Abstract
Background:
Donor cell chimerisms are tested at frequent intervals after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHSCT). However, the predictive value of this testing in patients with myelofibrosis (MF) is not well-defined. In this study, our primary objective is to evaluate the correlation of day 30 and day 100 donor cell chimerism and overall survival (OS) in patients (pts) who undergo alloHSCT for MF.
Methods:
Charts were reviewed for pts who underwent alloHSCT for MF at Mayo Clinic in Arizona, Minnesota and Florida between January 2005 and December 2015. Patients who died within 30 days of alloHSCT were excluded. Chimerism studies were evaluated in the peripheral blood for CD3 and CD33 fractions at day +30 (D30) and day +100 (D100). Cut-off value of 100% and less than 100% was used because of limited variability below 100%. Standard statistical methods were used to compare continuous and categorical variables. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to provide survival curves.
Results:
Baseline characteristics: Sixty three consecutive patients who underwent alloHSCT for MF since January 2005 until December 2015, and had D30 and/or D100 chimerism studies available were included in the study. Of these, 24 (38%) were female. Median age at diagnosis was 56 years (range, 19 - 73 years) and median age at AHSCT was 58 years (range, 19 - 73 years). Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System-Plus (DIPSS-Plus) risk category at the time of alloHSCT was high in 31 (49%), intermediate-2 in 30 (48%) and intermediate-1 in 2 (3%) pts. JAK2 V617F mutation status was available in 61 pts and was positive in 35 (57%) pts. Nineteen (30%) pts had been treated with a JAK2 inhibitor prior to alloHSCT. Fifty-two (83%) pts had at least grade-2 fibrosis in bone marrow at the time of HCT.
Transplantation: Median time from diagnosis to AHSCT was 12.9 months (range, 2.3 - 248.2 months). Fifty-five (87%) received a reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) regimen while 8 (13%) received myeloablative conditioning regimen. Of these 55 pts, RIC regimens used were busulfan fludarabine based regimen in 15 (27%), fludarabine melphalan based regimen in 18 (33%) and fludarabine melphalan carmustine in 22 (40%) pts. Donor source was matched related in 30 (48 %), matched unrelated in 28 (44%), single-antigen mismatched related in 4 (6%) and mismatched unrelated in 1 (2%). Peripheral blood stem cells were used in all AHSCTs.
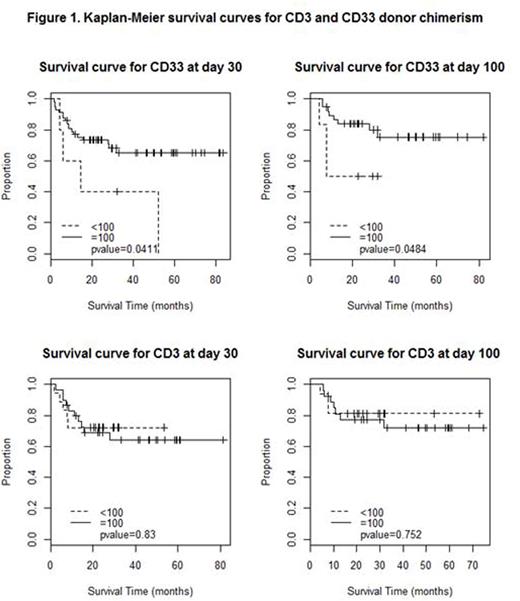
Outcomes: Median follow-up was 24.4 months (range, 1.5 - 83.6 months). Amongst pts who had <100% donor chimerism at D30 in CD33 fraction, 2 had 90%, 1 had 80% and 2 had zero% donor chimerism. At D100, 1 pt had 95%, 1 had 90%, 1 had 60%, 2 had 5% and 1 had zero% donor chimerism. Eighteen out of 57 (32%) pts who had 100% donor chimerism in CD33 fraction at D30 had died at the time of analysis compared to 4 out of 5 (80%) patients with less than 100% (p=0.03). Eight out of 38 pts (21%) who had 100% donor chimerism in CD33 fraction at D100 died versus 3 out of 6 (50%) with less than 100% (p=0.12). There was no significant survival effect of CD3 chimerism (p values=0.68, 0.59). Of the 23 deaths that had occurred at the time of analysis, cause of death was disease progression or relapse in 8 (35%), graft versus host disease in 6 (26%), transplant related (sepsis / engraftment failure) in 5 (22%) and unrelated causes in 4 (17%).
Survival analysis: As depicted in the Kaplan Meier curve (figure 1), median overall survival (OS) for pts with 100% donor chimerism in CD33 fraction at day 30 was not reached while for <100% donor chimerism was 16 months (p=0.04). Survival at 3 years for patients with 100% CD33 donor chimerism at D30 was 65% while it was 40% for pts with less than 100%. Also, survival at 3 years for patients with 100% CD33 donor chimerism at day 100 was 75% compared to 50% for patients with less than 100%.
Conclusions:
In our study, 100% donor chimerism in CD33 fraction is associated with improved survival after alloHSCT for MF compared to pts with less than 100%. Further understanding regarding the reason for this relationship is critical. Larger studies to replicate these results would be imperative to validate these findings.
Mesa:Incyte: Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy; Promedior: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; CTI Biopharma: Research Funding; Galena: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.