Abstract
Introduction
Genetic aberrations of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily 14 (TNFRSF14, also known as HVEM) have been shown to occur at high frequencies in patients (pts) with follicular lymphoma (FL). HVEM is a ligand for B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) which negatively regulates T cell responses and BTLA stimulation reduces acute graft-versus-host disease (aGvHD) in murine allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (AHCT) models. As activated FL B cells are potent alloantigen presenting cells, we hypothesized that TNFRSF14 aberrations in FL B cells would reduce expression of HVEM and potentiate capacity of FL B cells to stimulate allogeneic T cell responses. We therefore sought to determine the functional effect of TNFRSF14 aberrations on FL B cell-stimulated donor T cell alloresponses in vitro. We also examined the impact of TNFRSF14 aberrations on the outcome of FL pts after HLA-matched reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) AHCT.
Results
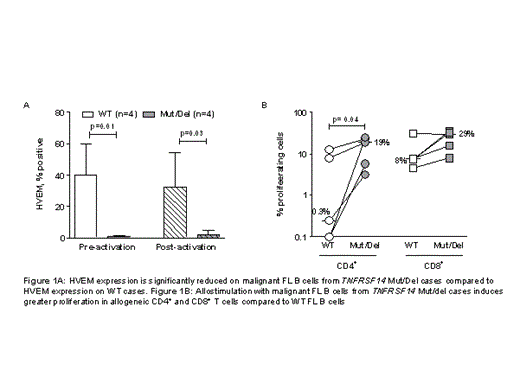
FL B cells from lymph nodes were FACS-sorted (>90% purity and > 95% light chain restriction), activated and used as stimulators in mixed lymphocyte reactions with purified allogeneic responder CD3+ T cells. HVEM expression on FL B cells from pts with biallelic TNFRSF14 aberrations (Mut/Del cases) was undetectable whereas 40% of FL B cells from TNFRSF14 WT cases expressed HVEM (Fig 1 A). In contrast, FL B cells from Mut/Del and WT cases expressed similar levels of MHC class I/II, CD80, CD86 and CD58 before and after activation. Allostimulation with Mut/Del FL B cells resulted in significantly greater expression of activation markers on responder CD4+ T cells, increased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2) measured by ELISA and increased frequencies of cytokine-secreting CD4+ and CD8+ T cells enumerated by intracellular cytokine staining. Responder T cell proliferation by thymidine incorporation was significantly greater after stimulation with Mut/Del FL B cells compared to WT FL B cells. CFSE labeling studies demonstrated that this effect resulted from increased proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ responder T cells after both primary (Fig 1B) and secondary allostimulation. To determine if the increased alloresponses we observed using FL B cells from TNFRSF14 Mut/Del cases was due to reduced HVEM-BTLA signaling, we performed allogeneic co-cultures in the presence of antagonist or agonist BTLA antibodies (ab). Antagonist anti-BTLA ab increased proliferation of responder T cells after stimulation with WT FL B cells confirming that BTLA limits alloresponses in our in vitro model. Importantly, agonist BTLA ab reduced alloresponses stimulated by Mut/Del FL B cells.
We next sought to determine if the increased alloresponses we detected in vitro in FL pts with TNFRSF14 aberrations resulted in an increase in clinical alloreactivity after AHCT. DNA from lymph nodes from FL pts undergoing T-cell replete RIC AHSCT was screened for TNFRSF14 mutations and deletions by Sanger sequencing and multiplex ligation-probe amplification respectively. Cumulative incidences (CI) of aGvHD and GvHD-related death were calculated with FL progression as a competing risk. TNFRSF14 aberrations were identified in 10/21 pts prior to RIC AHCT (4 Mut/Del, 1 Del/Del, 1 Mut/WT, 4 Del/WT). Most (18/21) pts had evidence of ongoing FL pre-transplant. Disease and donor characteristics were similar in pts with and without aberrations. There was no significant difference in CI of aGvHD in pts with or without TNFRSF14 aberrations. However there was a significantly higher CI of fatal aGvHD in patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations (45%) compared to those without aberrations (0%, p<0.01). Interestingly, relapse was less frequent in patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations consistent with increased graft-versus-tumor effects, although this did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusion
This study is the first to describe the impact of TNFRSF14 aberrations on the allostimulatory capacity of FL B cells. TNFRSF14 aberrations were associated with enhanced T-cell alloresponses in vitro and increased death from aGvHD. Importantly, our results suggest FL patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations may benefit from more aggressive immunosuppression to prevent fatal aGvHD after AHCT. The increased antigen-presenting capacity of FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations could also influence autologous anti-tumor responses and impact outcome after other treatment modalities.
Gribben:Celgene: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.