Abstract
Background: Follicular lymphoma (FL) is an indolent lymphoma generally considered incurable with current standard therapies. Recent advances have resulted in prolongation of overall survival (OS) for patients with FL such that death from competing causes may now limit the mortality impact of FL in some patient groups. Identification of patients for whom FL related mortality is expected to be minimal, or conversely those at high risk of disease related mortality, is highly clinically relevant. We recently reported (Maurer et al, JCO 2014;32:1066-73) that event-free survival (EFS) at 24 months from diagnosis is a robust endpoint for disease related outcome in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Here we use the same approach to assess if landmark timepoints of EFS can stratify subsequent OS in FL.
Methods: All newly diagnosed grade 1-3a FL patients enrolled on the University of Iowa/Mayo Clinic Lymphoma SPORE Molecular Epidemiology Resource (MER) from 2002-2011 were eligible. Patients with grade 3b FL, transformation, or presence of DLBCL at diagnosis were excluded. EFS was defined as time from diagnosis to progression, relapse, re-treatment, or death due to any cause. EFS12 was defined based on EFS status 12 months after date of diagnosis; we also assessed EFS at 24 months. OS was defined as time from a specific timepoint (diagnosis, event, or EFS12) until death due to any cause. OS was compared to age and sex matched survival in the general US population using an expected survival approach and standardized mortality ratios (SMR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Outcomes were examined in all patients as well as selected subsets defined by initial treatment. Replication was performed using a Lyon, France hospital registry of newly diagnosed grade 1-3a FL patients enrolled from 2002-2010 with survival compared to French population data.
Results: 936 patients with grade 1-3a FL were eligible from the MER. The median age at diagnosis was 60 years (range 19-91) and 53% were male. 86% had grade 1-2 disease and 14% grade 3a disease. 23% had high-risk disease (FLIPI score ≥3). 347 (37%) were initially treated with alkylator or anthracyline based immunochemotherapy (IC), 113 (12%) rituximab monotherapy (RM), and 318 (34%) were initially observed; the remaining patients received radiation for limited stage disease (8%), chemotherapy without rituximab (4%), or other therapy (5%). At a median follow-up of 59 months (range 1-131), 403 patients (43%) had an event and 120 patients (13%) had died; 155 patients (17%) failed to achieve EFS12.
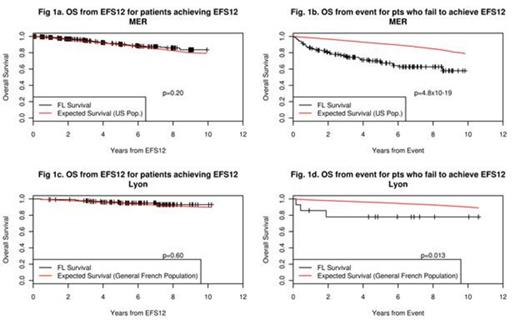
From diagnosis, patients with FL had inferior OS compared to the general population (SMR=1.24, 95% CI: 1.03-1.48, p=0.018); results were similar for patients with grade 1-2 (SMR=1.23) and grade 3a (SMR=1.29) disease. The survival deficit was eliminated in patients who achieved EFS12 (SMR=0.85, 95% CI: 0.66-1.09, p=0.20, Fig 1a), and so we did not pursue modeling EFS24. In contrast, patients with a non-death event (relapse, retreatment, or progression) within 12 months of diagnosis had inferior subsequent OS (SMR=3.90, 95% CI: 2.89-5.25, p=4.8x10-19, Fig 1b). These results were replicated in 153 FL patients from the Lyon registry: patients who achieved EFS12 had equivalent subsequent OS to the general French population (SMR=0.82, 95% CI: 0.39-1.72, p=0.60, Fig 1c), while patients who failed to achieve EFS12 had poor subsequent OS (SMR=4.16, 95% CI: 1.34-12.91, p=0.013, Fig 1d). In subset analysis of the MER, patients achieving EFS12 initially treated with IC (SMR=0.98, 95% CI: 0.63-1.54, p=0.93), RM (SMR=0.66, 95% CI: 0.31-1.38, p=0.27), or observation (SMR=0.73, 95% CI: 0.47-1.15, p=0.18) had equivalent OS to the population. In contrast, for patients not achieving EFS12, OS after event was inferior for those treated with IC (SMR=15.0, 95% CI: 10.22-22.05, p=2.0x10-43) or RM (SMR=4.96, 95% CI: 1.24-19.84, p=0.023), while trending towards inferior for those initially observed (SMR=1.55, 95% CI: 0.81-2.99, p=0.19).
Summary: Events within the first 12 months of diagnosis are associated with poor OS in FL, especially in patients treated with IC, while patients achieving EFS12 have excellent subsequent survival, overall and in the main treatment subsets. Prognosis for FL patients should be recalibrated at 12 months from diagnosis. EFS12 will be useful in counseling and should be considered as an endpoint in studies of newly diagnosed FL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.