Abstract
Abstract 3714
Pre-clinical studies demonstrated the potential therapeutic value of targeting the PI3K Delta (PI3Kδ) pathway in lymphoma. A selective PI3Kδ inhibitor, GS-1101, shows promising single agent response rates in patients with a variety of lymphoid malignancies. Previously, we showed that inhibition of PKCβ/AKT pathways (pathways that augments survival and proliferation signals) augments histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor-induced stress response, and the irreversible engagement of the apoptotic cascade in lymphoma cells. In the present study, we investigated the cytotoxicity and mechanisms of cell death induced by GS-1101 in combination with HDAC inhibitors panobinostat (LBH589) and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA).
Cytotoxicity was determined by WST-1 proliferation assay. Apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry, caspase activation and PARP cleavage. Cell signaling transduction pathways were analyzed by Western blot and by phosphoproteome array.
Six DLBCL, two MCL and two Burkitt lymphoma cell lines were treated with different concentration of GS-1101. To determine the molecular mechanisms by which GS-1101 decreases the viability in various cell lines differently, three cell models (SU-DHL-6 as the most sensitive cells, SU-DHL-16 with moderate sensitivity, and Raji the most resistant cells) were selected for phosphoproteome profiling. SU-DHL-6 cells with IC50 only 0.2 μM had constitutively active AKT pathway and highly active ERK pathway. GS-1101 treatment significantly decreased the level p-AKT in this cell line, but more interestingly it also resulted in a decrease in the level of p-ERK. Significant dephosphorylation of ERK was observed also in SU-DHL-16 cells, however with a minimal effect on p-AKT levels. In contrast, the analysis of Raji cells highlighted a very low activity of AKT pathway and no changes in p-ERK levels after GS-1101 treatment.
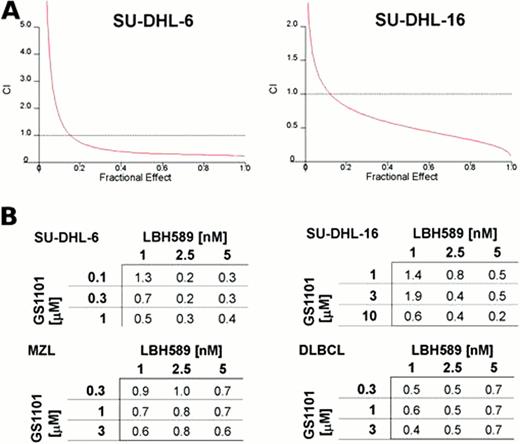
To enhance the effect of GS-1101, SU-DHL-6/16 cells and NHL primary cells were simultaneously treated with the HDAC inhibitor LBH589. An interaction of the LBH589/GS-1101 combination was formally examined by using various concentrations of LBH589 and GS-1101. Combined treatment resulted in a synergistic inhibition of proliferation in all tested cells and induced a significant increase of caspase-dependent apoptosis in SU-DHL-6/16 cells. For example, in SU-DHL-6 cells co-treatment of 0.1 μM GS-1101 with 2.5 nM LBH589 induced 62% increase of apoptotic population in comparison to the untreated sample, while GS-1101 alone induced 13% increase and LBH589 induced 11% increase. Moreover, substituting SAHA for LBH589 suggests that the synergy between GS-1101 and LBH589 is a class effect between HDAC inhibitors and GS-1101, rather than specific to LBH589.
Mechanistically, in SU-DHL-6 cells, LBH589 single treatment increased the level of many phosphoproteins; such as p-ERK, p-AKT, p-CREB, p-AMPKα1/2, p-GSK3α/β, p-HSP27, p-MEK1/2, p-MSK1/2, p-P38a, and p-STAT2. Phosphoproteome analysis of cells treated simultaneously with both agents mostly recapitulated the profile of cells treated with GS-1101 only. Exceptions are p-Chk2, p-c-Jun, p-JNK, and p-STAT5, where levels were significantly higher than in either GS-1101 or LBH589 single treatments. This suggests that GS-1101 and LBH589 may enhance stress-related responses through JNK pathway.
These data suggest that PI3Kδ inhibition in combination with HDAC inhibitors might have potential therapeutic value in lymphoma treatment, and provide pre-clinical rationale for combination therapy in patients with lymphoid malignancies.
Interaction between GS-1101 and LBH589 is dose dependent and synergistic. A) GS-1101 and LBH589 synergistically inhibit proliferation/survival of SU-DHL-6/16 cells. Cytotoxicity was determined by WST-1 proliferation assay. The combination index curves were calculated according to Chou-Talalay method. B) Combination indexes for SU-DHL-6/16 cell lines and primary MZL and DLBCL cells treated with different combinations of GS-1101 and LBH589 concentrations.
Interaction between GS-1101 and LBH589 is dose dependent and synergistic. A) GS-1101 and LBH589 synergistically inhibit proliferation/survival of SU-DHL-6/16 cells. Cytotoxicity was determined by WST-1 proliferation assay. The combination index curves were calculated according to Chou-Talalay method. B) Combination indexes for SU-DHL-6/16 cell lines and primary MZL and DLBCL cells treated with different combinations of GS-1101 and LBH589 concentrations.
Lannutti:Gilead Sciences Inc: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.