Abstract
Cdh1, one of the co-activators for anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome, plays a crucial role in the mitotic phase, but also has been reported as G2/M checkpoint regulator activated by irradiation-induced DNA damage. Focusing on Cdh1 functions in the hematopoietic system, we have generated Cdh1 conditional gene-trap (Cdh1f/f) mice and crossed them with Mx1-Cre transgenic mice to obtain Mx1-Cre (+) / Cdh1f/f mice. These animals illustrate that the irradiation-induced G2/M checkpoint is defective in Cdh1-deficient bone marrow (BM) cells, which causes the loss of stem/progenitor cells through mitotic catastrophe (Jo Ishizawa et al, Cancer Science 2011). We have also generated a Cdh1-deficient B cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL/LBL) mouse model, and reported that it is a promising model to investigate if Cdh1 affects the prognosis and therapy sensitivity of B-ALL/LBL.
We here report, with our mouse model, that Cdh1 downregulation causes cell fragility in lymphoma cells possibly due to aberrant G2/M checkpoint, which ultimately causes the generation of more resistant phenotype yeilding a poorer disease prognosis after secondary and tertiary transplantation.
We transduced Myc oncogene into Cdh1-intact and Cdh1-deficient BM mononuclear cells (BM-MNCs) and transplanted Myc-transduced BM-MNCs (GFP+) into sub-lethally irradiated wild type C57BL/6 mice, which developed B-ALL/LBL phenotype with similar incidence rates (70% versus 80%; p = 0.72, n = 20). There were no differences in leukemia cell morphology and immunophenotype between Cdh1-intact and Cdh1-deficient mice (CD3-/B220+/IgM-/Mac1-/Gr1- uniform blast cells with > 95% Ki67+). These results showed that Cdh1 is dispensable for Myc-related lymphoid leukemogenesis.
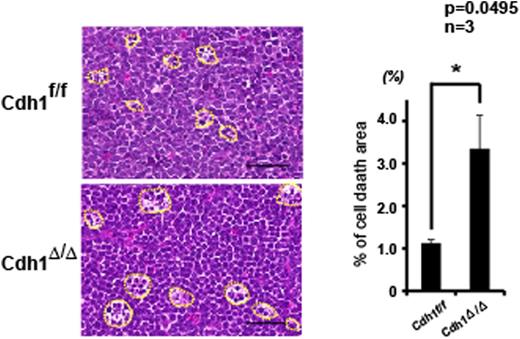
The survival of Cdh1-deficient B-ALL/LBL mice was slightly, but statistically significantly longer than the Cdh1-intact mice (median survival: 78 days versus 95 days in the Cdh1-deficient group; p = 0.0064, n = 14 and 9, respectively). In addition, histologic sections of affected lymph nodes showed more prominent “starry sky” pattern (focal cell death area) in the Cdh1-deficient group (Fig. 1, %area; 1.126 ± 0.083 versus 3.353 ± 0.788, p < 0.05, n = 3 for each), indicating that the cell fragility probably causes the better prognosis in this group. Furthermore, TUNEL-negative dead cells were observed in the Cdh1-deficient mice, suggesting non-apoptotic cell death.
We conducted DNA microarray analysis using GFP+ tumor cells derived from the bone marrow of Cdh1-intact or -deficient B-ALL/LBL mice (n = 3 for each). Biotin-labeled aRNA probes were synthesized from the total RNA and subjected to hybridization with a Mouse Genome 430 2.0 Array, Affymetrix. In GSEA analysis, three gene sets related to mitotic phase and DNA damage response were listed up in high normalized enrichment score (NES; 1.719 in “G2/M checkpoints”, 1.603 in “activation of ATR in response to replication stress” and 1.593 in “mitotic prometaphase”, p < 0.05). Furthermore, pHH3 or γH2A.X staining in the lesions showed that the event numbers of pHH3 or γH2A.X-positive cells in cell death area were significantly increased in Cdh1-deficient lymph node lesions (n=3, 3.0±1.0 vs 23.3±7.02/mm3, p < 0.01), indicating that the Cdh1-dificient tumor cells could be easily killed during mitotic phase due to DNA damage.
In order to investigate if Cdh1 loss affects the maintenance of B-ALL/LBL, we conducted secondary and tertiary transplantation. The prognosis apparently reversed, that is, the Cdh1-deficient group showed poorer prognosis in both of secondary and tertiary transplants (Fig. 2A, n = 6 for each, p = 0.0248 and p = 0.0004, respectively). Furthermore, we irradiated (4Gy) the mice on day 14 post-secondary transplantation and found that the Cdh1-deficient B-ALL/LBL mice were more radio-resistant than the others (Fig. 2B). These results can explain the hypothesis that Cdh1 loss-induced genetic instability due to abnormal G2/M checkpoint generated clones that were more resistant and had enhanced disease progression.
In conclusion, Cdh1 plays a crucial role in protecting Myc-induced B-ALL/LBL cells from genotoxic stress-induced cell death, probably as G2/M checkpoint regulator, and Cdh1 loss causes the generation of more resistant clones due to genetic instability.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


