Abstract
Introduction: AL amyloidosis is a very heterogeneous disease. Prognosis is a function of organ tropism, extent of organ damage, and ability of tissues to heal, the last of which relates both to hematologic response and intrinsic toxicity of the light chain. Using mass spectroscopy (MS) technology, we are able to distinguish immunoglobulin light chain variable gene family (IGVL) usage on clinical samples. The goal of this study was to evaluate if IGVL usage impacts patient outcomes in patients with light chain amyloidosis (AL).
Methods: IGVL usage was determined by mass spectroscopy (MS) of amyloid in clinical tissue specimens of Mayo Clinic patients. Specimens were from fat pad (n=257), bone marrow (n=172), myocardium (n=113), gastrointestinal (n=58), kidney (n=20), lung (n=15), and nerve (n=5). For those cases for which the IGVL could not be identified--not otherwise specified (NOS)—but constant region could be identified as lambda or kappa, we assume that the amyloid consisted primarily of immunoglobulin light chain gene constant regions or variable genes with somatic mutations making them uninterpretable to our matching algorithms. The medical records from these 700 patients were abstracted for relevant clinical and laboratory data.
Results: The baseline characteristics of patients are shown in table 1. Three hundred and thirty-two patients have died with a median follow-up of surviving patients of 38 months. The estimated median survival for the entire population is 59 months. Out of 700 patients, 214 (31%) achieved a CR or a VGPR, 432 (62%) were not evaluable (NE) for hematologic or organ response, and 54 (8%) achieved a PR or did not respond (NR).
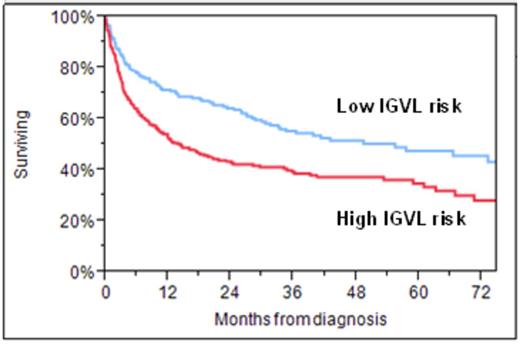
The distribution of IGVL cases is shown in table 2. Overall survival (OS) for the whole group was not different across different IGVLs on univariate analysis, but when corrected for hematologic response, outcomes differed significantly based on IGVL. Patients could be further assembled into two groups, based on risk for death on univariate analyses: an IGVL high risk, which included KV1, LV1, LV2, LV3, and LV6; and low risk, which included all other cases (Figure). In a multivariate model that included level of hematologic response (CR/VGPR versus PR/NR/NE) and IGVL, IGVL family was independently associated with overall survival (RR=1.5 (95% CI 1.2-1.9, p=0.008). The risk ratio for CR/VGPR was 0.28 (95% CI 0.20-0.38, p<0.0001). This effect persisted when either the Mayo 2006 or the 2012 staging system was included in the multivariate.
Conclusion: IGVL usage appears to have prognostic significance in patients who have not achieved VGPR or better to initial chemotherapy.
Baseline characteristics of patients
| . | N= 700 . |
|---|---|
| Age | 63 (32-94) |
| Male, (%) | 447 (64%) |
| Biopsy site | |
| Solid organ/Soft tissue | 271 (39%) |
| Fat pad | 257 (37%) |
| Bone Marrow | 172 (25%) |
| Organ involvement | |
| Cardiac | 432 (62%) |
| Renal | 346 (49%) |
| Gastrointestinal | 168 (24%) |
| Liver | 56 (8%) |
| Nerve | 107 (15%) |
| Lung | 42 (6%) |
| Soft Tissue | 92 (13%) |
| Organs involved | |
| 1 | 321 (46%) |
| 2 | 228 (33%) |
| ≥3 | 151 (22%) |
| Laboratory characteristics | |
| NTBNP, pg/ml | 2547 (11.3-70000) |
| Troponin, ng/ml | 0.03 (0.001-0.84) |
| dFLC, mg/dl | 26 (0.04-2330) |
| Cardiac Stage | |
| 1 | 59 (18%) |
| 2 | 125 (38%) |
| 3 | 144 (44%) |
| . | N= 700 . |
|---|---|
| Age | 63 (32-94) |
| Male, (%) | 447 (64%) |
| Biopsy site | |
| Solid organ/Soft tissue | 271 (39%) |
| Fat pad | 257 (37%) |
| Bone Marrow | 172 (25%) |
| Organ involvement | |
| Cardiac | 432 (62%) |
| Renal | 346 (49%) |
| Gastrointestinal | 168 (24%) |
| Liver | 56 (8%) |
| Nerve | 107 (15%) |
| Lung | 42 (6%) |
| Soft Tissue | 92 (13%) |
| Organs involved | |
| 1 | 321 (46%) |
| 2 | 228 (33%) |
| ≥3 | 151 (22%) |
| Laboratory characteristics | |
| NTBNP, pg/ml | 2547 (11.3-70000) |
| Troponin, ng/ml | 0.03 (0.001-0.84) |
| dFLC, mg/dl | 26 (0.04-2330) |
| Cardiac Stage | |
| 1 | 59 (18%) |
| 2 | 125 (38%) |
| 3 | 144 (44%) |
Variable region family distribution.
| Light Chain N=700 . | N (%) . |
|---|---|
| KV1 | 107 (15%) |
| KV2 | 3 (0.4%) |
| KV3 | 17 (2%) |
| KV4 | 25 (4%) |
| KV6 | 1 (0.1%) |
| LV1 | 85 (12%) |
| LV2 | 64 (9%) |
| LV3 | 118 (17%) |
| LV4 | 3 (0.4%) |
| LV6 | 97 (14%) |
| LV8 | 1 (0.1%) |
| LV9 | 1 (0.1%) |
| Kappa NOS1 | 34 (4%) |
| Lambda NOS1 | 140 (19%) |
| Heavy chain amyloidosis | 4 (0.6%) |
| Light Chain N=700 . | N (%) . |
|---|---|
| KV1 | 107 (15%) |
| KV2 | 3 (0.4%) |
| KV3 | 17 (2%) |
| KV4 | 25 (4%) |
| KV6 | 1 (0.1%) |
| LV1 | 85 (12%) |
| LV2 | 64 (9%) |
| LV3 | 118 (17%) |
| LV4 | 3 (0.4%) |
| LV6 | 97 (14%) |
| LV8 | 1 (0.1%) |
| LV9 | 1 (0.1%) |
| Kappa NOS1 | 34 (4%) |
| Lambda NOS1 | 140 (19%) |
| Heavy chain amyloidosis | 4 (0.6%) |
1 No IGVL family could be identified
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.