Abstract
Lower Gastrointestinal Graft versus Host Disease (GI GVHD) is a major cause for GVHD related non-relapsed mortality (NRM). High dose corticosteroid is the initial therapy for suspected lower GI GVHD, and additional therapy is often required for steroid refractory cases. The identification of high-risk patients is critical as timely intensification of treatment through early institution of second line therapy improves outcomes. To develop a reliable lower GI GVHD risk scoring system, Gastrointestinal Acuity Score (GAS), we evaluated 210 consecutive patients who underwent endoscopic biopsy for suspected lower GI GVHD within 6 months from the transplant from 2009 to 2012 at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.
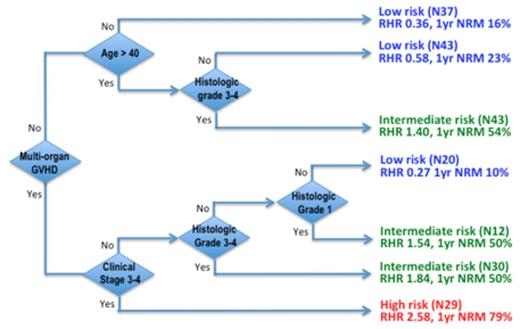
We first identified 5 significant prognostic factors that accounted for the increased NRM in lower GI GVHD using univariate analysis: histologic grade, clinical stage, age, multi-organ GVHD, and donor type (Table 1). Gender, donor cell type, conditioning regimen (myeloablative vs non-myeloablative), time of diagnosis, disease status did not significantly influence NRM. Next, we performed multivariate Classification and Regression Tree (CART) analysis that utilizes sequential binary decision nodes to categorize 197 patients into subgroups according to their risk profile and outcome (Figure 1). The decision tree identified 7 subgroups starting with the presence of multi-organ GVHD as the first major decision node. This was followed by clinical stage 3/4, Age > 40 years, histology grade 3/4, and histology grade 1. We then consolidated subgroups with comparable risk profiles into low, intermediate, and high NRM risk groups (Figure 1).
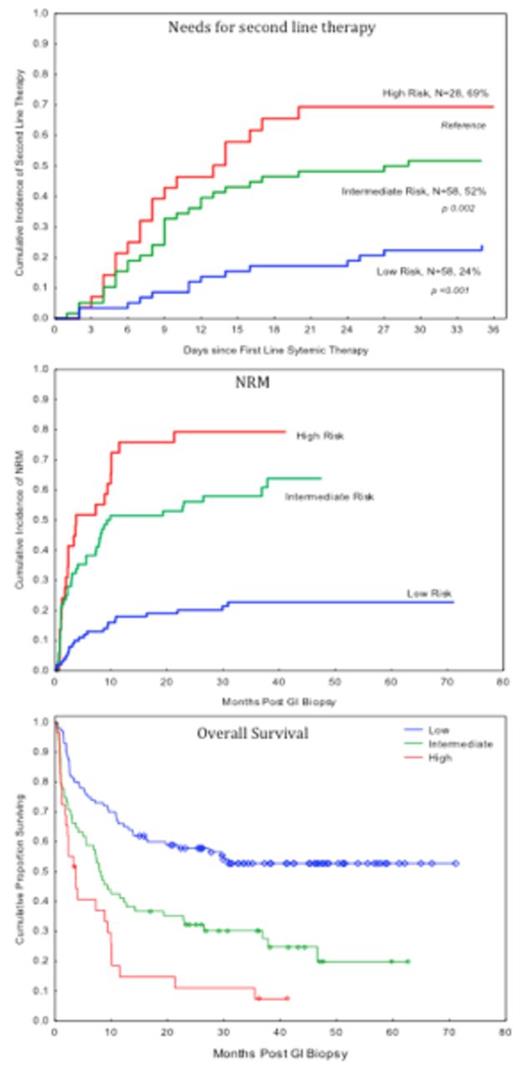
The 3 NRM risk groups correlated with day 28 response, the need for second line therapy and overall survival (Figure 2). The complete response rates at day 28 from the initiation of steroid therapy were significantly lower in the high (15%, p<0.001) and intermediate (43%, p=0.003) risk group compared to the low-risk group (70%). Accordingly, the high-risk patients were 4.3 (p < 0.001) and 1.6 (p=0.02) folds more likely to need second line therapy compared to low and intermediate risk patients, respectively. The intermediate risk patients were 2.7 (p=0.02) folds more likely to need second line therapy compared to the low risk group. In addition, the high-risk group was associated with the highest NRM (HR 5.4, p<0.001), followed by the intermediate risk (HR 3.8, p<0.001) compared to the low risk group. This translated into worse overall survival at 1 year for the high-risk patients. Lastly, there was a trend towards a lower chronic GVHD rate in the low risk group (25%, HR=0.6, p 0.06) compared to the high and intermediate risk groups (37%).
In conclusion, we developed a novel risk scoring system, Gastrointestinal Acuity Score (GAS), incorporating histologic grades and clinical factors through multivariate CART analysis, and demonstrated that GAS predicts both early outcomes (day 28 CR rate and need for second line therapy) and late outcomes (NRM and overall survival) in patients with lower GI GVHD. Once prospectively validated in a larger cohort of lower GI GVHD patients, it will be of great use for clinicians with limited access to GVHD biomarker analysis in making treatment decisions as our new risk scoring system utilizes readily available variables.
Univariate Analysis of risk factors for NRM at 1 year in Lower GI GVHD
Alousi:Therakos, Inc: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.