2H-I). The increase of BM engraftment was accompanied by increased numbers of CD34− LSKs (26.3-fold increase) and MMPs (27.6-fold increase; Figure 2J-K).
In all serial transplantations, we detected myeloid and lymphoid engraftment. Interestingly, at each serial transplantation, engraftment of myeloid progenitors CMP, GMP, and myeloerythroid progenitor was increased in mice serially transplanted with cells from first-degree Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− recipients (supplemental Figure 4B,H,K). This finding suggests a progressive dominance of myeloid and a loss of lymphoid engraftment (supplemental Figure 4F,I,L).
Thus, the loss of Ptn in the environment of first-degree recipients in vivo results in a persisting improvement in HSC maintenance in serial transplantations associated with an increased ability to regenerate both Cd34− LSK and MMP compartments in lethally irradiated recipients.
Loss of microenvironmental Ptn enhances stem cell repopulation ability in vitro
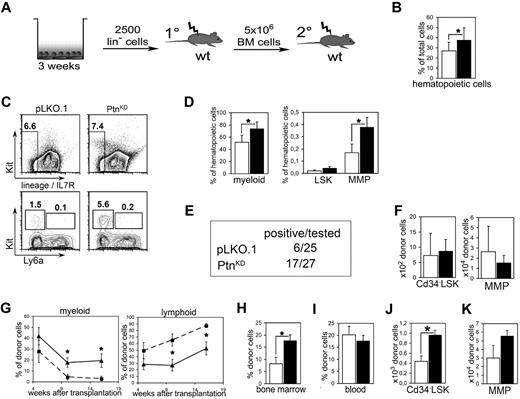
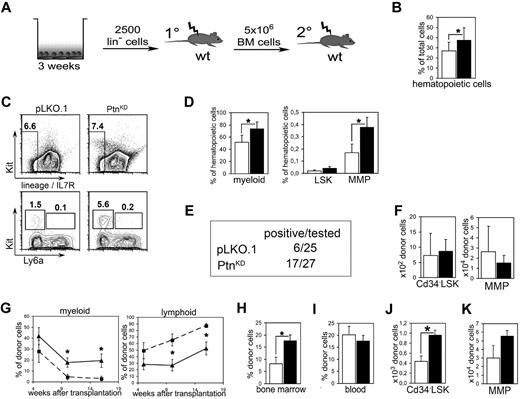
Because a detailed study of the molecular mechanisms of the effects of the primary Ptn−/− recipient environment is not practical in the above-described in vivo experiments, we decided to return to our study of the cocultures we described earlier (Figure 3A). A closer look at the 2-week cultures showed an increased amount of hematopoietic cells in cocultures with PtnKD stroma cells than with pLKO.1 (Figure 3B). Moreover, in the cocultures on PtnKD stromal cells myeloid cells were increased as well as the population of MMPs (Figure 3C-D).
Loss of microenvironmental Ptn leads to enhanced stem cell maintenance in vitro. (A) Scheme of coculture experiment. In brief, Lin− cells from Ly-5.2+ WT BM were cocultured with PtnKD and pLKO.1 stroma in contact. After 3 weeks, cultures were transplanted into irradiated WT mice. Recipients were killed 16 weeks after injection, and 5 × 106 BM cells were again transplanted into irradiated WT recipients. (B) Total number of hematopoietic cells as percentage of the total cell number (hematopoietic + stromal cells) recovered from the culture. Statistics were performed with a paired Student t test. (C) Example of the flow cytometric analyses after coculture. (D) Hematopoietic subpopulations in stromal cocultures. Myeloid cells were gated as Gr1low−high, CD11b+. LSKs and MMPs were gated as Lin− Ly6a+ Kit+ cells and Lin− Ly6a− Kit+ cells, respectively. Statistics were performed with a paired Student t test. (E) Engraftment in PB 16 weeks after primary transplantation. Animals were counted positive with ≥ 1% engraftment in blood and with donor cells containing ≥ 1% myeloid and lymphoid cells, respectively. (F) Enumeration of Cd34− LSK and MMP populations in BM 16 weeks after primary transplantation of cocultured cells. Shown are the results of mice with ≥ 1% engraftment in BM (n = 4, white bars, pLKO.1 stroma in cocultures; n = 8, black bars, PtnKD stroma in cocultures). (G) Frequency of lymphoid and myeloid cells within the donor cell population in PB of transplanted mice, 5, 10, and 16 weeks after transplantation (pLKO.1 = 6; PtnKD = 8). Secondary transplantation, donor engraftment levels in BM (H; n = 9), and in PB (I). (J) Secondary transplantation, total number of donor-derived Cd34− LSKs in BM 16 weeks after the start of secondary transplantation, as well as (K) donor-derived MMPs in BM. All values are mean ± SEM; *P < .05.
Loss of microenvironmental Ptn leads to enhanced stem cell maintenance in vitro. (A) Scheme of coculture experiment. In brief, Lin− cells from Ly-5.2+ WT BM were cocultured with PtnKD and pLKO.1 stroma in contact. After 3 weeks, cultures were transplanted into irradiated WT mice. Recipients were killed 16 weeks after injection, and 5 × 106 BM cells were again transplanted into irradiated WT recipients. (B) Total number of hematopoietic cells as percentage of the total cell number (hematopoietic + stromal cells) recovered from the culture. Statistics were performed with a paired Student t test. (C) Example of the flow cytometric analyses after coculture. (D) Hematopoietic subpopulations in stromal cocultures. Myeloid cells were gated as Gr1low−high, CD11b+. LSKs and MMPs were gated as Lin− Ly6a+ Kit+ cells and Lin− Ly6a− Kit+ cells, respectively. Statistics were performed with a paired Student t test. (E) Engraftment in PB 16 weeks after primary transplantation. Animals were counted positive with ≥ 1% engraftment in blood and with donor cells containing ≥ 1% myeloid and lymphoid cells, respectively. (F) Enumeration of Cd34− LSK and MMP populations in BM 16 weeks after primary transplantation of cocultured cells. Shown are the results of mice with ≥ 1% engraftment in BM (n = 4, white bars, pLKO.1 stroma in cocultures; n = 8, black bars, PtnKD stroma in cocultures). (G) Frequency of lymphoid and myeloid cells within the donor cell population in PB of transplanted mice, 5, 10, and 16 weeks after transplantation (pLKO.1 = 6; PtnKD = 8). Secondary transplantation, donor engraftment levels in BM (H; n = 9), and in PB (I). (J) Secondary transplantation, total number of donor-derived Cd34− LSKs in BM 16 weeks after the start of secondary transplantation, as well as (K) donor-derived MMPs in BM. All values are mean ± SEM; *P < .05.
To find out whether the cocultures with PtnKD stromal cells cause a similar increase in HSC repopulation ability as found in the transplants of Ptn−/− first-degree recipients (Figure 2), whole cultures were transplanted into lethally irradiated WT mice. Sixteen weeks after transplantation, only 6 of 25 mice that received cells from pLKO.1 cultures were positive (estimated frequency, 1 in 9100; 95% confidence interval, 1 in 4080-20 300). In contrast, 17 of 27 (estimated frequency 1 in 2200; 95% confidence interval, 1 in 1330-3620) of mice that received a transplant with cells from cocultures on PtnKD stromal cells were positive (Figure 3E). With the average of all animals that received a transplant, the earliest donor cell populations do not appear to be affected (Figure 3F), suggesting that the loss of stromal Ptn in cocultures mainly affects the regenerative capacity of the more mature progenitor populations, as is also suggested by analysis of the cultures themselves, whereby an obvious increase in the MMP compartment is noticeable (Figure 3D). In line with the transplantation experiments in primary Ptn−/− recipients, we detected an increase in myeloid and a concomitant decrease in lymphoid engraftment in the mice that received cells cocultured with PtnKD stroma (Figure 3G). In addition, HSCs cocultured on PtnKD stromal cells engrafted the BM of second-degree WT recipients at significantly higher levels compared with HSCs cocultured on pLKO.1 stromal cells (Figure 3H). In addition, in these second-degree recipients, the population of donor-derived CD34− LSKs as well as the CMPs were more than twice as high as in mice that received cells from PtnKD cocultures than in pLKO.1 mice (Figure 3J; supplemental Figure 5D). However, the number of MMPs was not statistically different in mice that received cells from PtnKD cocultures (Figure 3L).
These results indicate that the PtnKD expression in stromal cells enhances the maintenance of the number of stem cells in vitro. As such, the coculture results imply that the increased HSC-repopulating ability of cells transplanted into Ptn−/− mice (Figure 2) is because of the lack of Ptn in the stromal cell compartment.
Enhanced stem cell repopulation ability is caused by a direct effect on donor LSK cells
In the above-described experiments, the first-degree Ptn−/− recipients present with a higher BM reconstitution. Hence, it is possible that this increase may be carried over to subsequent secondary second-degree and further serial transplants, thus explaining the increased repopulating ability. In fact, when we calculate the carryover of donor cells, the third-degree and fourth-degree recipients receive a significantly larger donor transplant from the first-degree Ptn−/− recipients (supplemental Figure 6A), whereas the estimated number of donor marrow cells generated per Cd34− LSK cells (supplemental Figure 6B) remains similar. The reconstitution itself is therefore not a measure of stem cell quality per se, and changes in stem cell quality may be masked by changes in cell number.
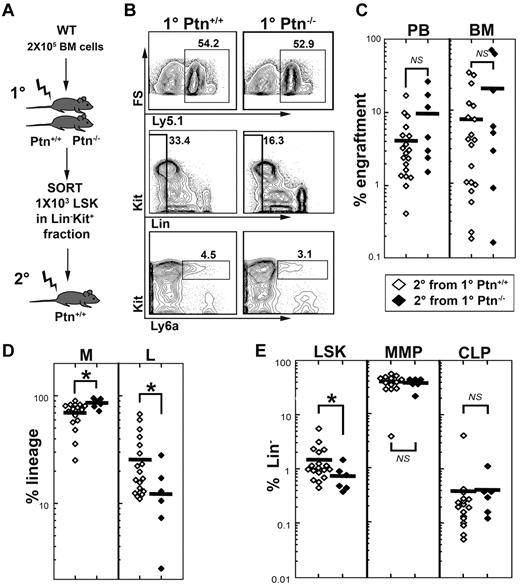
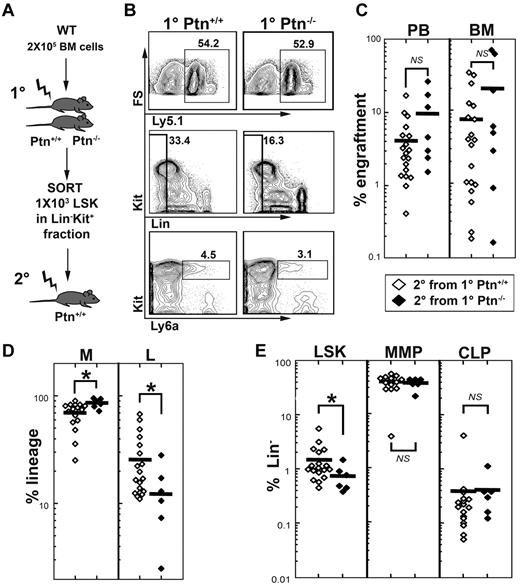
To test whether stem cell quality is altered in the first-degree recipients, we sorted donor LSK cells from first-degree Ptn+/+ or Ptn−/− recipients (Figure 4A) and transplanted these in equal numbers (1000 per animal) into second-degree WT recipients. To include competitive ability in the study of stem cell quality, we performed this experiment in a 1:1 competitive manner (1 × 105 Ly5.1 donor cells, and 1 × 105 competitor cells). These experiments confirmed that LSK cells from first-degree Ptn−/− recipients show a tendency for higher engraftment, as well as increased myeloid and decreased lymphoid engraftment after 16 weeks in the second-degree WT recipients (Figure 4C-D). Interestingly, we noted a significantly decreased LSK population in mice receiving LSK cells from first-degree Ptn−/− recipients. However, more mature progenitors, such as the MMP and common lymphoid progenitor were not different from those in second-degree recipients that received a transplant with LSK cells from first-degree WT recipients (Figure 4E). These results indicate that the Ptn−/− environment directly modulates the repopulation behavior of HSCs.
Lack of Ptn modulates repopulating behavior of HSCs. Changes in self-renewal and stem cell quality can be masked by alterations in proliferation. (A) Experimental design to address this issue, we sorted Lin− Kit+ donor (Ly-5.1) cells from primary 129S2B6 (Ly-5.2) Ptn+/+ or Ptn−/− recipients (see Figure 2A) and transplanted equal numbers of LSK cells into second-degree WT recipients in a competitive manner (ie, together with 2 × 105 recipient-type BM cells). (B) FACS plots from the pool of BM from Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− primary recipients. (C) Level of engraftment, 16 weeks after transplantation of 1000 LSK cells from first-degree recipients. (D) Relative contribution of donor myeloid cells (non-T, non-B, Gr1+) and lymphoid cells (T plus B) to the total population in the second-degree recipient mice. (E) Relative numbers of LSK, MMP, and IL-7R+ CLPs (common lymphoid progenitors) within the donor Lin− population of second-degree recipients, 16 weeks after transplantation.
Lack of Ptn modulates repopulating behavior of HSCs. Changes in self-renewal and stem cell quality can be masked by alterations in proliferation. (A) Experimental design to address this issue, we sorted Lin− Kit+ donor (Ly-5.1) cells from primary 129S2B6 (Ly-5.2) Ptn+/+ or Ptn−/− recipients (see Figure 2A) and transplanted equal numbers of LSK cells into second-degree WT recipients in a competitive manner (ie, together with 2 × 105 recipient-type BM cells). (B) FACS plots from the pool of BM from Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− primary recipients. (C) Level of engraftment, 16 weeks after transplantation of 1000 LSK cells from first-degree recipients. (D) Relative contribution of donor myeloid cells (non-T, non-B, Gr1+) and lymphoid cells (T plus B) to the total population in the second-degree recipient mice. (E) Relative numbers of LSK, MMP, and IL-7R+ CLPs (common lymphoid progenitors) within the donor Lin− population of second-degree recipients, 16 weeks after transplantation.
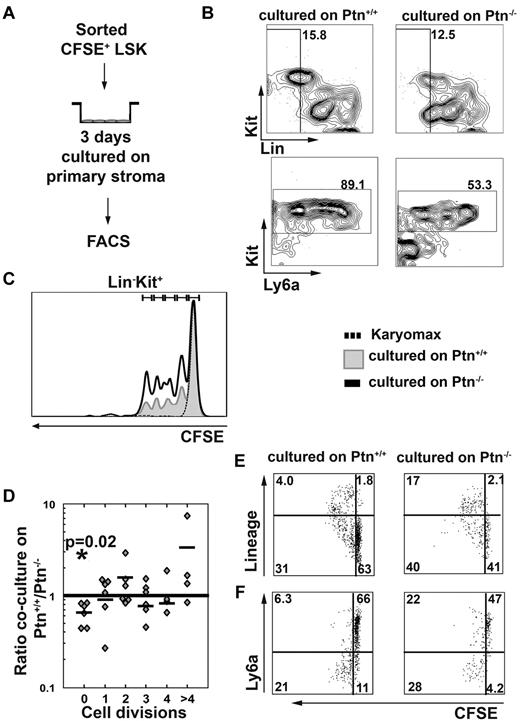
Loss of Ptn alters cell division behavior of LSK cells
The above-described results show that Ptn-dependent effects on HSC maintenance could be caused by an altered regulation of the cell cycle. To find out whether cell division recruitment of WT LSK cells was affected by loss of Ptn in stromal cells, we studied cell division behavior of CFSE-labeled WT LSK cells (Figure 5A). These experiments showed that cells from 3-day cocultures on primary Ptn−/− stroma lost their LSK phenotype more quickly than cells cultured on WT stroma (Figure 5B,F), which was associated with a smaller proportion of cells remaining undivided (Figure 5C-D). The LSK cells cultured on Ptn−/− stroma did not only lose Sca-1 (Ly6a) expression more quickly, but they also generated a higher proportion of cells expressing lineage markers (Figure 5E-F). These results show that LSK cells proliferate more quickly on Ptn−/− stromal cells, with increased expression of differentiation markers within the first 3 days of coculture.
Lack of Ptn promotes cell division recruitment. In the experiments presented here, LSK cells were first sorted from WT donors and then labeled with CFSE. Cells were cultured overnight in long-term culture medium. The next day, a tight peak of CFSE+ cells was sorted to facilitate detection of single divisions51 cocultured in the presence of primary stromal cells (A). After 3 days of coculture, cells were analyzed for the presence of Lin−, Kit+, and Ly6a+ cells (B). (C) Representative histogram of the cell division kinetics of Kit+ cells. The fraction of undivided and divided cells was then determined in cocultures on either Ptn+/+ or Ptn−/− stromal cells and was compared with the use of a paired Student t test. The ratio of these fractions (fraction of division n in Ptn−/−)/(fraction of division n in Ptn+/+) was then calculated. These fractions are shown per division (D). (E) The acquisition of lineage markers of the LSK cells per division and (F) the loss of Ly6a in those divisions in LSK cells cocultured with Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− stromal cells. A total of 6 independent repeats of this experiment were performed (D) of which representative plots and histograms are shown. The experiment in panels E and F was performed independently 3 times; a representative example is shown.
Lack of Ptn promotes cell division recruitment. In the experiments presented here, LSK cells were first sorted from WT donors and then labeled with CFSE. Cells were cultured overnight in long-term culture medium. The next day, a tight peak of CFSE+ cells was sorted to facilitate detection of single divisions51 cocultured in the presence of primary stromal cells (A). After 3 days of coculture, cells were analyzed for the presence of Lin−, Kit+, and Ly6a+ cells (B). (C) Representative histogram of the cell division kinetics of Kit+ cells. The fraction of undivided and divided cells was then determined in cocultures on either Ptn+/+ or Ptn−/− stromal cells and was compared with the use of a paired Student t test. The ratio of these fractions (fraction of division n in Ptn−/−)/(fraction of division n in Ptn+/+) was then calculated. These fractions are shown per division (D). (E) The acquisition of lineage markers of the LSK cells per division and (F) the loss of Ly6a in those divisions in LSK cells cocultured with Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− stromal cells. A total of 6 independent repeats of this experiment were performed (D) of which representative plots and histograms are shown. The experiment in panels E and F was performed independently 3 times; a representative example is shown.
Loss of Ptn in the stromal microenvironment modulates gene expression in hematopoietic progenitors
Because cell division behavior of LSK cells on Ptn-deficient stromal cells was already affected in short-term cultures, we investigated the earliest gene expression changes in 3-day cocultures and sorted LSK, CMP, and GMP to study mRNA expression.
Real-time PCR analysis of these cells showed an unaltered level of Ctnnb1 mRNA expression (Figure 4A) as well as Cdkn1 and Cdkn2 family members and other molecules known to be involved in hematopoietic regulation (supplemental Figure 7). Coculture on PtnKD stromal cells caused a suppression of the transcription factor Pparg in all populations analyzed (Figure 6A). Interestingly, Cyclin D1 (Ccnd1) and C/EBPα (Cebpa) were both higher expressed in LSK cells recovered from cocultures on PtnKD stromal cells. However, in more mature populations (GMP), expression of both Ccnd1 and Cebpa decreased to significantly lower expression levels relative to cocultures on pLKO stromal cells (supplemental Figure 7). Similarly, although Hes1 and Dlk1 expression levels were unaltered in LSK cells recovered from cocultures, their expression decreased in GMPs recovered from cocultures on PtnKD stromal cells (supplemental Figure 7A).
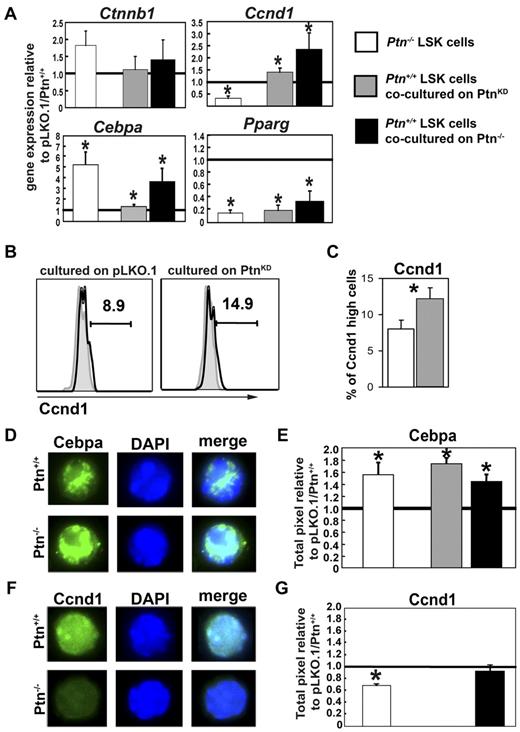
Altered gene expression and protein levels in stem cells and progenitors lacking microenvironmental Ptn. (A) Gene expression analysis in sorted LSK cells from Ptn−/− BM, from cocultures with PtnKD (n = 5), or from cocultures on primary Ptn−/−stromal cells (n = 3). Gene expression was normalized relative to the housekeeping gene Gorasp2. Shown is the ratio of the normalized gene expression to Ptn+/+, pLKO.1, and primary Ptn+/+ stroma. (B) Ccnd1 protein levels in 3-day cocultures on PtnKD or pLKO.1 UG26-1B6 obtained by intracellular flow cytometry. Shown is a representative example. (C) Percentages of Ccnd1high cells in LSK cells recovered from 3-day cocultures on pLKO.1− or PtnKD UG26-1B6 cells. (D) Cebpa protein levels in LSK cells sorted from the BM of Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− mice. (E) Pixel quantitation of stained LSK cells from Ptn−/− mice (white bars, n = 3), cocultures on PtnKD (gray bars, n = 6), or primary Ptn−/− stromal cells (black bars, n = 3). Shown is the ratio of pixels to Ptn+/+, pLKO, or WT stroma, respectively. (F-G) Similar measurements of Ccnd1 protein levels in LSK cells from the BM of Ptn−/− mice, cocultures on primary Ptn−/− stromal cells. Cocultures on PtnKD stroma could not be analyzed. All values are mean ± SEM; statistics were performed with the paired Student t test, *P < .05.
Altered gene expression and protein levels in stem cells and progenitors lacking microenvironmental Ptn. (A) Gene expression analysis in sorted LSK cells from Ptn−/− BM, from cocultures with PtnKD (n = 5), or from cocultures on primary Ptn−/−stromal cells (n = 3). Gene expression was normalized relative to the housekeeping gene Gorasp2. Shown is the ratio of the normalized gene expression to Ptn+/+, pLKO.1, and primary Ptn+/+ stroma. (B) Ccnd1 protein levels in 3-day cocultures on PtnKD or pLKO.1 UG26-1B6 obtained by intracellular flow cytometry. Shown is a representative example. (C) Percentages of Ccnd1high cells in LSK cells recovered from 3-day cocultures on pLKO.1− or PtnKD UG26-1B6 cells. (D) Cebpa protein levels in LSK cells sorted from the BM of Ptn+/+ and Ptn−/− mice. (E) Pixel quantitation of stained LSK cells from Ptn−/− mice (white bars, n = 3), cocultures on PtnKD (gray bars, n = 6), or primary Ptn−/− stromal cells (black bars, n = 3). Shown is the ratio of pixels to Ptn+/+, pLKO, or WT stroma, respectively. (F-G) Similar measurements of Ccnd1 protein levels in LSK cells from the BM of Ptn−/− mice, cocultures on primary Ptn−/− stromal cells. Cocultures on PtnKD stroma could not be analyzed. All values are mean ± SEM; statistics were performed with the paired Student t test, *P < .05.
We also studied some selected genes expressed in cells recovered from cocultures with primary Ptn−/− stromal cells. We confirmed that Ctnnb1 expression remained unaltered, whereas we found a decrease in Pparg expression and both Ccnd1 and Cebpa were increased (Figure 6), confirming the regulation of these genes in both PtnKD and Ptn−/− stromal cell cocultures.
Loss of Ptn may cause a possible “priming” effect of the Ptn−/− environment (supplemental Figure 2). We therefore also looked at gene expression of selected genes in LSK cells recovered from steady-state WT and Ptn−/− mice. Interestingly, despite the lack of detectable changes in long-term function of Ptn−/− cells, we found clear modulation of Cebpa and Pparg in primary LSK cells from Ptn−/− mice. Most surprisingly, we observed a decrease of Ccnd1 in Ptn−/− LSK cells (Figure 6A), suggesting that Ccnd1 is differentially regulated during steady-state hematopoiesis in vivo and the triggering of hematopoietic regeneration in vitro.
Because mRNA levels do not always correlate to protein levels, we also studied the expression of selected proteins in sorted LSK cells from steady-state Ptn−/− animals and cells cocultured on PtnKD or Ptn−/− stromal cells. In flow cytometric experiments, we found that Ccnd1 high-expressing cells showed a similar increase compared in the real-time PCR analysis (Figure 6A-B). In single-cell immunofluorescence staining of sorted LSKs and GMPs from coculture experiments, we found that, in line with the unchanged transcriptional regulation of Ctnnb1, the total protein level of Ctnnb1 was not affected in either LSKs or GMPs nor was its intracellular localization (supplemental Figure 8). In addition, these sorting experiments showed that the transcriptional increase in Cebpa was mirrored by an increase at the protein level in LSK cells from primary Ptn−/− mice (Figure 6D-E), as well as LSK cells cocultured on PtnKD UG26-1B6 or on primary Ptn−/− stroma (Figure 6E; supplemental Figure 9). Down-regulation of Ccnd1 protein in LSK cells from primary Ptn−/− mice (Figure 6F-G) and up-regulation in cocultures on Ptn−/− stromal cells were also confirmed. Thus, the gene expression changes we found at the transcriptional level were also represented at the protein level in sorted LSK cells from primary mice or stromal cocultures.
Discussion
The secreted 17-kDa cytokine Ptn is known to be involved in diverse cellular functions in various cell types.8 However, the role of Ptn in niche-associated regulation of hematopoiesis has, so far, not been explored. We show that Ptn is not required for maintenance of the HSC pool in steady-state hematopoiesis. In contrast, the knockdown of Ptn in stromal cells increases the production of hematopoietic progenitors and, more importantly, the number of HSCs maintained in cocultures. This functional observation is associated with an up-regulation of Ccnd1 and Cebpa in LSK cells. In the HSC downstream CMP and GMP, we find further deregulation of a number of cell cycle–related genes, but survival-associated genes (Trp53, Pten) were not altered in any of the cell populations sorted from the cocultures. Interestingly, our experiments suggest a long-lasting enhancement of donor stem cell regeneration and self-renewal in primary Ptn-deficient recipients and on PtnKD stromal cells. In addition, we show that the lack of environmental Ptn increases the number of donor cells generated per stem cell, as well as promoting myeloid engraftment.
Ptn is known to bind and inhibit the receptor tyrosine phosphatase RPTPβ/ζ (Ptprz1).10 Thus, Ptn increases the phosphorylation status of various substrates of Ptprz1, including Ctnnb1.10,23,24 We and others have previously shown that Ctnnb1 is an important regulator of HSC self-renewal and differentiation.4,25,26 However, coculture with Ptn-knockdown stromal cells did not affect Ctnnb1 expression, neither at the mRNA or at the protein level nor in the distribution between cytoplasm and nucleus in sorted LSK, CMP, or GMP from stromal cocultures. Hence, in line with another study of the in vitro effects of Ptn on HSCs,6 the effects of Ptn knockdown in stromal cells on HSCs does not involve regulation of Ctnnb1 levels in HSCs.
Nevertheless, Ccnd1, an important regulator of G1/S cell cycle transition, is up-regulated in cultured LSK cells, suggesting that in the absence of stromal Ptn Ccnd1 is up-regulated independent of Ctnnb1 regulation. This finding may be related to our observation that Pparg expression is strongly down-regulated not only in progenitors but also in LSK cells. Because HSC stimulation through the noncanonical Wnt signaling (which represses Pparg transcription), enhances self-renewal,27,28 our findings support the idea that the absence of Ptn may promote noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways normally associated with enhanced self-renewal. Further support for this notion is the reported observation that Pparg induces cell cycle withdrawal.29 Thus, the suppression of Pparg expression contributes to enhanced cycling through up-regulation of Ccnd1 expression. Because Pparg regulates Ccnd1 through Creb rather than Ctnnb1,30 canonical Wnt signaling may not be required for the regulation of Ccnd1.
Another pathway that is potentially affected by Ptn is Notch signaling.14,31 Deregulation of Notch signaling might be involved in our observations, because gene expression of Hes1 and Dlk1, which are both known as targets of Notch signaling,32,33 is reduced in GMPs (and for Hes1, also in CMPs) cultured with PtnKD stroma cells. The effects of this transcriptional regulation may be related to the recent observation that Hes1 confers self-renewal activity on CMPs and GMPs carrying the Bcr-Abl oncogene.34 Because we observe that Hes1 and Dlk1 expressions are unchanged in LSK cells, the down-regulation of these molecules would be consistent with the idea that Ptn acts, instead, more on Notch signals in the differentiated cells, such as CMPs and GMPs, and prevents self-renewal of these progenitors.
Because Ptn was overexpressed in cell lines supporting HSCs in long-term cultures,3,5,7 and the addition of Ptn to in vitro cultures increases HSC numbers,6 we anticipated that the loss of stromal Ptn would have a negative effect on HSC behavior. However, our observations do not support such a view, because HSCs cocultured on PtnKD stromal cells or transplanted into Ptn−/− deficient recipients show increased donor cell repopulation that is progressively skewed toward the myeloid lineage and is consistently associated with an increase donor-derived MMP and other myeloid progenitors. At the same time, 16 weeks after transplantation, the relative number of Cd34− LSK cells in mice is increased. These in vivo data suggest that the hematopoietic hierarchy generated from HSCs previously primed by a Ptn−/− environment may be more shallow.35 Direct comparisons with current reported data from others,6 about myeloid skewing or HSC expansion, are complicated by the use of different experimental systems. Because in the present study, all experiments were performed in the presence of stroma, it is highly probable that Ptn may exert the effects we have observed in part through regulation of other microenvironmental cells.
We have found that the loss of Ptn under steady-state conditions or after triggering a repopulation response lead to different outcomes. It is known, that under steady-state conditions, HSCs are present mainly in a quiescent or dormant state and that on total body irradiation, chemostatic treatment, or transplantation HSCs are rapidly recruited into cell cycle. We found that under steady-state conditions, Ccnd1 was expressed at a lower level in Ptn−/− LSK cells, whereas Ccnd1 was up-regulated under conditions triggering HSCs into cycle. Our findings that the absence of Ptn in stromal cells increases the amount of cell divisions in short-term cultures may well be related to the up-regulation of Ccnd1. Although entry into cell cycle is obviously required for self-renewal to occur, cell cycle kinetics are, by themselves, not reliable predictors of self-renewal. In most published knockout models that affect HSC cycle kinetics, entry into cell cycle leads to HSC exhaustion.36 However, in a few models, HSC engraftment and enhanced self-renewal have also been shown, for example in HSCs deficient in Cdkn2c.37,38 However, our results cannot be explained by a secondary down-regulation of Cdkn2c, because none of the Cdkn1 and Cdkn2 family members we examined showed alterations in expression when cultured on PtnKD cells. Hence, our results suggest that Ptn differentially regulates Ccnd1 under steady-state conditions and HSC activation.
The cause of the myeloid skewing is not clear from our observations, and several hypotheses can be formulated which would explain our findings. First, as described earlier, they could be the result of the observed regulation of Ccnd1 and Cebpa which are both involved in regulation of HSC self-renewal.39,40 In addition, Cebpa is known as a master regulator of myeloid differentiation.41 This does, however, not explain why myeloid engraftment is still favored in quaternary recipients, or why we observed a significant peak of this behavior in third-degree recipients. Second, our observations of myeloid skewed engraftment and increase in marrow Cd34− LSK cells are consistent with those reported for aging HSCs,42-45 a phenomenon that may depend on soluble factors emanating from niche cells. However, our observations are not entirely consistent with these data because aged HSCs show a functional defect in engraftment that is not detectable in our experiments. A third explanation could also be that stromal Ptn deficiency differentially affects HSC subsets. Myeloid-skewed engraftment is also observed in studies with the myeloid-biased α subset of HSCs, which show robust engraftment and self-renewal capacity compared with lymphoid-biased (γ and δ) HSCs.46,47 Thus, like that recently shown for Tgfb1,48 the absence of Ptn in the microenvironment may favor maintenance of α-type, myeloid/biased HSCs. In this case, the lack of Ptn could be interpreted as an imbalance in the regulation of myeloid- and lymphoid-biased HSCs.
In conclusion, the present study shows that steady-state hemostasis, maintenance of HSCs in stromal cocultures, and hematopoietic engraftment of myeloablated recipients are subject to different regulatory mechanisms. The loss of Ptn in the steady-state environment does not affect the ability of HSCs to uphold normal hemostasis throughout the lifetime of a mouse. In contrast, activation of a regenerative hematopoietic response in coculture or after transplantation into myeloablated recipients modulates HSC repopulation behavior toward a more proliferative, myeloid-favoring behavior, which results in an enhanced engraftment of donor HSCs initially exposed to a Ptn-deficient environment. We show that loss of stromal Ptn leads to subtle changes in gene expression that have profound and late-acting effects on HSC repopulation behavior, detectable even after quaternary transplantation. The dominance of myeloid engraftment and the accumulation of Cd34− LSK detectable in serial transplants indicates that the secreted factor Ptn is required in an environmental context to maintain the balance of myeloid and lymphoid potential of regenerating HSCs.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the animal facility (Zentrum für Präklinische Forschung), in particular Dr Christine Baumgartner and Dr Thomas Brill, of the Klinikum Rechts der Isar for help in setting up the animal experiments and taking care of the experimental animals. They also thank Lynette Henkel (Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Technical University, Munich, Germany) for excellent technical assistance with cell sorting; Dr Achim Krüger (Institute of Experimental Oncology, Klinikum Rechts der Isar, Munich, Germany) for access to the ABI-7900 real-time PCR equipment used in this study; and Dr Sabine Schill (Department of Radiotherapy, Kilinikum Rechts der Isar, Munich, Germany) for help in irradiation of the animals and cells used in this study.
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (grants OO 8/2-2 and -3 and OO 8/5-1).
Authorship
Contribution: R.I., M.K., and R.A.J.O. designed and performed research, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote the manuscript; C.E., S.G., B.V., F.B., S.G., and M.S. performed research; and U.B.K. and C.P. designed research.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Robert A. J. Oostendorp, III Medizinische Klinik und Poliklinik Ismaningerstrasse 22, 81675 München, Germany; e-mail: Oostendorp@lrz.tum.de.
References
Author notes
R.I. and M.K. contributed equally to this study.