Abstract
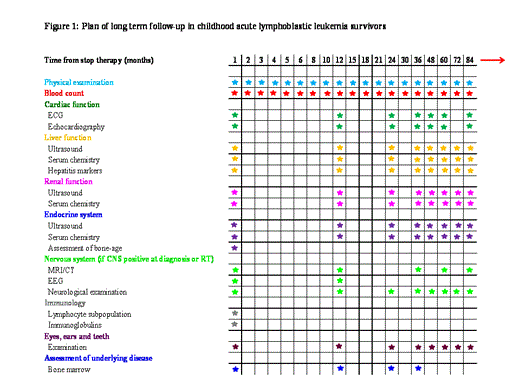
The advent of more intensive chemotherapy and the improvement of supportive cares have dramatically changed the natural history of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), with current estimated 5-year overall survival of about 80%. The increased survival rate and the establishment of follow-up survey for long term survivors (LTS) have allowed the identification of late chemo-radiotherapy adverse effects on psychological and general health. We retrospectively evaluate the incidence and type of sequelae and / or late effects in a cohort of 301 childhood ALL LTS, followed in a single pediatric AIEOP center.
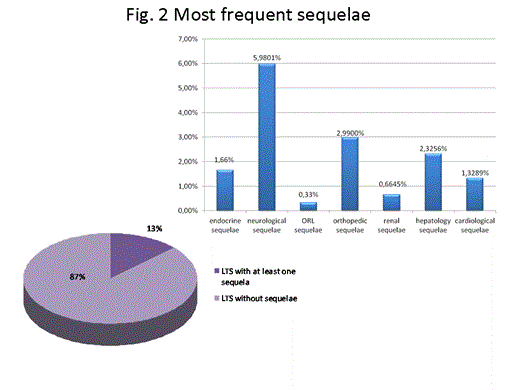
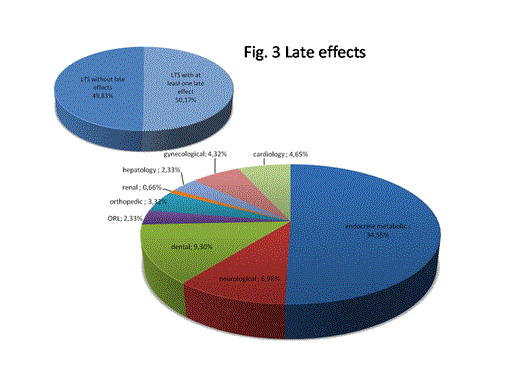
In our experience at least one late effect occurred in 50.17% of LTS; these late complications affect negatively the quality of life of survivors. Endocrine-metabolic events are the most frequent late effect (34,5%). 13% of LTS have at least one sequelae mainly neurological and orthopedic. Prevention and/or early identification of complications during follow-up survey of LTS are crucial in order to decrease the long-term health risks associated with curative treatment for childhood ALL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.