Abstract
Background:
Prognosis of follicular lymphoma (FL) has long been defined by the FLIPI score (Solal-Céligny et al., 2004) which is a 5 factor risk model consisting of age, stage, lactate dehydrogenase, hemoglobin and number of nodal areas. The FLIPI model has been validated at diagnosis in both the pre- and post-Rituximab eras. However, many patients are initially observed and have prolonged lead time from diagnosis to first treatment. In this study, we investigated whether FLIPI risk group at diagnosis changed by the time of initial treatment, and whether change of FLIPI risk group impacted treated outcome.
Patients and Methods:
All adult (≥18 yo) patients with de novo follicular lymphoma (FL) treated at our center between 1998 and 2007 were evaluated. Study excluded patients with ≤2 follow up visits, known divergent of composite histology at diagnosis, and active concurrent malignancies. FLIPI was scored at diagnosis and at initiation of first treatment. For patients with missing FLIPI data, FLIPI category was scored if the omission did not alter the FLIPI category. Stable FLIPI risk group was defined as FLIPI score being low or intermediate at diagnosis and at initiation of first treatment (Low-Low, Int-Int). Progressed FLIPI risk group was defined by the population which changed categories from low or intermediate at diagnosis to a higher category at initiation of treatment (Low-Int, Low-High, Int-High). FLIPI scores were available for 570 patients at both diagnosis and initial treatment. Overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) were evaluated by Kaplan-Meier method and compared by log-rank tests. Time of diagnosis was used as time origin for OS analyses. When OS analyses involved FLIPI score at the first treatment, time of the first treatment was used as the entry time to adjust the risk sets to account for the fact that FLIPI at first treatment is unknown before the onset of the first treatment. Chi-squared tests and Fisher's exact tests were used to compare categorical variables by FLIPI score change status. Progression free survival before and after 24 months (PFS24) of initial therapy were calculated.
Results:
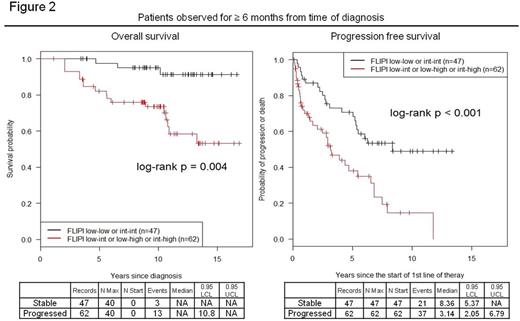
For 898 FL patients, median follow up was 9.2 years (range 0.23 - 16.84), median OS not reached. Based on FLIPI at diagnosis, the 5 year OS is 97.2% for low risk, 93.0% for int risk, and 80.2% for high risk, 10 yr OS is 90.9% for low risk, 77.7% for int risk, and 67.6% for high risk. Of 570 patients with FLIPI at diagnosis and first treatment, median time to first treatment was 0.18 years (range 0-12.5) for patients with stable FLIPI (N=280) and 2.70 years (range 0.01-13.33) for patients with progressed FLIPI (N=83). For patients observed ≥ 6 and 12 months, the median time to first treatment was 1.21 years (N=47, range 0.51-12.5) and 2.49 years (N=29, range 1.0-12.5) for patients with stable FLIPI and 3.77 years (N=62, range 0.54-13.3) and 3.92 years (N=57, range 1.13-13.3) for patients with progressed FLIPI, respectively. Progressed FLIPI was observed in 14.6% (83/570) of patients. The incidence of progressed FLIPI was 51.4% (57/111) in patients observed ≥1 year before initiating therapy. Parameters contributing to progressed FLIPI compared to stable FLIPI were decreased hemoglobin (29% versus 6%), increased nodal areas affected (43% versus 2%) and higher LDH (37% versus 5%). Patients with stable FLIPI had longer PFS at 12 and 24 months, 88.6% versus 73.8% (P=0.006) and 79.3% versus 66.1% (P= 0.031) (Figure 1). Analysis of patients initially observed ≥ 6 or 12 months demonstrated that progressed FLIPI negatively affected OS and PFS (Figure 2, observed ≥ 12 month data not shown). Median PFS for patients observed ≥ 6 months was 8.36 years for stable FLIPI, 3.14 years for progressed FLIPI. At observation of ≥ 12 months, median PFS was 6.25 and 3.22 years for stable and progressed FLIPI, respectively. Increased FLIPI was associated with increased risk of transformation throughout the disease course (25% vs 16%, P=0.039).
Conclusion:
Progressed FLIPI between diagnosis and first line treatment is associated with a reduced PFS, and increased incidence of histologic transformation. In patients who are initially observed, a progressed FLIPI reduces OS and PFS. The effect on PFS may be related to treatment bias and ongoing analysis is underway. Progressed FLIPI potentially identifies a population with heightened risk of transformation.
Hamlin:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Portola: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Molecular Templates: Research Funding; Xencor: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Horwitz:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Huya: Consultancy; Infinity: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kyowa Hakka Kirin: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; ADCT Therapeutics: Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Kumar:Celgene: Honoraria, Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Moskowitz:Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Merck: Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria, Research Funding. Moskowitz:Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Palomba:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Zelenetz:Gilead Sciences: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.