Abstract
Background: The response to treatment and overall survival of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are heterogeneous. A number of prognostic factors related to patient and tumor characteristics have been described for AML, including age, performance status, and karyotype. The depletion of skeletal muscle (sarcopenia) and adipose tissue (adipopenia) are known to be associated with unfavorable prognosis in patients with some malignant diseases including lymphoma. Here, we studied the impact of sarcopenia and adipopenia on clinical outcomes of adult AML.
Patients and Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 70 patients with adult AML (age ≥ 18 years) who received chemotherapy at Gifu University Hospital between December 2004 and September 2014. Skeletal muscle and adipose tissue were measured by the analysis of CT images at the L3 level before treatment. CT images were analyzed using SliceOMatic version 4.3 software (TomoVision, Montreal, QB, Canada), which enables specific tissue demarcation using previously reported Hounsfield unit (HU) thresholds. The CT HU thresholds were -29 to 150 for skeletal muscles and -190 to -30 and -50 to -150 for subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue, respectively. These values were normalized for stature in order to calculate skeletal muscle index (SMI, cm2/m2) and adipose tissue index (ATI, cm2/m2).
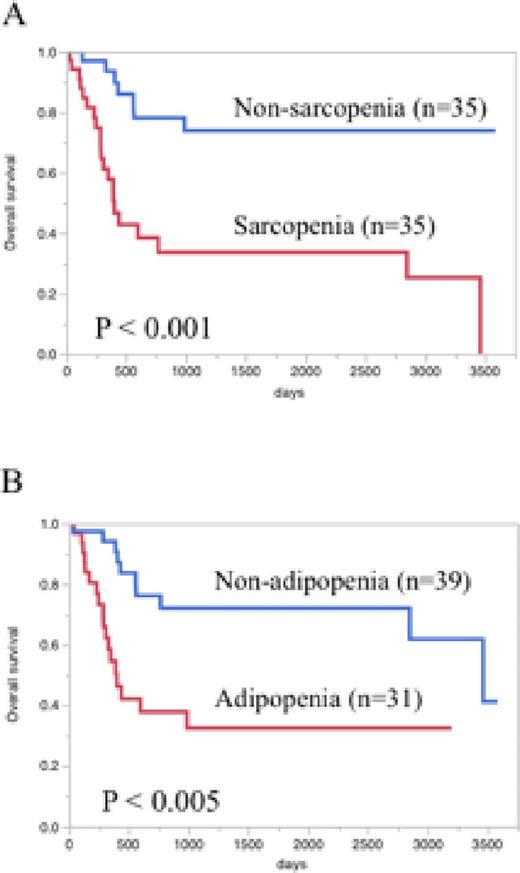
Results: Median age at diagnosis was 57 years (18-84 years), with 37 males and 33 females. SMI was significantly higher in male than female patients (P < 0.001). ATI was significantly higher in patients aged 60 years and over than in those under 60 years (P < 0.05). The sex-specific cut-offs for the SMI and ATI were determined by ROC curve analysis. Thirty-five (50%) and 31 (44%) patients were defined as sarcopenia and adipopenia, respectively. Sarcopenia and adipopenia did not significantly differ among various FAB subtypes or cytogenetic risk profiles. The rate of patients with poor performance status (ECOG ≥ 2) was significantly higher in the sarcopenic group (80% vs 45%, P < 0.05), whereas not in the adipopenic group (40% vs 47%). With a median follow-up of 33.5 months, the 3-year overall survival (OS) in the sarcopeniac group was 34% compared with 74% in the non-sarcopenic group (P < 0.001, Figure 1A) and 32% in the adipopenic group compared with 72% in the non-adipopenic group (P < 0.005, Figure 1B). In a multivariate analysis, sarcopenia (HR = 2.84, CI = 1.08-8.08, P < 0.05) and adipopenia (HR = 2.85, CI = 1.19-7.24, P < 0.05) remained predictive of OS.
Conclusion: Sarcopenia and adipopenia are independent prognostic factors in patients with AML. Evaluation of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue depletion by CT imaging is a useful objective tool to predict patient outcomes, but a larger prospective study is needed to confirm this effect.
Overall survival according to sarcopenic (A) and adipopenic (B) status.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.