Abstract
BCR-ABL1 inhibitors have revolutionized treatment of CML patients. However several drawbacks remain, including therapy resistance of T315I-mutated CML and incapability of current drugs to eliminate quiescent CML stem cells warranting development of novel therapies. In addition, drugs with the potential to enhance efficacy of BCR-ABL1 targeting agents could improve treatment of CML patients. Members of the Tyro3, Axl, Mer receptor (TAMR) tyrosine kinase family are abundantly expressed in physiological and malignant hematopoiesis and their ligand Gas6 can support hematopoietic (progenitor) cells. Evidence in the literature indicates that Axl is upregulated upon treatment with imatinib (IM).
In this study, we investigated the relevance of the Gas6-Axl axis in CML patients and the therapeutic potential of the clinically applicable small molecule Axl inhibitor BGB324 (former designation R428) in primary CML (stem cell) samples, cell lines and preclinical models.
In a first step we quantified Axl-expressing cells by flow cytometry in chronic phase (CP) CML bone marrow at primary diagnosis and healthy bone marrow donors. Here, we found higher numbers of Axl-positive cells in CML bone marrow compared to controls (11.42±0.42% (n=5) vs. 0.65±0.10% (n=6), respectively; p=0.0015). In addition, we determined Gas6 plasma levels by ELISA in healthy controls and CML patients in CP and blast crisis (BC). These analyses revealed that Gas6 plasma levels were upregulated in a stage specific manner (plasma levels of Gas6: healthy controls 1290±684 pg/ml (n=14), CP 3465±405 pg/ml (n=50), BC 10940±3868 pg/ml (n=7); p=0.0001). Thus, the Gas6-Axl axis represents a potential therapeutic target in CML patients.
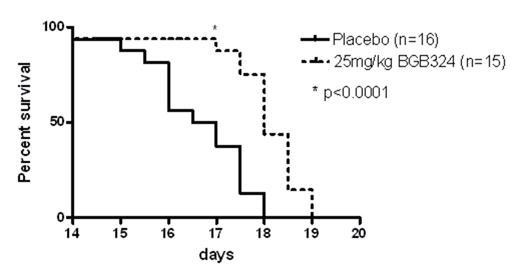
Based on this finding we analyzed efficacy of BGB324 in Axl-expressing BV173, KCL22, K562, BaF3_BCR-ABL1-wt and BaF3_BCR-ABL1-T315I cell lines in vitro. We found inhibition of proliferation in all analyzed cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 500-3000 nM. Combination experiments with the IC50 dose of BGB324 and IM revealed additive effects of both treatments in all cell lines. Dose finding experiments with BGB324 in sorted CD34+ primary CML cells grown in the presence of physiological growth factors yielded a mean IC50 of 1.1 ± 0.3 mM (n=3), which was similar to nilotinib. BGB324 did not accumulate CD34+CFSEmax (undivided) cells any more than nilotinib but enhanced apoptosis of CD34+ cells in combination with nilotinib. Notably, there was a consistent inhibitory effect of 3 mM BGB324 alone or in combination with nilotinib against colony forming cells (CFC) with the more primitive BFU-E and GEMM being most sensitive to inhibition (n=4). Interestingly, the Ph- lymphocytes (confirmed by FISH) sorted simultaneously with Ph+ CD34+ cells from the same CML patient were unaffected in terms of viability when treated with Axl inhibitor; thus the BGB324’s activity is cell context specific.
Taken together, these data suggest that the Gas6-Axl axis represents a therapeutic target and that BGB324 is a potent molecule effective against T315I-mutated and wt CML alone and in combination with TKI. Furthermore, BGB324 induces apoptosis of quiescent Ph+ CML stem/progenitor cells. Thus
BGB324 might open up novel therapeutic avenues in CML patients.
Loges:BerGenBio: research support Other.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.