Abstract
Targeting the epigenetic apparatus has become a successful treatment paradigm for the treatment of T-cell lymphomas (TCL), as demonstrated by the FDA approval of two histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, romidepsin and vorinostat. Romidepsin and vorinostat are pan-HDAC inhibitors, and their lack of enzyme specificity may be associated with toxicities that limit their clinical application. There is emerging evidence that the 11 classical HDAC isoforms, HDAC1-11, play different roles in oncogenesis, depending on the disease context. For example, HDAC3 has been strongly implicated in the survival of diffuse large B cell lymphoma, by interacting with STAT3. In T cells, HDAC1 and HDAC2 suppress lymphomagenesis in a dosage dependent manner, and are required to maintain the survival of TCL. Our hypothesis is that if different HDAC isoforms are involved in distinct cellular functions, then isoform selective HDAC inhibitors may be active in select subtypes of lymphoma, and that unique combinations of isofrom selective inhibitors could be used to more precisely target the relevant biology.
Cytotoxicity of isoform selective and nonselective HDAC inhibitors was determined in a panel of T cell lymphoma cell lines using a High Throughput Screening approach. Growth inhibition was determined using Cell TiterGlo that measures ATP produced by live and proliferating cells. The concentrations required to reach 50% of inhibition (IC50) were calculated from cells treated for 48 hours, using the CalcuSyn software. Cell death was determined by flow cytometry, using both Annexin V and propidium iodide as the probes. Finally, drug : drug synergy was determined by calculating relative risk ratio (RRR), as published previously. Values below 1 indicates synergy, and the smaller the RRR values the higher the level of synergy.
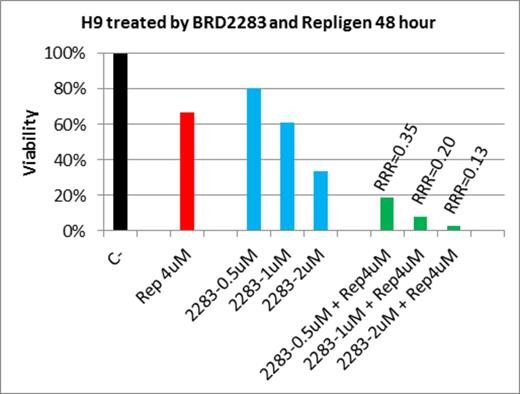
Isoform selective HDAC inhibitors as a rule were much less potent than nonselective HDAC inhibitors in their ability to inhibit the growth of TCL cells (Table 1). However, two HDAC1/2 selective inhibitors, BRD2283 and BRD6597, demonstrated IC50 values comparable to vorinostat in the H9 cell line, but not in any other cell lines. This may be due to unique epigenetic features in H9 that are sufficiently sensitive to the inhibition of only HDAC1 and 2. In contrast, other cell lines may have complex epigenetic abnormalities that are not sensitive to the inhibition of only HDAC1 and 2, but were nevertheless sensitive to inhibition of a broader spectrum of HDAC isoforms. To further confirm that inhibiting a broader array of HDAC enzymes may lead to more efficient growth inhibition, we investigated the effect of combining the HDAC1/2 inhibitor BRD2283 and the selective HDAC3 inhibitor repligen-136 on TCL cell growth. Figure 1 demonstrates that repligen-136 at the concentration of 4uM produced only 30% growth inhibition at 48-hour exposure. BRD2283 as a single agent produced 20, 30, and 65% of growth inhibition at the concentration of 0.5, 1, and 2uM, respectively. BRD2283 at these concentrations, combined with the mildly active repligen-136 at 4uM, produced 80, 90, and 95% of growth inhibition, respectively. The calculated RRR values were 0.35, 0.20, and 0.13, respectively, highly significant for synergistic drug : drug interaction. These results serve as a proof of principle that inhibition of a narrow spectrum of isoform specific HDAC enzymes may be sufficient to inhibit select lymphoma characterized by 'uncomplicated' epigenetic apparatus. In contrast, lymphoma with 'complicated' epigenetic abnormalities may require simultaneous inhibition of multiple HDAC isoforms, which may be achieved by combining HDAC inhibitors that target different HDAC enzymes. The combination approach, as compared to a single, non-selective HDAC inhibitor, may allow for more opportunity of personalized cancer treatment based on improved understanding of the precise epigenetic abnormalities in the lymphoma. We have begun a broader combinatorial screening approach to explore what specific set of isoform selective inhibitors recapitulate, or perhaps even improve upon, the activity seen with the pan HDAC inhibitors.
Synergy of HDAC1/2 and HDAC3 inhibitors in T cell lymphoma model H9
Synergy of HDAC1/2 and HDAC3 inhibitors in T cell lymphoma model H9
C-: Negative control
Rep: Repligen-136
2283: BRD2283 RRR: Relative risk ratio
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.