Abstract
Hypomethylating agents have changed treatment and outcomes in MDS and are active in AML patients. However a significant number of patients do not respond to 5-Azacytidine or Decitabine and there is no clinically validated assay that predicts response to 5-Azacytidine (5-Aza) or Decitabine (DAC). Clinical parameters and recently TET2 mutations have been identified as genetic predictors of response to 5-Aza. Several recent papers report on the possible predictive value of anti-apoptotic proteins, for example BCL2L10. In previous genome-scale RNA-interference (RNAi) screens anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members, most potently BCL-XL, were identified as top targets whose down-regulation sensitize to 5-Aza. Results were confirmed with the BCL-XL and BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-737, as well as the BCL-2-specific inhibitor ABT-199, both of which sensitized myeloid cells to 5-Aza. Although it is expected that interfering with anti-apoptotic genes would sensitize to hypomethylating similar to cytotoxics, few of the other >900 genes from our RNAi sensitizer screens, including few of the 571 kinases, sensitized to 5-Aza as potently as inhibition of BCL-XL. Thus BCL-2 family members constitute an especially potent context to modulate the activity of 5-Aza.
To assess if protein expression of the top targets BCL-XL, BCL-2 or MCL-1 correlate with and may explain a preferential sensitization, 577 primary AML samples were examined by Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA). There was substantial overlap of expression across and within FAB subgroups and cytogenetics, and expression of neither of these genes/proteins could explain the observed effects. This may be expected due to functional redundancies amongst the different anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members, as well as distinct, yet overlapping binding affinities between anti- and pro-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins and BH3 peptides.
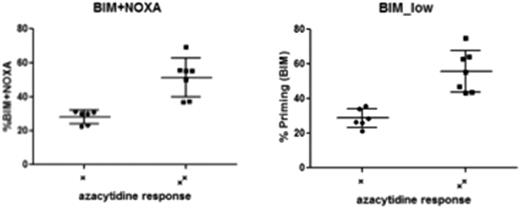
Thus, we next aimed to functionally interrogate the overall balance of pro- and anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members, also described as “primedness” by BH3 profiling. This assay uses peptides derived from pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins to determine the capacity of cells to initiate apoptosis in response to pro-apoptotic BH3 molecules [anti-apoptotic BCL-2 molecules like BCL-XL and BCL-2 bind and inhibit BH3-only molecules]. This assay is a broad functional readout that incorporates many parameters including the consequences of varying BCL2L10 expression.
BH3 metrics distinguish cell lines with higher EC 50 (> 2uM) from those with lower EC50 (generally < 1uM).
BH3 metrics distinguish cell lines with higher EC 50 (> 2uM) from those with lower EC50 (generally < 1uM).
In conclusion, due to significant expression overlap and functional redundancies of the BCL-2 family proteins, expression does not correlate with 5-Aza clinical or in vitro responses. However, BH3 profiling as a general functional readout of apoptotic primedness, significantly discriminated responses in patients as well as in vitro. Thus, BH3 profiling incorporates the entirety of pro- and anti-apoptotic molecules (including BCL2L10) and is promising to predict responses to hypomethylating agents. We propose to prospectively validate BH3 profiling as a predictive biomarker assay for 5-Aza or DAC based regimens.
Pierceall:Eutropics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Lena:Eutropics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Cardone:Eutropics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Elashoff:Eutropics: Employment. Blake:Noel Blake: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.