Abstract
Introduction: TCD with Transfusions Changing toHydroxyurea (TWiTCH Clinical Trials.gov NCT01425307), an NHLBI-sponsored multicenter trial, compared transfusion pluschelation (Standard Arm) tohydroxyurea (HU) plus phlebotomy (Alternative Arm) in children with sickle cell disease at high risk for stroke. Alternative arm patients underwent serial phlebotomy (10mL/kg, maximum 500mL) every 4 weeks after reaching maximal tolerated dose (MTD) of HU and discontinuing transfusions. Changes in liver iron concentration (dLIC), measured as mg Fe per gram dry weight liver, by both MRI R2 (FerriScan) and R2* were key secondary outcome measures. R2 and R2* are two, different MRI techniques that exploit the magnetic properties of tissue iron to estimate iron concentration. We previously reported significant differences between the two approaches at the baselinetimepoint. The purpose of this investigation was to determine the limits of agreement between measurements ofdLIC over a period of one year by R2 and R2* methods in both arms of the study.
Methods: MRI R2 and R2* data were collected prior to randomization, and after 1 year (midpoint) and 2 years of therapy (study exit). dLIC between baseline to midpoint and midpoint to study completion was calculated for both R2 and R2* LIC values. Since LIC measurement variability increases with iron burden, each dLIC pair (R2 and R2*) were normalized to the patients iron burden at the start of the observation interval. That is, dLIC from baseline to midpoint was normalized to baseline LIC, while dLIC from midpoint to study end was normalized to midpoint LIC. The geometric mean of LICR2 and LICR2* was used to represent the baseline and midpoint LIC. Bland Altman analysis was performed on measurements of the percent change of dLICR2 and dLICR2* to determine the limits of agreement between the two techniques.
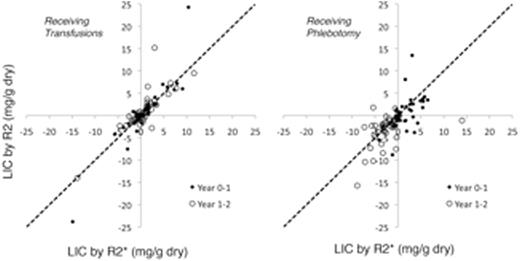
Results: R2 measurements were performed in 104 patients at baseline, 94 at midpoint and 99 at study end, while R2* measurements were performed in 101, 87, and 89 patients, respectively. However, missing data limited Bland Altman comparisons ofdLIC to 74 patients between baseline to midpoint and 69 patients from midpoint to study end. Figure 1 (left) plots the measureddLIC using R2 (vertical axis) against the measureddLIC change by R2* (horizontal axis) for the Standard Arm participants. Dots represent LIC change over the first year and open circles represent LIC changes over the second year. The dotted line represents perfect agreement. Figure 1 (right) demonstrates the corresponding relationship for the patients in the Alternative Arm.
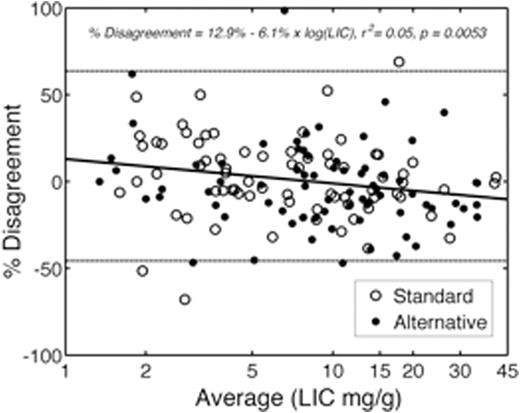
Although the alternative arm appears to have greater disagreement, this represents an artifactcause by the transient increases in LIC that occurred as patients bridged from standard to alternative therapy. Iron chelationwas stopped when patients began hydroxyureabut patients required an overlap period of transfusions for stroke prophylaxis. Figure 2 demonstrates the difference in dLIC measured by R2 and R2*, expressed as a percentage of starting LIC, plotted against the starting LIC value. The standard arm (open circles) and alternative arms (dots) completely overlap. 95% limits of agreement between the two measures ofdLIC were -45.7% to 63.7% (light lines). At LIC values > 8.3 mg/g,dLIC predicted by R2 was larger than predicted by R2*, while the converse was true for LIC values below 8.3 mg/g, similar to our published baseline findings for LIC measurements.
Conclusions: LIC by R2 and R2* tracked one another closely over time in patients in both study arms. These data indicate that either technique can be used with confidence to monitor patients on iron removal therapy (chelation or phlebotomy), but that the techniques should not be interchanged.
Wood:Vifor: Consultancy; Ionis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Vifor: Consultancy; Biomed Informatics: Consultancy; World Care Clinical: Consultancy; Ionis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; World Care Clinical: Consultancy; AMAG: Consultancy; AMAG: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Biomed Informatics: Consultancy; Apopharma: Consultancy; Apopharma: Consultancy. St Pierre:Resonance Health: Consultancy, Equity Ownership. Piccone:Novartis: Other: Speaker. Hankins:Novartis: Research Funding. Rogers:Apopharma: Consultancy. Ware:Bayer Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Global Blood Therapeutics: Consultancy; Biomedomics: Research Funding; Addmedica: Research Funding; Nova Laboratories: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract