Abstract
Abstract 3745
Despite the remarkable efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), Ph+ CD34+ progenitor cells remain detectable even in patients with stable complete cytogenetic response. Over 40% of patients in stable complete molecular remission will develop molecular relapse within 6 months of stopping imatinib. While the exact causes are largely unknown, one of the proposed mechanisms is the protection of leukemic stem and early progenitor cells by the paracrine or autocrine production of cytokines, such as IL-3, GM-CSF and G-CSF, which activate survival pathways that bypass TKI-induced cytocidal effects. In acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the IL-3 receptor α chain (CD123) is recognized as a specific marker for CD34+/CD38− stem cells and therefore is attracting increasing interest as a therapeutic target. However, the function of CD123 in CML remains to date mostly unexplored.
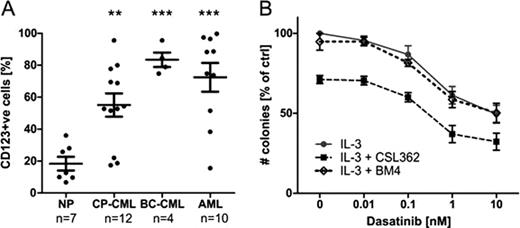
The aim of this study is to investigate potential synergy between TKIs and CSL362 (a humanized antibody version of 7G3 against CD123) in targeting CML progenitor and stem cells. CD34+ and CD34+/CD38− cells were isolated from mononuclear cells of newly diagnosed CML chronic phase and blast crisis patients. Flow cytometry studies indicated significantly increased CD123 expression on CD34+/CD38− cells of CML patients in both chronic phase and blast crisis when compared to normal hematopoietic stem cells (p<0.01 and p<0.001 for chronic phase and blast crisis, respectively; Figure A). A functional relevance of increased CD123 expression was demonstrated by IL-3-dependent increase in STAT5 phosphorylation (260.5% of baseline with 20 ng/ml IL-3; n=12; p<0.001) in CML CD34+ cells. Dasatinib inhibits STAT5 phosphorylation by blocking BCR-ABL signaling but only in the absence of IL-3 (62.5% of baseline for dasatinib alone vs. 130.8% for dasatinib + IL-3; n=3; p<0.01). In agreement, IL-3 effectively rescues dasatinib-induced cell death, as evaluated by AnnexinV/7-AAD staining (103.3% vs. 72.45%, n=5; p<0.01) and CFU-GM colony forming assays (69.39% vs. 46.13% relative to no treatment control; n=4; p<0.05). CSL362, in turn, revokes IL-3-mediated STAT5 phosphorylation (37.12% vs. 130.8%; n=3; p<0.001) and cytoprotection (45.05% vs. 69.39% CFC; n=4; p<0.01). In order to further elucidate the role of CSL362, CML CD34+ cells were cultured with increasing concentrations of dasatinib in the presence of IL-3 and CSL362 or BM4 isotype-matched control antibody. Even at very low dasatinib concentrations, CSL362 significantly reduces CML CD34+ colony forming cells (p<0.05; Figure B). Together these results substantiate a relevant role for IL-3-mediated resistance in CML progenitor cells and additionally confirming the ability of CSL362 to effectively bind to CD123 and impede IL-3 function. CSL362 furthermore has been optimized to mediate antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC). CSL362 causes specific cell lysis of CML CD34+ progenitor cells in co-culture with allogeneic Natural killer cells as determined by increased lactate dehydrogenase release (ADCC activity of 42.4% ± 8.1%; n=3) and a decrease in the number of CFU-GM colonies by 74.1 % ± 12.2% (n=3).
A: Flow cytometry analysis reveals that CD123 expression is significantly higher in CD34+/CD38− cells of CML patients in chronic phase (CML-CP) and blast crisis (BC-CML) as compared to normal patients (NP), as previously documented for AML patients. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001 by unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test. B: In the presence of IL-3, CSL362 significantly reduces the number of colony forming cells. CD34+ cells of de novo CML-CP patients were cultured with dasatinib (0 to 10 nM) +IL-3 (1 ng/ml) ± CSL362 or BM4 (isotype control for CSL362). After 72 hours of culture live cells were plated for CFU-GM assay and colonies were counted after 2 weeks. Mean ± SE of three independent experiments is shown, n=4, p<0.05 by two-way ANOVA.
Nievergall:CSL: Research Funding. White:CSL: Research Funding. Lopez:CSL: Research Funding. Hughes:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Ariad: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Hiwase:CSL: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.