Abstract
Abstract 4701
In Manitoba (MB), population 1.25 million, utilization of parenteral oncology drugs is captured through a provincial oncology drug program (PODP) database. The MB Oncology Drug Utility and Clinical Outcomes Program (MODUCO) evaluates drug/regimen utilization with correlation to clinical outcomes. Rituximab (R) accounts for a significant proportion of PODP expenditures, as such monitoring effectiveness at the population level is essential. First line treatment of CLL with FR or FCR was approved in MB in 2009. Prior to this, approval for R based regimens required a non-formulary request. This was a MODUCO initiative to determine effectiveness and cost of R based therapy for CLL in MB, prior to formulary approval of R as part of first line treatment.
Using the PODP database all patients in MB with CLL (and SLL) who received any form of R based therapy between January 14, 2003 and December 14, 2007 were identified. Using this cohort, treatment with R based regimens up until March 14, 2011 was analyzed with follow up until August 1, 2012. Treatment with R for transformed lymphoma was excluded.
The primary outcome measure of Treatment Free Survival (TFS) was defined as the interval from initiation of R to next treatment or death. Patients were censored if alive without further treatment at the date of last follow up. The following factors were analyzed for impact on TFS: age, gender, treatment line (greater than or equal to 1), R treatment line (greater than or equal to 1), regimen, treatment indication (symptomatic disease, lymphocyte doubling time (DT), autoimmune cytopenias, or stage 3/4 disease) and response (No /Yes). Response was defined as improvement in peripheral blood counts or reduction in lymphadenopathy and/or organomegaly. Exact dose of R received during each treatment was recorded for cost analysis.
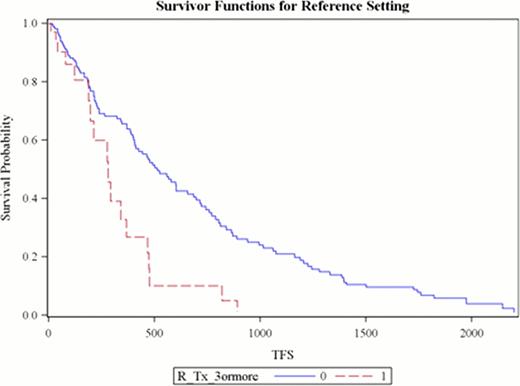
Between 2003–2007 R based therapy was administered for the first time to 86 patients (57 males) with mean age 65.1 years. Median number of prior treatments was 3 (range 1–9). Second time treatment with R was given to 40 patients (46.5%) while 12 (14%) received R on three or more occasions during the follow up period. Overall response was seen in 72.4%. The median time to next treatment or death (TFS) was 1.28 years (95% CI 1.01–1.64) with 50 deaths. Factors contributing to shorter TFS based on univariate analysis were (a) lack of response (p<0.0001), (b) 2nd or 3rd time R administration (p 0.04 and 0.0002), and (c) use of RCVP or RCHOP (p <0.02) or other regimens (p <0.001) compared to the reference (FR/FCR). Multivariate analysis revealed that treatment initiation due to DT, compared to all other indications, was associated with decreased rate of retreatment or death (HR 0.36, 95% CI 0.17–0.73). As seen in Figure 1, patients receiving R for the third time (or greater) had shorter median TFS (HR 2.54, 95% CI 1.48–4.36). Regimens other than FR, FCR, RCVP, RCHOP and RCD had increased risk of needing alternative treatment or dying (HR 1.82, 95% CI 1.08–3.06). Mean cost of R per regimen was $12,999.91. The total cost of R for this cohort was $1.87 million. Cost of R when used for the third time or greater was $410,698.
This population-based retrospective analysis of cost and effectiveness of R, prior to formulary inclusion for CLL, reveals that patients derive maximum benefit with 1st and 2nd administration of R. These patients had refractory or relapsed disease with multiple prior treatments, yet a high proportion responded to treatment confirming the utility of R for salvage therapy. Duration of response is an important consideration in cost-effectiveness, with the MODUCO experience suggesting that effectiveness diminishes with non-standard regimens and greater than 2 previous R containing regimens. Improving patient access to treatments in health care systems that are publically funded means balancing cost with effectiveness in the population.
Treatment Free Survival (days) when Rituximab is used for the Third Time or Greater compared to First or Second Time
Treatment Free Survival (days) when Rituximab is used for the Third Time or Greater compared to First or Second Time
Kumar:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Johnston:Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Bourrier:Roche: Grant Funding for Educational Initiatives Other.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.