Abstract
Abstract  2554
2554
Children with Ph+ALL generally have a poor prognosis when treated with chemotherapy alone. The timing and duration of the use of imatinib has not been determined. We investigated a role of imatinib immediately before HSCT.
All the patients with ALL were screened for diagnosis of Ph+ALL using RT-PCR. Children with Ph+ALL were enrolled on JPLSG Ph+ALL04 Study within 1 week of initiation of treatment for ALL. Treatment regimen consisted of 5 therapeutic phases: Induction phase (5-drug induction), Intensification phase (high-dose cytarabine and BFM Ib), Re-induction phase (4-drug re-induction), 2 weeks of Imatinib monotherapy phase (23 weeks after diagnosis), and HSCT phase (Etoposide+CY+TBI conditioning). Before and after each phase, minimal residual disease (MRD), the amount of BCR-ABL transcripts, was measured with the real-time PCR method (cut-off 50 copies/microgram RNA). The study was registered in UMIN-CTR (Medical Information, University hospital Medical Information Network - Clinical Trials Registry): UMIN ID C000000290.
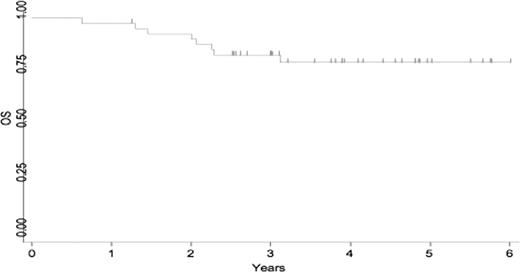
During the period 2004–08, 42 patients were registered in the Ph+ALL04 study. Out of 42 patients, 37 patients (88%) achieved CR and 7 of 37 patients also achieved MRD-negative after induction phase. There were 13 patients who had no MRD at the beginning of imatinib monotherapy phase, and 14 patients were MRD-negative after imatinib phase, consequently, 14 patients were MRD-negative at the time of HSCT. Six patients relapsed before HSCT. In total, 31 patients received HSCT in 1st CR. All the patients had engraftment and no patients died because of complications of HSCT. Five patients relapsed after HSCT and 4 of the 5 patients were MRD-negative before HSCT and the other patient had detectable MRD although it was less than 50 copies. Twenty-six patients continue to be in 1st CR and MRD-negative for median of 3 years after diagnosis. The 3-year event-free survival rate and over-all survival rate for all the patients was 57% and 80%, respectively (figure 1). Five patients did not achieve CR after induction phase and they were treated with imatinib-contained chemotherapy. Four of the 5 patients achieved CR. All of the 4 patients received cord blood transplantation and remains in continued CR.
The chemotherapy we employed was based on the previous high-risk regimen of TCCSG (Tokyo Children's Cancer Study Group) L-99-15 Study. The chemotherapy was intensive enough to induce MRD-negative in 13 at the time of imatinib phase and 31 of 42 patients were in CR at the time of HSCT (around 25–28 weeks after diagnosis). We planned to assess the efficacy of imatinib immediately before HSCT but it was not possible because of the low amount of MRD in most patients at the beginning of imatinib phase.
Although EFS and OS was excellent in this study, 88% of induction rate appeared unsatisfactory and relapse occurred before HSCT in 6 out of 37 patients who achieved CR after induction phase. Earlier and longer use of imatinib may improve EFS in children with Ph+ALL and HSCT may be omitted in a subset of patients who achieve an early and deep remission status.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract