Abstract
Background. Rituximab improved outcomes of all CD20+ non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) subtypes. Rituximab induces a transient B-cell depletion and a dose-dependent T-cell inactivation (Stroopinsky et al., Cancer Immunol Immunother 2012) predisposing to T-cell dependent infections and to a potential impaired T-cell immunosurveillance. Secondary neoplasms (SN) is infrequent in trials including rituximab and the SN risk associated to rituximab across multiple trials has not been reported. We performed a systematic review of published trials comparing chemotherapy with or without rituximab to evaluate SN occurrence.
Methods. Our primary endpoint was SN risk in patients with NHL treated with rituximab. We searched PubMed and Embase databases for randomised controlled trials on rituximab and lymphoma where rituximab constituted the only difference between treatment arms and where SN incidence or SN related death were reported. Authors were contacted for SN related rituximab exposure if not detailed. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and HIV-related lymphomas were excluded due to increased risk of SN. Updated follow-up of eligible trials presented at annual meetings of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and American Society of Hematology were retrieved. Data were extracted independently by two authors. A random effects DerSimonian-Laird meta-analysis was performed to estimate the summary effect of rituximab on the hazard of SN. Statistical heterogeneity was tested using Woolf test.
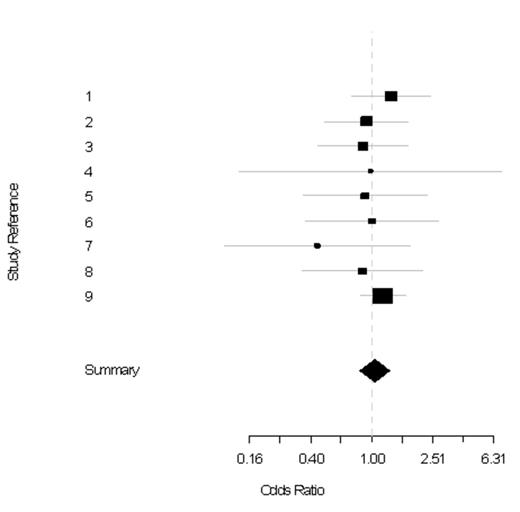
Results. We identified nine trials cumulating 4621 patients with 2312 exposed to rituximab and 2309 not exposed. These nine trials are known with the following names: PRIMA (1), GELA LNH98.5 (2), MINT (3), CORAL (4), IELSG-19 (5), EORTC20981 (6), OSHO#39 (7), SAKK 35/98 (8), RICOVER60 (9). Histology were diffuse large B cell (n=4), follicular (n=4) and marginal zone (n=1) lymphomas. Median age was 58.1 years. Sex distribution was available for seven trials with 1650 (47.6%) women and 1814 (52.4%) men. In all these trials but one (SAKK 35/98), rituximab was used associated with chemotherapy: CHOP, CHOEP, FCM, MCP, DHAP, ICE, or chlorambucil. At a median follow-up of 73 months [interquartile range: 72-84], a total of 334 SN was observed, including 169 SN in patients randomised to rituximab as compared to 165 SN in patients not randomised to rituximab (OR= 0.88; 95%CI: 0.66-1.19) (Figure 1). No evidence of significant heterogeneity was noticed across trials (p = 0.93). Notably, the proportion of females, histology subtypes, use of rituximab in first line, and use of rituximab over prolonged periods in maintenance did not influence SN risk (p = 0.94, p = 0.80, p = 0.87, p = 0.87 respectively). The SN risk was not increased in protocols administrating rituximab over periods of 8 months to 12 months (CORAL , OSHO#39) as opposed to periods of 24 months (PRIMA, EORTC20981) (p=0.86).
Conclusions. This meta-analysis of nine trials randomising rituximab in NHL patients suggests no SN predisposition at a median follow-up of 6 years. SN risk associated with the combination of rituximab and new targeted therapies warrants prospective monitoring.
Standard meta-analysis plot of the odds ratio of SN prevalence in the rituximab arm compared to the control arm
Standard meta-analysis plot of the odds ratio of SN prevalence in the rituximab arm compared to the control arm
Fleury:Lundbeck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Preceptorship Other. Pfreundschuh:Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Onyx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Spectrum: Research Funding. Salles:Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding. van Oers:Roche: Consultancy. Gisselbrecht:Roche: Research Funding. Zucca:Roche: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Johnson and Johnson: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Herold:Roche Pharma AG/Germany: Honoraria, Research Funding. Ghielmini:Roche: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.