Abstract
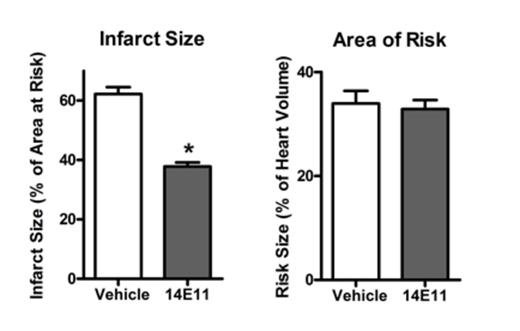
The role of the intrinsic coagulation pathway in acute myocardial infarction is poorly defined. Both coagulation factors XII (FXII) and XI (FXI) support experimental thrombus propagation in animals. Additionally, humans with FXI deficiency have a lower incidence of thrombosis and stroke, however no such association has been established for FXII. Curiously, the incidence of previously verified myocardial infarction (MI) among 96 surviving FXI deficient subjects that were interviewed in an epidemiologic study was found to be similar to or possibly even higher than the recorded incidence of MI in an age/sex matched dataset from morbidity/mortality statistics of the general Israeli population (Salomon et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:658). However, the outcome of these coronary events were not reported, except for the fact that all interviewed FXI subjects were alive at the time of the interview. To investigate the contribution of FXI activation by FXIIa in experimental MI, we used a standard mouse model of acute myocardial ischemia (AMI). To inhibit FXI in the mouse, we utilized our monoclonal antibody (14E11) that targets the Apple 2 domain of FXI, and has been shown in vitro to inhibit the activation of FXI by factor XIIa, while not significantly inhibiting activation of FXI by thrombin. To evaluate the efficacy of 14E11 in reducing ischemic injury in mice, the left coronary artery (LCA) of wildtype male mice was reversibly ligated for 40 min, and 14E11 (1 mg/kg; iv) or vehicle was infused during the last 15 min of occlusion. Occlusion was confirmed by sustained S-T elevation, regional cyanosis and wall motion abnormalities. Following occlusion, the ligature was removed and the heart reperfused for 2 hr. To delineate the area of risk and ischemia, the LCA was re-occluded at 2 hr post-reperfusion and fluorescent polymers infused into the apex of the heart. The heart was excised, cut into 1 mm thick transverse slices and photographed under UV light to identify the area at risk. Tissue sections were additionally stained with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride solution and infarcted areas evaluated via morphometric analysis. The area at risk was evaluated as the percent of total heart volume and infarct size was calculated as the percentage of area at risk. Our results indicated that the area of risk did not differ between treatment groups, however treatment with 14E11 reduced infarct volume by 33% (p<0.05, n=10) compared with vehicle control (n=10). These results suggest that FXII-mediated activation of FXI contributes to the pathology of experimental MI in mice. Since FXII has no hemostatic function, we conclude that the data warrant further evaluation of whether systemic anticoagulation by selective inhibition of FXII-mediated FXI activation before interventional reperfusion is safe and reduces infarct size in patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Lorentz:Aronora, Inc: Employment. Verbout:Aronora, Inc: Employment. Tucker:Aronora, Inc: Employment, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gruber:Aronora, Inc: Employment, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.