Key Points
Pericytes function as oxygen sensors and are major sites of erythropoietin production in the hypoxic brain.
The ability to synthesize erythropoietin is a functional feature of pericytes in the brain and kidney.
Abstract
A classic response to systemic hypoxia is the increased production of red blood cells due to hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-mediated induction of erythropoietin (EPO). EPO is a glycoprotein hormone that is essential for normal erythropoiesis and is predominantly synthesized by peritubular renal interstitial fibroblast-like cells, which express cellular markers characteristic of neuronal cells and pericytes. To investigate whether the ability to synthesize EPO is a general functional feature of pericytes, we used conditional gene targeting to examine the von Hippel-Lindau/prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain (PHD)/HIF axis in cell-expressing neural glial antigen 2, a known molecular marker of pericytes in multiple organs. We found that pericytes in the brain synthesized EPO in mice with genetic HIF activation and were capable of responding to systemic hypoxia with the induction of Epo. Using high-resolution multiplex in situ hybridization, we determined that brain pericytes represent an important cellular source of Epo in the hypoxic brain (up to 70% of all Epo-expressing cells). We furthermore determined that Epo transcription in brain pericytes was HIF-2 dependent and cocontrolled by PHD2 and PHD3, oxygen- and 2-oxoglutarate–dependent prolyl-4-hydroxylases that regulate HIF activity. In summary, our studies provide experimental evidence that pericytes in the brain have the ability to function as oxygen sensors and respond to hypoxia with EPO synthesis. Our findings furthermore suggest that the ability to synthesize EPO may represent a functional feature of pericytes in the brain and kidney.
Introduction
A classic response to hypoxia is the rise in red blood cell (RBC) numbers, which increases the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood and thus improves tissue oxygenation.1 This prototypical hypoxia response is mediated by the glycoprotein hormone erythropoietin (EPO), which is mainly produced in kidney and liver and induces erythropoiesis by preventing apoptosis of erythroid precursor cells.2
In the kidney, the main source of EPO in adults, a small number of erythropoietin-producing cells (EPCs) is found in the cortico-medullary region at baseline, whereas under hypoxic conditions, renal EPCs increase in number and expand spatially toward the outer cortex.2 Renal EPCs are derived from forkhead box D1 (FOXD1) stroma and express a variety of cellular markers characteristic of pericytes and neuronal cells.3,4 These include platelet derived growth factor receptor-β polypeptide (PDGFRB) and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 (CSPG4), also known as high-molecular-weight melanoma-associated antigen or neuro-glial antigen 2 (NG2), as well as microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2) and neurofilament protein light polypeptide (NF-L).3-5 Although the kidney is the main site of adult EPO synthesis, systemic hypoxia, anemia, or genetic defects in the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) pathway trigger EPO production in other tissues such as liver.6-10 Research into nonrenal sites of EPO production has also identified neurons and astrocytes as sources of EPO.6,11-13 However, the role and relative contribution of these and other cerebral cell types to the brain’s EPO response has not been defined.
Pericytes or vascular mural cells are perivascular cells that wrap around endothelial cells, embedd within the endothelial basement membrane, and thus form an integral part of the tissue’s microvasculature. In areas lacking a basement membrane, the cell membranes of pericytes and endothelial cells form peg-and-socket contacts allowing direct communication and exchange of molecules.14 Pericytes can be identified by their expression of PDGFRB, α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA), and/or NG2.15-18 Developmentally, cell fate tracing studies have suggested that pericytes in kidney and forebrain derive from the neural crest,5,19 whereas pericytes in other organs, such as liver, lung, heart, or gut are mesothelium derived.20-23
The hypoxic induction of EPO in kidney and liver is regulated by HIF-2, a heterodimeric basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor that consists of an oxygen-sensitive α-subunit and a constitutively expressed β-subunit.24-26 To date, 3 different HIF-α-subunits have been identified: HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and HIF-3α.27-29 Although continuously synthesized, HIF-α subunits are rapidly degraded in the presence of molecular oxygen. HIF degradation is controlled by oxygen-, iron-, and ascorbate-dependent prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain-containing proteins (PHD)-1, -2, and -3, also known as EGLN2, EGLN1, and EGLN3, respectively, which use 2-oxoglutarate (OG) as substrate for the hydroxylation of specific proline residues within HIF-α.30-33 This leads to binding to the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)–E3 ubiquitin ligase complex and subsequent degradation by the proteasome. When oxygen levels decrease, HIF proline-4-hydroxylation is reduced, and HIF-α subunits are no longer degraded, translocate to the nucleus, and hetero-dimerize with HIF-β, promoting the transcription of oxygen-regulated genes.27
Because of their functional relevance for vascular homeostasis and the molecular features shared with renal EPCs, we investigated the HIF-EPO axis in pericytes and targeted the main components of the HIF oxygen-sensing pathway in NG2-expressing cells. Here we report that pericytes in the brain responded to Vhl inactivation with an increase in Epo mRNA transcription. Using multiplex high-resolution RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), we identified brain pericytes as major contributors to the cerebral EPO response to hypoxia. We furthermore establish that Epo transcription in NG2 cells is controlled by both PHD2 and PHD3, as only the combined inactivation of Phd2 and Phd3 led to an increase in brain Epo, which was completely dependent on HIF-2 activity. Thus, our studies identify pericytes as major cellular sources of EPO in the brain and suggest that the ability to synthesize EPO represents a functional feature of pericytes in brain and kidney.
Materials and methods
Generation and genotyping of mice and animal procedures
The generation and genotyping of mice carrying Ng2-cre and floxed alleles for Vhl, Hif1a, Hif2a, Epo, Phd1 (Egln2), Phd2 (Egln1), and Phd3 (Egln3) has been described elsewhere.15,25,34-36 All procedures involving mice were performed in accordance with National Institutes of Health guidelines for the use and care of live animals and were approved by Vanderbilt University's Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. A detailed description of mouse studies can be found in supplemental Materials and Methods available on the Blood Web site.
DNA and RNA analysis
DNA analysis for genotyping was performed as described previously.36,37 RNA was isolated using the RNeasy kit according to manufacturer’s protocol (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). For real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis, mRNA expression levels were quantified with the relative standard curve method according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Further details can be found in supplemental Materials and Methods.
Immunofluorescence, RNA FISH, and immunoglobulin G extravasation studies
Detailed methodologic information can be found in supplemental Materials and Methods.
Statistical analysis
Data are reported as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analyses were performed with Prism 5 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA) using the unpaired 2-tailed Student t test or 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis to compare between 3 or more groups. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Vhl inactivation in NG2 cells results in polycythemia
To investigate the HIF/EPO axis in NG2 pericytes, we first activated HIF signaling by ablating the VHL tumor suppressor as proof-of-concept study. For this, we crossed female mice that expressed Cre-recombinase under the control of the Cspg-4/Ng2 promoter to mice homozygous for the Vhl floxed allele generating Ng2-cre Vhlf/f mutants, from hereon referred to as NG2-Vhl−/− mice. NG2 is a 300-kDa single membrane spanning chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan that acts as a coreceptor for platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and regulates cell proliferation and motility.38 Proteoglycan NG2 is expressed in vascular mural cells/pericytes, mesenchymal lineage cells such as chondrocytes, osteoblasts, myoblasts, and skin stem cells, and in polydendrocytes, which are CNS precursor cells that give rise to oligodendrocytes and gray matter protoplasmic astrocytes.18,39,40
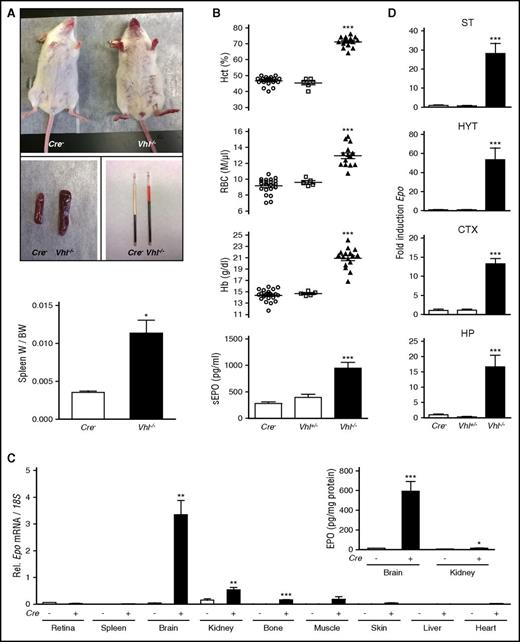
NG2-Vhl−/− mutant mice developed erythematous paws, ears, and muzzle and splenomegaly (Figure 1A). This was associated with elevated hematocrit (Hct), a significant increase in RBC numbers, hemoglobin (Hb), and plasma EPO concentration (Figure 1B). Despite severe polycythemia, NG2-Vhl−/− mice were viable and fertile. In contrast to NG2-Vhl−/− mice, mice with heterozygous Vhl deficiency (NG2-Vhl+/−) did not develop polycythemia and were characterized by normal serum EPO levels (Figure 1B).
NG2 cell-specific inactivation of Vhl results in polycythemia. (A) Mice with NG2 cell-specific inactivation of Vhl develop red paws, ears, and snout, splenomegaly, and polycythemia (n = 3-7). (B) Inactivation of Vhl in NG2 cells induces erythropoiesis and increases plasma EPO. Shown are individual Hct, RBC, and Hb values for Cre− control (n = 22), NG2-Vhl+/− (n = 6), and NG2-Vhl−/− mice (n = 16). Bar graphs show serum EPO levels (sEPO) for Cre− control (n = 20), NG2-Vhl+/− (n = 6), and NG2-Vhl−/− (n = 11) mice. Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with control group. (C) Relative Epo mRNA levels in retina, spleen, brain, kidney, bone, muscle, skin, liver, and heart in Cre− control and NG2-Vhl−/− mice (n = 3-7). (Inset) Brain and kidney EPO protein levels in Cre− control and NG2-Vhl−/− mice expressed as pg/mg total tissue protein (n = 5-7). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 2-tailed Student t test; *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001 compared with Cre− controls. (D) Epo mRNA levels in striatal (ST), hypothalamic (HYT), cortical (CTX), and hippocampal (HP) subregions from Cre− (n = 12), NG2-Vhl+/− (n = 3), and NG2-Vhl−/− mice (n = 4). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with the Cre− control group. BW, total body weight; W, organ weight.
NG2 cell-specific inactivation of Vhl results in polycythemia. (A) Mice with NG2 cell-specific inactivation of Vhl develop red paws, ears, and snout, splenomegaly, and polycythemia (n = 3-7). (B) Inactivation of Vhl in NG2 cells induces erythropoiesis and increases plasma EPO. Shown are individual Hct, RBC, and Hb values for Cre− control (n = 22), NG2-Vhl+/− (n = 6), and NG2-Vhl−/− mice (n = 16). Bar graphs show serum EPO levels (sEPO) for Cre− control (n = 20), NG2-Vhl+/− (n = 6), and NG2-Vhl−/− (n = 11) mice. Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with control group. (C) Relative Epo mRNA levels in retina, spleen, brain, kidney, bone, muscle, skin, liver, and heart in Cre− control and NG2-Vhl−/− mice (n = 3-7). (Inset) Brain and kidney EPO protein levels in Cre− control and NG2-Vhl−/− mice expressed as pg/mg total tissue protein (n = 5-7). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 2-tailed Student t test; *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001 compared with Cre− controls. (D) Epo mRNA levels in striatal (ST), hypothalamic (HYT), cortical (CTX), and hippocampal (HP) subregions from Cre− (n = 12), NG2-Vhl+/− (n = 3), and NG2-Vhl−/− mice (n = 4). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with the Cre− control group. BW, total body weight; W, organ weight.
Vhl inactivation in NG2 cells increases brain EPO production
Because NG2-Vhl−/− mice were characterized by elevated plasma EPO concentration, we asked whether this was a result of increased EPO synthesis in multiple organs41 and examined Epo transcript levels in different tissues. Whereas statistically significant differences in Epo expression were not detected in liver, heart, retina, spleen, muscle, and skin, Epo mRNA levels in brain, kidney, and bone were elevated compared with Cre− control, with the brain displaying the most pronounced increase (∼70-fold; Figure 1C). This rise in renal and brain Epo mRNA levels was associated with a ∼2-fold (6.5 ± 0.25 vs 15 ± 2.5 pg/mg total kidney tissue protein) and ∼40-fold (14.8 ± 1.1 vs 593 ± 99.1 pg/mg total brain tissue protein) increase in whole kidney and brain EPO protein levels (Figure 1C). These findings suggested that kidney, brain, and bone had contributed to the elevation in plasma EPO in NG2-Vhl−/− mice, however, the degree of contribution from individual tissues is unclear and difficult to assess with currently available technology.
To examine regional differences in cerebral Epo transcription, we dissected the brain and analyzed Epo expression levels in cortex, striatum, hypothalamus, and hippocampus by real-time PCR. Whereas NG2-Vhl+/− mice did not differ from their littermate controls, Epo levels in NG2-Vhl−/− mice were increased in all subregions, with hypothalamus displaying the highest level of increase (∼50-fold), followed by striatum (∼30-fold), and then cortex and hippocampus (∼15-fold each; Figure 1D).
To assess whether increased brain Epo expression resulted directly from enhanced Epo transcription in Vhl−/− cells or nontargeted adjacent cells, we generated NG2-Vhl−/−Epo−/− double mutant mice. Conditional coinactivation of Vhl and Epo in NG2 cells reduced brain Epo mRNA levels to control levels in cortex, striatum, and hippocampus, whereas Epo mRNA levels in hypothalamus were lower than in controls (Figure 2B). The normalization of brain Epo mRNA expression was furthermore associated with normal RBC parameters and serum EPO levels, demonstrating that polycythemia in NG2-Vhl−/− mice was a cell-autonomous phenotype that resulted directly from the deletion of Vhl in NG2-expressing cells (Figure 2A). The absence of polycythemia in NG2-Vhl−/−Epo−/− animals furthermore indicated that HIF activation in non–EPO-producing NG2 cells outside the brain, eg, in the bone marrow perivascular niche, had not contributed to erythropoiesis in these mice.42 Taken together, our data suggest that the induction of Epo in NG2-expressing cells and their derivatives was cell autonomous.
Epo induction in NG2-Vhl−/− mice is cell autonomous. (A) Shown are individual Hcts, RBC, and Hb values for Cre− control and in NG2-Vhl−/−Epo−/− mice (n = 8-10). Bar graphs show serum EPO levels (sEPO) for Cre− and NG2-Vhl−/−Epo−/− mice (n = 5-7). (B) Striatal (ST), hypothalamic (HYT), cortical (CTX), and hippocampal (HP) Epo mRNA levels in Cre− and NG2-Vhl−/−Epo−/− mice (n = 4 each). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 2-tailed Student t test; *P < .05 compared with Cre− control group.
Epo induction in NG2-Vhl−/− mice is cell autonomous. (A) Shown are individual Hcts, RBC, and Hb values for Cre− control and in NG2-Vhl−/−Epo−/− mice (n = 8-10). Bar graphs show serum EPO levels (sEPO) for Cre− and NG2-Vhl−/−Epo−/− mice (n = 5-7). (B) Striatal (ST), hypothalamic (HYT), cortical (CTX), and hippocampal (HP) Epo mRNA levels in Cre− and NG2-Vhl−/−Epo−/− mice (n = 4 each). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 2-tailed Student t test; *P < .05 compared with Cre− control group.
Brain pericytes synthesize EPO in NG2-Vhl−/− mice
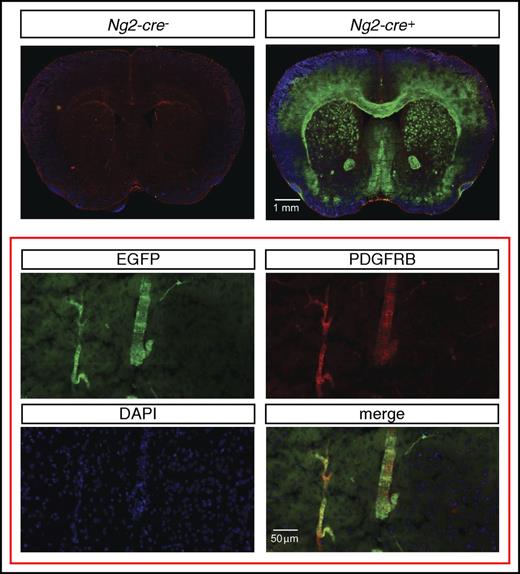
To assess the cellular source of Epo in NG2-Vhl−/− mice, we first examined to what degree pericytes were targeted by Ng2-cre. For this, we used a green fluorescence protein (GFP) Cre-reporter transgenic line, ROSA26-ACTBtdTomato,-EGFP, where EGFP is only expressed in cells that have a history of Cre-recombinase expression and have undergone Cre-loxP–mediated recombination. This Cre-reporter is under the control of the Rosa26 promoter. Because NG2-mT/mEGFP-Vhl−/− mice cannot be generated due to the close proximity of the Rosa26 and Vhl gene loci, we used mice for the analysis that were mutant for Phd2. Although Cre− littermate controls did not exhibit EGFP expression, reporter mice displayed widespread EGFP expression in the brain that colocalized with ∼35% of the PDGFRB-expressing cells (Figure 3).
Ng2-cre–mediated recombination in cerebral vascular mural cells. (Top) Representative images of EGFP (green signal) and PDGFRB (red signal) immunofluorescence in brains from control (Ng2-cre-) and NG2-mT/mEGFP mice that were deficient for Phd2 (Ng2-cre+). NG2-mT/mEGFP-Phd2−/− mice are phenotypically normal and did not develop polycythemia. (Bottom) Magnification shows coexpression of PDGFRB (red signal) and EGFP (green signal) in NG2 cells.
Ng2-cre–mediated recombination in cerebral vascular mural cells. (Top) Representative images of EGFP (green signal) and PDGFRB (red signal) immunofluorescence in brains from control (Ng2-cre-) and NG2-mT/mEGFP mice that were deficient for Phd2 (Ng2-cre+). NG2-mT/mEGFP-Phd2−/− mice are phenotypically normal and did not develop polycythemia. (Bottom) Magnification shows coexpression of PDGFRB (red signal) and EGFP (green signal) in NG2 cells.
Because NG2 is expressed in pericytes, and also polydendrocytes, which give rise to oligodendrocytes and gray matter astrocytes,40,43 we next determined the exact cellular localization of Epo transcripts in brains from NG2-Vhl−/− mice by performing high-resolution RNA FISH with probes specific for the Epo and pericyte marker Pdgfrb.16-18,44,45 We then quantified Epo- and Pdgfrb-expressing cells and determined the proportion of Epo+Pdgfrb+ cells among Epo- or Pdgfrb-expressing cells in cortex, striatum, hippocampus, and hypothalamus, as well as in the corpus callosum, where nonpericyte NG2 lineage cells are known to be more abundant. Although only 25% of all Pdgfrb+ cells expressed Epo, we found that the majority of Epo+ cells coexpressed Pdgfrb (∼60%) in all brain subregions. Epo+Pdgfrb− cells were found in vascular/perivascular regions and brain parenchyma (Figure 4). Taken together, our data indicate that pericytes are the main cellular source of Epo in the brain of NG2-Vhl−/− mice.
Brain pericytes express Epo mRNA. Shown are the results of multiplex RNA FISH studies for Epo and Pdgfrb transcripts using formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded brain tissue sections from NG2-Vhl−/− mutant mice. (A) (Left) Representative image of a striatal section (ST) containing pericytes that coexpress Epo (green signal) and Pdgfrb transcripts (red signal). Nuclei are stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue fluorescence). Bright white structures inside the vessels represent RBCs. (Right) Percentage of Pdgfrb+ cells coexpressing Epo mRNA (white bar) or Epo+ cells coexpressing Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) (n = 3). (B) (Left) Representative image of a hippocampal section (HP) containing pericytes that coexpress Epo (green signal) and Pdgfrb transcripts (red signal). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue signal). (Right) Percentages of Pdgfrb+ cells that coexpress Epo transcripts (white bar) or Epo+ cells that coexpress Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) (n = 3). (C) Percentages of Pdgfrb+ cells coexpressing Epo transcripts (white bar) or Epo+ cells that coexpress Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) in hypothalamus (HYT), cortex (CTX), and corpus callosum (CC) (n = 3 each).
Brain pericytes express Epo mRNA. Shown are the results of multiplex RNA FISH studies for Epo and Pdgfrb transcripts using formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded brain tissue sections from NG2-Vhl−/− mutant mice. (A) (Left) Representative image of a striatal section (ST) containing pericytes that coexpress Epo (green signal) and Pdgfrb transcripts (red signal). Nuclei are stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue fluorescence). Bright white structures inside the vessels represent RBCs. (Right) Percentage of Pdgfrb+ cells coexpressing Epo mRNA (white bar) or Epo+ cells coexpressing Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) (n = 3). (B) (Left) Representative image of a hippocampal section (HP) containing pericytes that coexpress Epo (green signal) and Pdgfrb transcripts (red signal). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue signal). (Right) Percentages of Pdgfrb+ cells that coexpress Epo transcripts (white bar) or Epo+ cells that coexpress Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) (n = 3). (C) Percentages of Pdgfrb+ cells coexpressing Epo transcripts (white bar) or Epo+ cells that coexpress Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) in hypothalamus (HYT), cortex (CTX), and corpus callosum (CC) (n = 3 each).
Hypoxia induces EPO production in brain pericytes
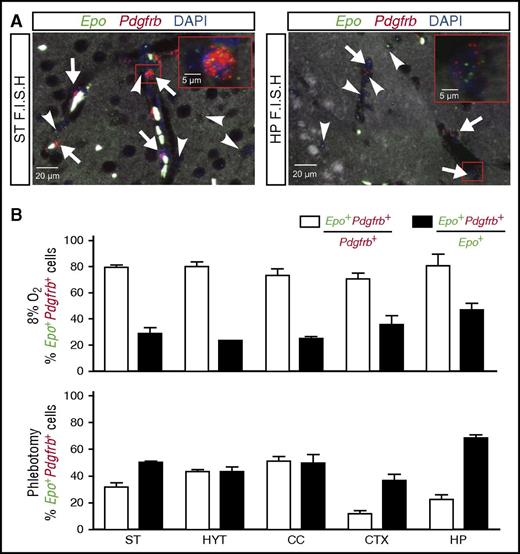
The analysis of NG2-Vhl−/− mice suggested a role for pericytes in cerebral EPO production. We next sought to examine whether brain pericytes were capable of producing EPO in an experimental model of systemic hypoxia. For this, we placed wild-type mice in a normobaric hypoxia chamber for 24 hours and analyzed the contribution of pericytes to the brain’s EPO response by multiplex RNA FISH. We exposed mice to 8% oxygen, which mimics an altitude of ∼7500 m and is known to robustly stimulate EPO synthesis in the brain12,13,46 ; the contribution of pericytes to this response, however, has never been examined. After demonstrating increased Epo transcript levels (supplemental Figure 1A), we quantified the total number of Epo-expressing cells per brain subregion, as well as the number of cells that expressed pericyte marker Pdgfrb. Exposure of mice to 8% O2 for 24 hours resulted in a widespread induction of Epo transcripts compared with normoxic controls, in which no signal was detected. Quantification of Epo+ cells in relation to Pdgfrb-expressing cells revealed that ∼80% of Pdgfrb+ cells coexpressed Epo transcripts and that these cells represented 25% to 45% of the total number of Epo+ cells (Figure 5). Interestingly, the number of Epo+Pdgfrb+ cells increased to ∼70% under conditions of anemic hypoxia (Figure 5; relative Epo levels are shown in supplemental Figure 1B). Epo+Pdgfrb− cells were identified as astrocytes and neurons (supplemental Figure 1C). Taken together, our data suggest that brain pericytes respond to hypoxia with the production of EPO, the degree of participation in this response being dependent on the type of the hypoxic stimulus.
Normobaric hypoxia and anemia stimulate EPO synthesis in brain pericytes. Shown are the results of multiplex RNA FISH studies for Epo and Pdgfrb transcripts using formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded brain tissue sections from wild-type mice exposed to normobaric hypoxia (8% O2 for 24 hours) or after phlebotomy (average Hct: 20.7%). (A) (Left) Representative image of a striatal section (ST) containing pericytes (white arrows) that coexpress Epo (green signal) and Pdgfrb transcripts (red signal) and nonpericytic Epo+ cells (white arrowhead). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue fluorescence). (Right) Representative image of a hippocampal section (HP) containing pericytes (white arrows) that coexpress Epo (green signal) and Pdgfrb transcripts (red signal) and Pdgfrb−Epo+ cells (white arrowhead). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue signal). (B) (Upper) Percentages of Pdgfrb+ cells that coexpress Epo (white bar) or Epo+ cells that coexpress Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) in striatum (ST), hypothalamus (HYT), corpus callosum (CC), cortex (CTX), and hippocampus (HP) from wild-type mice exposed to normobaric hypoxia (8% O2 for 24 hours) (n = 3). (Lower) Percentages of Pdgfrb+ cells that coexpress Epo (white bar) or Epo+ cells that coexpress Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) in striatum (ST), hypothalamus (HYT), corpus callosum (CC), cortex (CTX), and hippocampus (HP) from phlebotomized wild-type mice (n = 3).
Normobaric hypoxia and anemia stimulate EPO synthesis in brain pericytes. Shown are the results of multiplex RNA FISH studies for Epo and Pdgfrb transcripts using formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded brain tissue sections from wild-type mice exposed to normobaric hypoxia (8% O2 for 24 hours) or after phlebotomy (average Hct: 20.7%). (A) (Left) Representative image of a striatal section (ST) containing pericytes (white arrows) that coexpress Epo (green signal) and Pdgfrb transcripts (red signal) and nonpericytic Epo+ cells (white arrowhead). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue fluorescence). (Right) Representative image of a hippocampal section (HP) containing pericytes (white arrows) that coexpress Epo (green signal) and Pdgfrb transcripts (red signal) and Pdgfrb−Epo+ cells (white arrowhead). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue signal). (B) (Upper) Percentages of Pdgfrb+ cells that coexpress Epo (white bar) or Epo+ cells that coexpress Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) in striatum (ST), hypothalamus (HYT), corpus callosum (CC), cortex (CTX), and hippocampus (HP) from wild-type mice exposed to normobaric hypoxia (8% O2 for 24 hours) (n = 3). (Lower) Percentages of Pdgfrb+ cells that coexpress Epo (white bar) or Epo+ cells that coexpress Pdgfrb transcripts (black bar) in striatum (ST), hypothalamus (HYT), corpus callosum (CC), cortex (CTX), and hippocampus (HP) from phlebotomized wild-type mice (n = 3).
PHD2 and PHD3 coregulate EPO production in NG2 cells
PHD enzymes function as the oxygen sensors that control HIF activity and thus play a central role in the oxygen-dependent induction of EPO.27 In the kidney, EPO production can be stimulated by Phd2 inactivation alone, which leads to a dramatic increase in renal Epo transcription,4,35,47,48 whereas a combined inactivation of Phds is required to induce Epo in hepatocytes.8,10 To investigate the role of individual PHDs in the regulation of EPO in brain pericytes, we generated mice with conditional deletions of Phd1, Phd2, and/or Phd3 using Ng2-cre. We first inactivated Phd2 in NG2-cells to examine whether Phd2 deletion alone would mimic the phenotype of NG2-Vhl−/− mice. Conditional deletion of Phd2 in NG2 cells (NG2-Phd2−/−) did not result in polycythemia, abnormal plasma EPO, or increased brain Epo mRNA levels (Figure 6A), suggesting that Phd2 deletion in NG2 cells was not sufficient to stabilize HIF-α and that the hypoxic regulation of Epo in brain pericytes differed from renal EPCs.
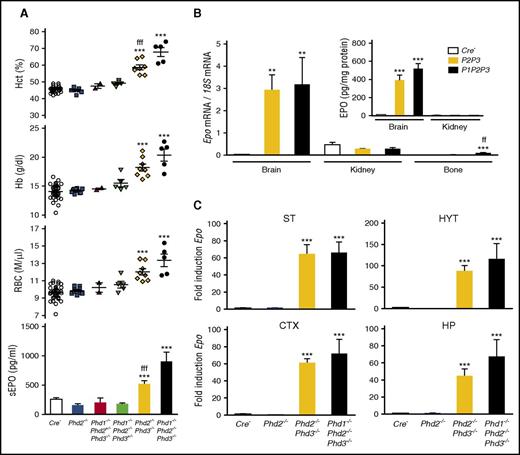
PHD2 and PHD3 control Epo transcription in NG2 cells. (A) Shown are Hct, RBC, and Hb values for individual Cre− control (n = 38), NG2-Phd2−/− (n = 9), NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2+/−Phd3−/− (n = 2), NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3+/− (n = 5), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 8), and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice (n = 5). Bar graphs show serum EPO levels (sEPO) for control (Cre−, n = 18), NG2-Phd2−/− (n = 8), NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2+/−Phd3−/− (n = 2), NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3+/− (n = 4), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 5), and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice (n = 4). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with control group and fffP < .001 when the NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− group was compared with the NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− group. (B) Relative Epo mRNA levels in brain, kidney, and bone from control (Cre−), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−, and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice (n = 3-7). (Inset) Brain and kidney EPO protein levels in Cre− control and NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (P2P3) and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (P1P2P3) mice expressed as pg/mg total tissue protein (n = 3-6). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; **P < .01, ***P < .001 compared with control group; ffP < .01 for NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice compared with NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice. (C) Striatal (ST), hypothalamic (HYT), cortical (CTX), and hippocampal (HP) Epo mRNA levels in Cre− control (n = 9), NG2-Phd2−/− (n = 5), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 4), and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with Cre− control group.
PHD2 and PHD3 control Epo transcription in NG2 cells. (A) Shown are Hct, RBC, and Hb values for individual Cre− control (n = 38), NG2-Phd2−/− (n = 9), NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2+/−Phd3−/− (n = 2), NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3+/− (n = 5), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 8), and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice (n = 5). Bar graphs show serum EPO levels (sEPO) for control (Cre−, n = 18), NG2-Phd2−/− (n = 8), NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2+/−Phd3−/− (n = 2), NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3+/− (n = 4), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 5), and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice (n = 4). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with control group and fffP < .001 when the NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− group was compared with the NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− group. (B) Relative Epo mRNA levels in brain, kidney, and bone from control (Cre−), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−, and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice (n = 3-7). (Inset) Brain and kidney EPO protein levels in Cre− control and NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (P2P3) and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (P1P2P3) mice expressed as pg/mg total tissue protein (n = 3-6). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; **P < .01, ***P < .001 compared with control group; ffP < .01 for NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice compared with NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice. (C) Striatal (ST), hypothalamic (HYT), cortical (CTX), and hippocampal (HP) Epo mRNA levels in Cre− control (n = 9), NG2-Phd2−/− (n = 5), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 4), and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with Cre− control group.
PHD1 and PHD3 have been shown to fine-tune HIF responses, especially under reoxygenation conditions, as PHD3 itself is hypoxia inducible.49,50 To examine the role of PHD1 and PHD3 in pericytes, we generated compound conditional knockout mice in which PHDs were inactivated in combination. Whereas RBC parameters and plasma EPO in mice homozygously deficient for Phd1 and Phd2 and heterozygously deficient for Phd3 (NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3+/−) or completely deficient for Phd1 and Phd3 but heterozygously deficient for Phd2 (NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2+/−Phd3−/−) were not different from littermate controls, the combined loss of either Phd2 and Phd3 (NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−) or Phd1, Phd2, and Phd3 together (NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/−) resulted in elevated plasma EPO concentration (two- and fourfold increase, respectively) and polycythemia, and thus mimicked the NG2-Vhl−/− phenotype (Figure 6A). In contrast to NG2-Vhl−/− mice, Epo mRNA expression levels in kidney and bone from NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mutants were not different from controls. However, Epo mRNA and EPO protein levels in brain were strongly increased by 111- and 44-fold (8.9 ± 1.1 vs 390.6 ± 56.9 pg/mg total protein), respectively (Figure 6B). These results suggested that Ng2-cre–targeted cells in brain were responsible for the elevated plasma EPO levels found in NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice. Taken together, our data provide evidence that brain-derived EPO contributes to the regulation of erythropoiesis under conditions of PHD inactivation.
We hypothesized that the degree of contribution of brain-derived EPO to plasma EPO was most likely dependent on tissue EPO levels and blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability, as only 1% of circulating EPO has been shown to cross the BBB under baseline conditions.51-53 We therefore examined whether inactivation of Phds in NG2 cells affected BBB permeability. We found a significant increase in BBB permeability in NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice (supplemental Figure 2). This finding raises the possibility that Phd inactivation in NG2 cells may have facilitated delivery of brain pericyte-derived EPO to the systemic circulation through effects on BBB permeability.
Dual fluorescence RNA FISH in NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− brain tissue demonstrated that the distribution and cellular location of Epo transcripts was similar to NG2-Vhl−/− mice (data not shown). Although mice with complete inactivation of either Phd2 and Phd3 (NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−) or Phd1, Phd2, and Phd3 together (NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/−) developed severe polycythemia and were characterized by increased plasma EPO concentrations, the degree of polycythemia and increase in plasma EPO were more pronounced in NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− triple mutants (Figure 6A). However, we did not find a statistically significant difference in either brain Epo mRNA or EPO protein levels between NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice (Figure 6B-C). This is in contrast to the results from the endogenous IgG extravasation study, which suggested that BBB permeability was relatively more increased in NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− triple mutants, thus possibly facilitating the delivery of more EPO to the systemic circulation (supplemental Figure 2). Taken together, our results indicate that the hypoxic induction of EPO in brain pericytes is predominantly cocontrolled by PHD2 and PHD3. In this regard, EPO regulation in brain pericytes differs from the kidney, where Phd2 inactivation alone is sufficient to induce EPO in a subset of perivascular cells.4
EPO production in NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice requires HIF-2
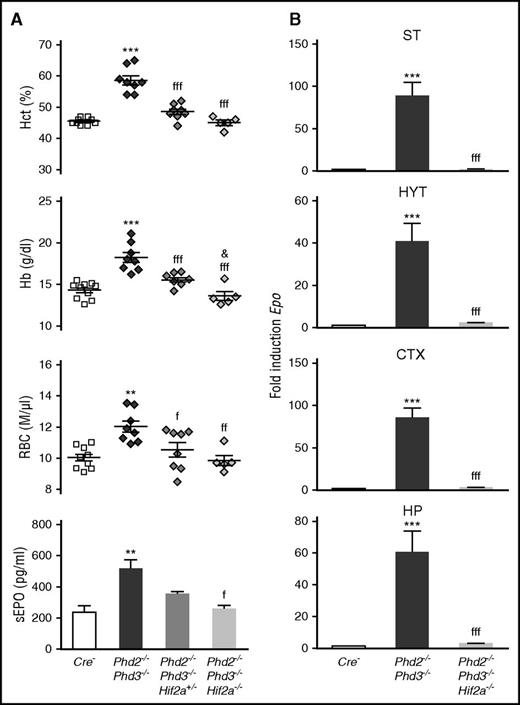
Although in vitro experiments demonstrated a role for HIF-1 in the regulation of EPO, genetic and immunohistochemical studies in humans and mice have now established that HIF-2 is the key transcription factor in the hypoxic induction of EPO in vivo.9 Because of these findings, we focused our investigation on the role HIF-2 in Phd-deficient brain pericytes and generated mice with conditional inactivation of Phd2, Phd3, and Hif2a. Homozygous deletion of Hif2a in NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice corrected their polycythemic phenotype and suppressed brain Epo mRNA levels completely, establishing that under conditions of PHD inactivation, HIF-2 is required for EPO synthesis in brain pericytes (Figure 7).
HIF-2 controls Epo transcription in NG2 cells. (A) Shown are individual Hct, RBC, and Hb values for Cre− control (n = 10), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 8), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a+/− (n = 8), and NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a−/− mice (n = 5). Bar graphs show serum EPO levels (sEPO) for Cre− control (n = 4), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 6), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a+/− (n = 3), and NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a−/− mice (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; **P < .01 and ***P < .001 compared with Cre− control group; fP < .05, ffP < .01, and fffP < .001 compared with NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− group; &P < .05, NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a+/− was compared with NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a−/− group. (B) Striatal (ST), hypothalamic (HYT), cortical (CTX), and hippocampal (HP) Epo mRNA levels in Cre− (n = 7), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 4), and NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a−/− mice (n = 4). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with Cre− control group and fffP < .001 compared with the NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− group.
HIF-2 controls Epo transcription in NG2 cells. (A) Shown are individual Hct, RBC, and Hb values for Cre− control (n = 10), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 8), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a+/− (n = 8), and NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a−/− mice (n = 5). Bar graphs show serum EPO levels (sEPO) for Cre− control (n = 4), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 6), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a+/− (n = 3), and NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a−/− mice (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; **P < .01 and ***P < .001 compared with Cre− control group; fP < .05, ffP < .01, and fffP < .001 compared with NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− group; &P < .05, NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a+/− was compared with NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a−/− group. (B) Striatal (ST), hypothalamic (HYT), cortical (CTX), and hippocampal (HP) Epo mRNA levels in Cre− (n = 7), NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− (n = 4), and NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/−Hif2a−/− mice (n = 4). Data are represented as mean ± SEM; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis; ***P < .001 compared with Cre− control group and fffP < .001 compared with the NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− group.
Discussion
Here we used a genetic approach to investigate the PHD/HIF/VHL axis in NG2 cells. Our data establish that brain pericytes function as oxygen sensors and represent a major cellular source of EPO in the hypoxic brain, as they respond to systemic hypoxia with the induction of Epo transcription. We furthermore provide experimental evidence for a HIF-2–dependent contribution of brain pericytes to the regulation of erythropoiesis under conditions of combined inactivation of Phd2 and Phd3.
To study the PHD/HIF/VHL axis in pericytes, we made use of a Cre-recombinase transgene under the control of the Cspg4/Ng2 promoter. As NG2 is not only expressed in pericytes but also in polydendrocytes, which are cellular precursors of oligodendrocytes and protoplasmic astrocytes,43 both pericytes and NG2-derived glia were subjected to Cre-mediated gene targeting in our model.15,16 In the brain, pericytes can be easily differentiated from astrocytes and oligodendrocytes by their close association with vessel wall and capillaries, their morphologic features, and their expression of certain molecular markers such as PDGFRB.16-18,45 We used these criteria to determine that the majority of EPO-producing cells in the brain of polycythemic Ng2-cre–based knockout mice were pericytes. As expected, we also found Epo-expressing cells that were Pdgfrb−, which we identified as astrocytes and neurons, cell types that are known to synthesize EPO under conditions of hypoxia or Vhl inactivation.12,13,54
Pericytes play a key role in brain tissue homeostasis, as they are located at the interface of parenchyma and systemic circulation, where they control the formation, stability, and function of the BBB.55,56 Pericytes regulate microvessel maturation and cerebral blood flow and are thus an integral part of the neurovascular unit.16,45 Under conditions of systemic hypoxia, the majority of Pdgfrb+ cells in wild-type mice expressed Epo and, depending on the hypoxic stimulus, accounted for ∼30% to 70% of all Epo-expressing cells in the brain, suggesting that pericytes function as oxygen sensors and contribute to at least one third of the brain’s EPO response to hypoxia.
The implications of our findings for human biology implications are broad. The role of EPO in the biology of the neurovascular unit is unclear, and our findings will very likely stimulate further investigations in this area. Furthermore, phase 2 and 3 anemia clinical trials with HIF-stabilizing PHD inhibitors are currently under way.2 Whether some of these compounds cross the BBB and induce Epo in brain pericytes is not known but warrants investigation.
Although the BBB is quite impermeable to EPO51-53 and the contribution of brain-derived EPO to circulating EPO has been contested,57 our data provide indirect evidence that brain pericyte-derived EPO may be able to reach the bloodstream. Although specific assays that permit plasma concentration measurements of tissue-specific EPO isoforms, eg, mass spectrometry–based assays, are currently not available, the analysis of polycythemic NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice provides indirect evidence for a contribution of brain-derived EPO to the plasma EPO pool. In this mouse strain, which is characterized by an approximate twofold increase in plasma EPO levels, only 2 tissue sources of EPO were identified: brain and kidney. Because kidney EPO output did not change compared with control, our data support the notion that the increase in plasma EPO is brain derived, as brain was the only extrarenal tissue in which increased EPO was detected.
Although EPO is predicted to enter the systemic circulation directly in areas that lack a normal BBB, such as in the circumventricular organs or the choroid plexus,58 the mechanism by which EPO crosses the BBB in other areas is not understood. However, under hypoxic conditions, the endothelial barrier becomes leaky,59 which is predicted to facilitate the delivery of pericyte-derived EPO into the blood stream. We believe that the severity and duration of hypoxia are important variables that affect BBB permeability60 and thus likely modulate to what degree brain-derived EPO enters the systemic circulation.
In adults, the main source of EPO are renal peritubular interstitial fibroblast-like cells, which represent a heterogeneous and relatively ill-defined population of cells that includes pericytes and perivascular fibroblasts.2 Recent studies have indicated that the majority of interstitial fibroblast-like cells in the renal cortex and outer medulla have the capacity to synthesize EPO in a HIF-2–dependent fashion,4 whereas morphologic and molecular analysis indicates that a large fraction of renal EPCs are pericytes.3,4,61 Interestingly, lineage tracing studies have suggested that pericytes in brain and kidney are neural crest derived5,18,19 and that HIF-2α expression is associated with a neural crest–like phenotype.62,63 Thus, the ability to produce EPO may be a functional feature of pericytes of neural crest origin.
Although NG2 is marker of pericytes, only a small subpopulation of Pdgfrb-expressing renal pericytes is targeted by Ng2-cre (supplemental Figure 3). Inactivation of either Vhl or Phd2/3 in these cells resulted in constitutive HIF-2 activation and led to inappropriate EPO production, as renal synthesis EPO is normally suppressed in the presence of polycythemia. In contrast to NG2-Vhl−/− mice, renal Epo levels in NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− and NG2-Phd1−/−Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice were lower, although statistically not significant, whereas in the bone Epo was induced in the Vhl and triple Phd knockout but not in NG2-Phd2−/−Phd3−/− mice. Phenotypic differences between Vhl and the 2 Phd knockout models are expected as cell type–specific regulation of HIF activity and EPO synthesis has been associated with differences in PHD expression levels and catalytic activity,4 whereas Vhl inactivation leads to a complete block of HIF ubiquitylation, representing the least physiologic model of HIF activation.
We were able to demonstrate that PHD2 and PHD3 coregulate EPO production in brain pericytes, as the combined inactivation of Phd2 and Phd3 was required for Epo induction. This is in contrast to the kidney, where Phd2 inactivation alone is sufficient for Epo induction in a subset of cells.4,35,47,48 PHD2 is the main HIF prolyl-4-hydroxylase that controls HIF activity under normoxia,27 and loss-of-function mutations are associated with familial erythrocytosis in humans,64,65 whereas gain-of-function mutations protect from high altitude–induced polycythemia or other diseases.1,66,67 However, only a subset of renal interstitial cells responds to Phd2 inactivation alone.4 It is not surprising that cells with EPO-producing capacity behave differently with regard to HIF pathway regulation and thus EPO production, as the combined deletion of ≥2 PHDs is required to increase EPO production in hepatocytes, whereas the inactivation of all 3 PHDs is needed for a very strong and sustained Epo induction in the liver.8,10 These tissue- and cell type–dependent differences are most likely a reflection of differences in PHD protein expression levels and catalytic activity.
In summary, our studies provide novel insights into the regulation of hypoxia responses in the brain microvasculature, as we provide experimental evidence for a role of brain pericytes as oxygen sensors. Our findings provide a basis for further research into the role of oxygen metabolism in brain microvascular function and pathogenesis.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Joseph Roland (Digital Histology Shared Resource Core of Vanderbilt University) for assistance with image analysis.
This work was supported by the Krick-Brooks chair in Nephrology; National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases grants R01-DK101791, R01-DK081646, and R01-DK080821; and Department of Veterans Affairs merit award 1I01BX002348 (all to V.H.H.).
Authorship
Contribution: A.A.U. and V.H.H. conceived and designed the research studies, analyzed and interpreted data, wrote the manuscript, and made the figures; A.A.U., A.A., J.N., and O.D. performed experiments and acquired and analyzed data; and K.W.G. contributed reagents and interpreted data.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Volker H. Haase, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, C-3119A MCN, 1161 21st Ave S, Nashville, TN 37232-2372; e-mail: volker.haase@vanderbilt.edu.