Abstract
Background: Limited data is available on expression levels of checkpoint receptors, respective ligands, and other immune markers in patients with CLL (Ramsay et al. Blood 2012). Checkpoint blockade has been a successful therapy of many cancers including melanoma, and more recently, Hodgkin's lymphoma. Understanding expression patterns of checkpoint receptors and ligands may help in the clinical development of checkpoint blockade as a therapy for patients with CLL.
Methods: Between September 2015 and April 2016, we performed 17-color multi-parameter flow-cytometry (MFC) in paired peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) samples from 30 patients with CLL who presented as new patients for evaluation at MDACC. Patients may have received prior CLL therapy. We evaluated expression of immune receptors (inhibitory receptors: PD1, CTLA4, LAG3, TIM3; activating receptors: GITR, OX40, 41BB, ICOS) on T cell subsets: CD4 T effector cells [Teff]: CD3+CD4+CD127lo/+Foxp3-, CD4 T regulatory cells [Treg]: CD3+CD4+CD127-Foxp3+, and CD8 T cells. CLL cells were assessed for both immune receptors (as above), and ligands (4-1BBL, B7-1, B7-2, ICOSL, PDL-1, PDL-2, OX40L). These analyses were performed on freshly collected PB and BM samples by the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Immunotherapy Platform.
Results: A total of 30 patients with CLL were enrolled. The median age was 66 years (range, 35-83). Nine were women. Nineteen were treatment-naive. Prognostic markers included FISH [del(17p) = 6; del(13q) = 9, del(11q) = 4, trisomy 12 = 3, negative = 8]. IGHV mutation status was available for 19 patients (13 unmutated IGHV, 6 mutated IGHV). B2M was ≥3.5 in 11 pts.
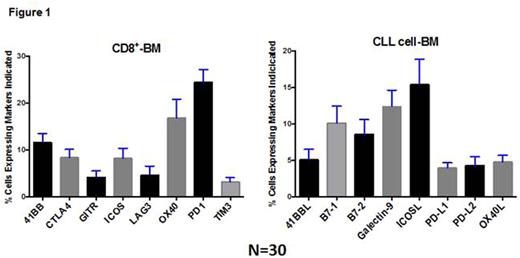
Baseline expression of costimulatory receptors in CD8 T cells in the marrow, and of the ligands in CLL cells in the marrow is shown in Figure 1. In paired PB and BM sample analysis, there was a high correlation between expression level of PD1 on Treg (Pearson correlation, r = 0.90, p<0.00001), Teff (r = 0.87, p<0.00001), CD8+ cells (r = 0.80, p<0.00001), and CLL cells (r = 0.75, p<0.00001). PD-L1 expression on CLL cells was moderately correlated between PB and BM (r = 0.57, p<0.001).
Patients with prior therapy had significantly higher expression of PDL1 on the CLL cells in both PB and BM (p=0.01 and p=0.002, respectively) compared to previously untreated patients. OX40 expression on CD8 cells was significantly higher in both PB and BM in previously treated patients (compared to previously untreated patients). Patients with unmutated IGHV (p = 0.003) and del17p (p = .03) had higher PDL1 expression on CLL cells in the marrow.
Conclusions: There is a strong correlation in the expression levels of PD1 on various T cell subsets between PB and BM. Clinically targetable checkpoint receptors including PD1, OX40, CTLA4, and ICOS are consistently expressed across patients with CLL, and present on cells in both PB and BM.
Jain:BMS: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novimmune: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Burger:Roche: Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Pharmacyclics, LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Portola: Consultancy; Gilead: Research Funding. Thompson:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria. Daver:Otsuka: Consultancy, Honoraria; Ariad: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding. Wierda:Acerta: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.