Abstract
Abstract 781 FN2
FN2
Data on second line therapy with second generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) in CML treatment were generated mainly from phase II/III industry initiated trials (Review Hehlmann Exp Op. 2011). 24-month overall survival (OS) varies between 88% and 94% after intolerance and/or resistance to imatinib for chronic phase (CP) and between 67% and 72% for accelerated phase (AP) or blast crisis (BC). Intention to treat analyses including outcome of patients after discontinuation of first line therapies have not been available as yet. We thought to evaluate overall and progression-free survival (OS and PFS) of imatinib intolerant vs. resistant patients under second line TKI with long-term follow-up within an investigator initiated trial.
We analyzed data of the German CML study IV, a randomized 5-arm trial to optimize imatinib therapy on an intention to treat basis. According to protocol, follow-up of patients on and after second generation TKI after imatinib intolerance and/or resistance was continued for OS and PFS. Analysis of PFS was only relevant, if intolerance and resistance to imatinib therapy occurred while a patient was still in chronic phase (CP). Patients were censored at the time of allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT).
From July 2002 to December 2010, 1,502 patients with Philadelphia chromosome and /or BCR-ABL positive CML in CP were randomized. 129 patients of the “imatinib after interferon arm” and 36 other patients had to be excluded (14 due to incorrect randomization or withdrawal of consent, 22 with missing baseline information). 1337 were randomized to primary imatinib treatment (imatinib 400 mg vs. imatinib 800 mg vs. imatinib in combination with either interferon alpha or araC). Of these, 234 (17%) discontinued imatinib therapy. 156 patients were treated with 2nd generation TKI, 61 were directly referred to allo-SCT, 17 patients received other regimens (including interferon alpha only or hydroxyurea).
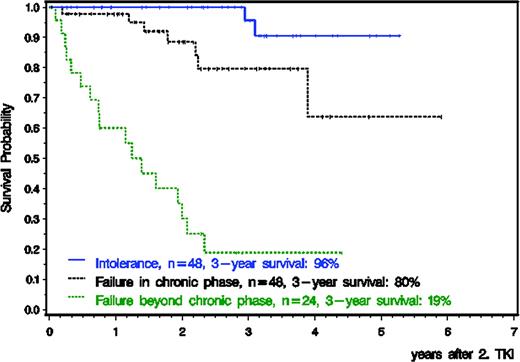
120 of 156 patients started second generation TKI therapy (nilotinib, n=41, dasatinib, n=75, bosutinib, n=2, nilotinib and dasatinib, n=2) within 3 months after stopping imatinib, received treatment for at least one week and were evaluable for PFS and OS. 36 patients received second TKI later (median 10 months, range 3.5–61.4). Median age was 50 years (range 16–78), 42.5% were female. 48 patients were intolerant, 48 failed imatinib within CP and 24 after loss of CP (accelerated phase, n=10, blast crisis, n=14). Median time to second generation TKI was 17 months (range 1.4–97 months) and median follow-up after start of second-line TKI 31 months (range 0.2–71 months). Risk stratification according to the EUTOS Score was high in 20 patients (17%) and low in 94 patients (78%) and unknown in 6 patients (5%). OS for all 120 patients 3 years after start of second generation TKI was 73%, 96% for intolerant and 80% for resistant patients in CP and 19% for resistant patients in advanced disease (s. Fig. 1). According to EUTOS score, 3-year OS was 78% for low and 56% for high risk patients. Probability of PFS of the 96 patients in 1st CP after 3 years was 96% for intolerant and 76% for resistant patients. After 2nd generation TKI, 18 patients received an allo-SCT: all were in CP, 2 patients after imatinib intolerance, 16 patients after imatinib resistance.
Survival on second generation TKI is high for imatinib intolerant patients in first CP but much lower for resistant patients in first CP or for patients with advanced disease phases. Alternative treatment strategies are warranted for these patient groups.
Krause:Micromet: Research Funding. Kneba:Hoffmann La Roche: Honoraria. Hochhaus:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Ariad: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. German CML Study Group:Deutsche Krebshilfe: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; BMBF: Research Funding; EU: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Essex: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract