Abstract
Regulatory T cells (Tregs), in particular CD4+ Foxp3+ T cells (CD4+Tregs), have been shown to play important roles in the maintenance of tolerance after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Allo-HSCT). CD8+ Foxp3+ T cells (CD8+Treg) have also been shown to control alloimmune responses in preclinical and clinical models (Renee J. Robb et al, Blood, 2012;119(24):5898-5908). In our previous study, we found that Foxp3+ gamma delta TCR+ Treg cells (gamma delta Tregs) played important regulatory roles in alloimmunity and in xenogeneic GVHD protection (Hu Yong-xian, et al. Leukemia, 2013;27(7):1580-5). Whether these Treg subsets are simultaneously present or have synergetic functional roles in allo-HSCT or, more specifically, GVHD biology is not known. To address this, we analyzed the frequency and possible roles of these Treg cell subsets in patients after allo-HSCT.
Patients who underwent allo-HSCT in our single center from January 2000 to July 2012 were selected. They were divided into 3 groups according to cGVHD criteria including non-cGVHD group, limited cGVHD group and extensive cGVHD group. We also selected healthy volunteers as healthy group. 10ml peripheral blood was drawn from all the selected patients and volunteers for CD4+Tregs, CD8+Tregs and gamma delta Tregs percentage and CD4/CD8 ratio analysis by flow cytometry. Serum cytokine levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interferon-gamma (INF-gamma) and transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) were evaluated by ELISA. Data were processed and analyzed using statistical software (SPSS 17.0). Statistical significance for the difference in different groups was assessed by two-sample t-test and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Spearman’s correlation was used to test the correlation between two continuous variables.
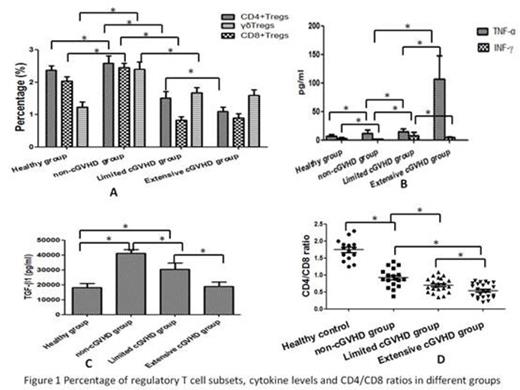
21, 18 and 23 patients were selected in non-cGVHD group, limited cGVHD group and extensive cGVHD group respectively. 15 healthy volunteers were also selected in healthy group. As shown in Figure 1A, the percentages of CD4+Tregs, CD8+Tregs and gamma delta Tregs percentage were all significantly increased in non-cGVHD group compared to healthy group, limited cGVHD group and extensive cGVHD group while these 3 types of Tregs were increased in limited cGVHD group compared with extensive cGVHD group (p<0.05 respectively). TNF-alpha, INF-gamma, and CD4/CD8 have been reported to be associated with cGVHD severity. Our results got similar results (Figure 1B and 1D). Foxp3+ Tregs play their immunosuppressive roles partly via TGF-beta1 secretion. As shown in Figure 1C, the levels of TGF-beta1 increased dramatically in non-cGVHD group compared to healthy controls and cGVHD patients (P < 0.05). Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed that the increased level of TGF-beta1 was positively associated with increased regulatory T cell subsets but was negatively associated with cGVHD severity (p<0.05). We also found that all the 3 types of Treg cell percentages were positively correlated with CD4/CD8 ratio in cGVHD cohort.
Foxp3+ regulatory T cell subsets (CD4+ Tregs, CD8+ Tregs and gamma delta Tregs) can be simultaneously induced in alloreactive microenvironment and may be associated with cGVHD severity after allo-HSCT. They may play synergetic functional roles in controlling cGVHD. Our findings support the development of new strategies to increase the number of 3 types of Treg cells including CD4+ Tregs, CD8+ Tregs and gamma delta Tregs following allo-HSCT to prevent or correct cGVHD.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.