Abstract
Elevated levels of fetal hemoglobin (HbF) ameliorate the clinical symptoms of beta-thalassemia and sickle cell anemia. The transcription factor B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A (BCL11A) is required for silencing of gamma-globin expression in adult erythroid cells and functions as a switch from fetal to adult hemoglobin production in humans. BCL11A therefore constitutes a therapeutic target for the treatment of hemoglobinopathies. We inactivated BCL11A function by double-strand DNA break-induced mutagenesis using Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs). 20 to 30% gene editing could be achieved in vitro in human and nonhuman primate CD34+ cells by TALEN mRNAs electroporation targeting exon 2 of Bcl11a. Colony-forming efficiency was slightly lower in Bcl11a-edited CD34+ cells but lineage differentiation potential was unchanged. Erythroid differentiation of CD34+ cells in culture showed increased Fetal to Beta hemoglobin ratio in both human and primate Bcl11a-modified cells as compared to control cells, thus validating our editing approach to increase HbF production.
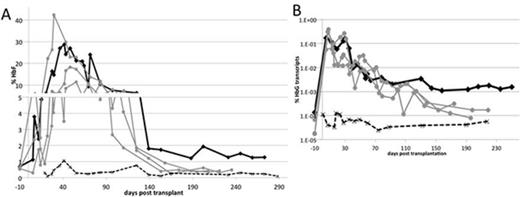
To determine if Bcl11a-edited hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) could be engrafted and give rise to HbF-producing erythrocytes, we transplanted a pigtail macaque with autologous CD34+ electroporated with Bcl11a TALEN mRNA following conditioning by total body irradiation. We detected about 1 % gene disruption in vivo early post-transplant and disruption frequency gradually declined to reach a set point of about 0.3% starting at day 28 post-transplantation. In this analysis, which we have so far taken out to 42 days, single clones could be tracked based on their mutation signature, and we found that several clones persisted over time, confirming engraftment of Bcl11a-modified cells. Since the transplantation procedure and chemo-radiotherapy conditioning can raise HbF production, three control animals that were transplanted using similar conditions as with the Bcl11a-edited HSCs and one untransplanted animal were also included in our analysis. Flow cytometry measurement of HbF in peripheral blood showed a rapid increase in F-cell production in all animals, reaching levels that ranged from 10% to 40% by 30 days, while the untransplanted control showed basal HbF expression of about 0.5% (Fig. 1A). The peak for HbF expression lasted for about 140 days and eventually returned to basal levels that averaged 0.5% for all control animals. In comparison, the animal transplanted with Bcl11a-edited cells showed significantly higher HbF levels starting at day 140 post-treatment (1-1.5%), and HbF production has remained constant for at least 150 days. This result was confirmed by hemoglobin mRNA analysis in peripheral blood using real-time PCR. We found a rapid increase in gamma globin expression following transplantation, before returning to near basal levels. As compared to controls, the animal transplanted with Bcl11a-edited cells showed a 5 to 10-fold increase in gamma to beta globin ratio at day 140 and this ratio has remained constant ever since (Fig. 1B). We are currently working on ways to enhance Bcl11a-editing and to select for Bcl11a-modified HSCs using targeted integration of the chemoselection cassette P140K MGMT to ultimately achieve curative HbF production. Potential TALEN off-target sites will also be examined as well as any side effect associated with the inactivation of BCL11A. Overall, our data demonstrate that transplantation of Bcl11a-edited HSCs results in elevated HbF production in nonhuman primates. Furthermore, we show that nonhuman primates can serve as a useful model for novel gene editing strategies toward the treatment of hemoglobinopathies.
In vivo monitoring of HbF expression by flow cytometry and real-time PCR. (A) Intracellular HbF staining of peripheral blood measured by flow cytometry. (B) Real-time PCR analysis of hemoglobin transcripts in RNA isolated from peripheral blood. Expression was normalized to GAPDH and %HbG is calculated as HbG/(HbG+HbB). HbG=gamma globin; HbB=beta globin. Black line=Bcl11a transplant; grey line=control transplant; dashed line=untransplanted control.
In vivo monitoring of HbF expression by flow cytometry and real-time PCR. (A) Intracellular HbF staining of peripheral blood measured by flow cytometry. (B) Real-time PCR analysis of hemoglobin transcripts in RNA isolated from peripheral blood. Expression was normalized to GAPDH and %HbG is calculated as HbG/(HbG+HbB). HbG=gamma globin; HbB=beta globin. Black line=Bcl11a transplant; grey line=control transplant; dashed line=untransplanted control.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.