Abstract
Abstract 3140
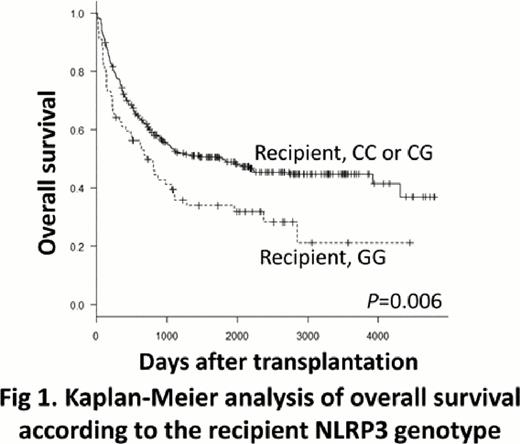
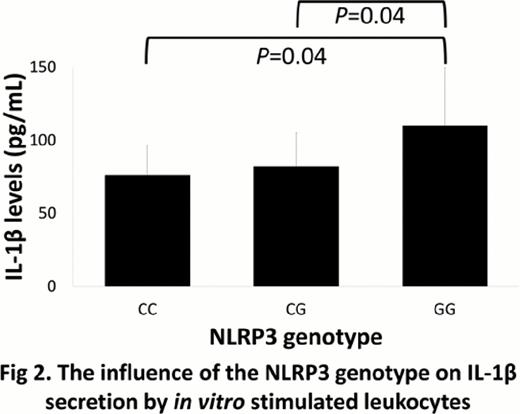
NLRP3 is an intracellular trigger of IL-1β production that plays important roles in the regulation of inflammation and apoptosis. A single nucleotide variation in the 3'-untranslated region of the NLRP3 gene, rs10754558 (+29940G>C), is linked to several immunological diseases. When we examined the impact of the NLRP3 genotype in a cohort consisting of 392 pairs of patients with hematologic malignancies and their unrelated HLA 12/12 matched bone marrow donors transplanted through the Japan Donor Marrow Program, the recipient NLRP3 GG genotype was found to be associated with a significantly worse 5-year overall survival (OS) rate (34% vs. 50%, P=0.006) (Fig. 1) and a trend toward a higher transplant-related mortality (TRM) rate (39% vs. 27%, P=0.09) than the recipient CC or CG genotype. The recipient GG genotype remained statistically significant in the multivariate analysis for OS (hazard ratio [HR], 1.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.22 to 2.22; P=0.004) and TRM (HR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.20 to 4.35; P=0.01). The donor NLRP3 genotype did not significantly influence the transplant outcomes. Next, we investigated the functional relevance of the NLRP3 +29940G>C variant. When leukocytes from healthy individuals were stimulated in vitro with NLRP3 ligand, the leukocytes with the NLRP3 GG genotype produced significantly more IL-1β than those with the NLRP3 CC or CG genotype (Fig. 2). These findings substantiate the functional relevance of the NLRP3 variant, and suggest that the higher IL-1β secretion in the peri-transplant period by recipients with the NLRP3 GG genotype likely accounts for their poor transplant outcomes. NLRP3 genotyping could therefore be useful in predicting prognoses and creating therapeutic strategies for improving the final outcomes of patients who undergo allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.