Abstract
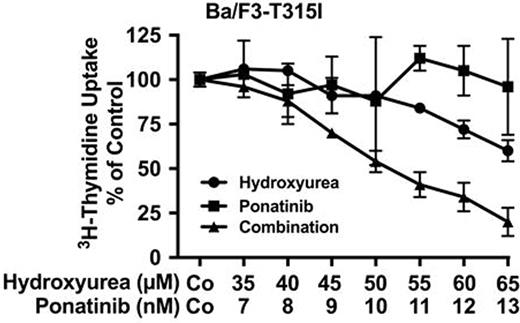
In chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the occurrence of BCR-ABL1 T315I is associated with resistance against first- and second-generation BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). Ponatinib is a third generation TKI that exerts strong anti-neoplastic effects in advanced CML and is capable of suppressing the kinase activity of BCR-ABL1 T315I. However, therapy with ponatinib is associated with potentially severe side effects. In addition, resistance against ponatinib may develop in sub-clones carrying multiple (compound) mutations in BCR-ABL1. In addition, BCR-ABL1-independent oncogenic pathways contribute to drug resistance. For these patients, alternative therapies such as stem cell transplantation (SCT) or various drug combinations are often considered.Hydroxyurea (HU) is used for initial or palliative cytoreduction in CML. However, the effects of HU on TKI-resistant mutant sub-clones have not been examined so far. The aims of this study were to explore the effects of HU on CML clones carrying BCR-ABL1 T315I as individual mutation or in compound-context, and to investigate anti-leukemic effects of the drug combination ponatinib+HU. In in vitro studies, primary patient-derived cells, human CML cell lines (K562, KU812, KCL-22), and Ba/F3 cells expressing wild type (wt) BCR-ABL1, BCR-ABL1 T315I, or BCR-ABL1 compound mutants involving T315 were examined. Cell proliferation was quantified by measuring 3H-thymidine uptake. Drug effects on competitive clonal growth were analyzed by mixing two Ba/F3 clones, one expressing BCR-ABL1 T315I with GFP and one BCR-ABL1 T315I/E255V labeled by tdTomato, at a 1:1 ratio. Then, cells were exposed to HU, pontinib, or HU+ponatinib for 72 hours, and the percentage of viable cells in each clone was analyzed by flow cytometry. The in vivo response of primary CML cells carrying BCR-ABL1 T315I to HU was examined in 4 TKI-resistant CML patients who were treated with HU (1-3 g/day) for up to 18 months. In these patients, we measured white blood counts (WBC), differential counts, and BCR-ABL1 transcript levels in peripheral blood (PB) by qPCR. The percentage of BCR-ABL1 T315I compared to total BCR-ABL1 was determined by ligation-dependent PCR. In all 4 patients treated with HU, WBC and total BCR-ABL1 mRNA levels remained stable for 3-12 months. Surprisingly, in 3 of 4 patients, the leukemic sub-clone expressing BCR-ABL1 T315Iwas no longer detectable after HU-treatment. After 3 months, 2/4 patients received allogenic SCT. In the other 2 patients, the disease remained stable for 6 and 12 months, respectively. In our in vitro studies, HU was found to inhibit the growth of all BCR-ABL1+ cell lines, including K562 (IC50: 1120±89 µM), KU812 (IC50: 216±32 µM), and KCL-22 (IC50: 196±23 µM) as well as Ba/F3 cells harboring BCR-ABL1 T315I as single mutation (IC50: 74±25 µM) or as compound together with E255V (IC50: 86±2 µM), F311L (IC50: 76±20 µM), F359V (IC50: 69±10 µM), or G250E (IC50: 89±4 µM). Interestingly, Ba/F3 cells exhibiting BCR-ABL1 T315I alone or in compound configuration were more sensitive to HU compared to Ba/F3 cells expressing wt BCR-ABL1 (IC50: 236±49 µM). As expected, HU was also found to inhibit growth of primary CML cells. In subsequent experiments, HU and ponatinib were found to synergize with each other in inhibiting growth of K562, KU812, and KCL-22 cells as well as Ba/F3 cells carrying BCR-ABL1 T315I (Figure) or BCR-ABL1-T315I/F359V. In cell mix experiments, ponatinib exerted strong growth-inhibitory effects on Ba/F3-T315I cells but not on Ba/F3-T315I/E255V cells, whereas HU was found to produce stronger effects on Ba/F3-T315I/E255V cells, and only the combination of both drugs resulted in complete suppression of both cell lines. In conclusion, HU exerts strong sub-clone-specific anti-neoplastic effects in TKI-resistant CML cells, both in patients with BCR-ABL1 T315I+CML and in various cell line models, including sub-clones harboring BCR-ABL1 T315I as single mutation or in compound configuration. In addition, we show that HU and ponatinib produce strong synergistic anti-neoplastic effects on TKI resistant CML cells, including sub-clones carrying T315I. These observations may have clinical implications and may pave the way for more effective sub-clone-eradicating but also palliative or bridging-to-SCT concepts in advanced CML. Clinical studies are now warranted to define the exact value of the drug combination ponatinib+HU in TKI-resistant CML.
Sperr:Novartis: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Lion:Ariad: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding. Hoermann:Ariad: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Gilead: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria. Deininger:CTI BioPharma Corp.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Valent:Amgen: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Deciphera Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.