Abstract

The TIDEL-II trial used imatinib (IM) upfront in patients (pts) newly diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase (CML-CP), and switched selected pts to nilotinib (NIL) on the basis of IM intolerance or failure to achieve time-dependent molecular response. We previously reported major molecular response (MMR; BCR-ABL ≤0.1% IS) at 12 months (mths) and transformation-free survival (TFS) at 3 years. This abstract reports the final analysis with minimum follow-up of 60 months.
Patients were enrolled across 27 Australasian sites in 2 equal and sequential cohorts. All started treatment with IM 600mg OD and dose escalated to IM 800mg OD if IM trough levels were <1000ng/mL on day 22. A series of time-dependent molecular targets were set: BCR-ABL (IS) ≤10% at 3 mths (early molecular response: EMR), ≤1% at 6 mths and ≤0.1% at 12 mths. In cohort 1 (C1), pts failing to meet these targets dose escalated to IM 800 mg OD. Pts who failed to improve molecular response after another 3 mths, or were already on IM 800mg OD, switched to NIL 400mg BID. In cohort 2 (C2), pts who failed these targets switched to NIL directly. In addition, pts with grade III/IV or persistent grade II toxicity were also allowed to switch from IM to NIL. Data analysed were limited to 60 mths of follow-up.
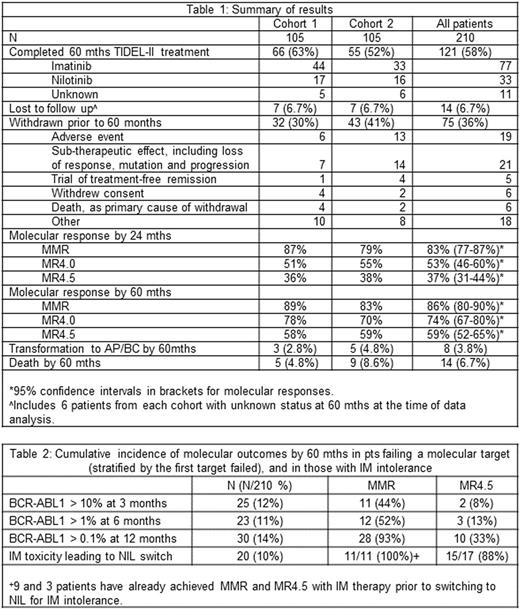
The study enrolled 210 pts with a median age of 49.7 years (range 16-81); 42% were female. Baseline demographics and outcomes were similar across 2 cohorts. Forty pts had day 22 IM trough <1000ng/mL, and 31 had dose escalation. Switching to NIL occurred in 75 pts prior to 24 mths, 55 for failing TIDEL-II targets and 20 for IM intolerance. Table 1 summarises key results. In combination, 5 year overall survival (OS) and TFS and associated 95% confidence intervals, including withdrawn pts, were 95% (88-98%) and 92% (84-95%) respectively. Cumulative incidence by 60 mths of MMR was 86%, MR4 (BCR-ABL1 ≤ 0.01% IS) was 75% and MR4.5 (BCR-ABL1 ≤0.0032%) was 59%. Of the 181 pts achieving MMR on study, 44 (24%) did so after switching to NIL; of the 119 pts achieving MR4.5, 27 (23%) did so after switching to NIL.
At 60 mths, 75 (36%) pts had withdrawn from study, and 14 were lost to follow up (including 12 with outstanding data queries). Of the 121 pts (58%) who remained on TIDEL-II until 60 mths, 33 were on NIL (30 in MMR), 77 on IM (76 in MMR); treatment was unknown for 11 (10 in MMR). The median dose of IM was 600mg OD. Of the 51 pts who dose escalated to IM 800mg OD (31 for low IM trough level and 20 for failing to achieve molecular targets), only 9 remained on this dose until mth 60 (5 and 4 pts form the respective groups). Eight pts transformed to accelerated or blastic phase; 5 within the 1st year, 2 in the 3rd and 1 in the 5th year; 2/8 occurred after study withdrawal. There were 14 deaths, mostly due to cardiac events (n=5) or progressive leukaemia (n=6). In all, 13/210 pts (6%) had cardiac, cerebral or peripheral vascular disease, 9 while on NIL and 4 having only had IM.
Pts failing to meet molecular targets (analysed according to the 1st target failed) at 3, 6 and 12 mths numbered 25 (12%), 23 (11%) and 30 (14%) respectively with 19, 16 and 20 switching to NIL (subsequent molecular outcomes, Table 2). Pts failing to achieve EMR had poor achievement of MMR and MR4.5 (44% and 8% respectively by 60 mths). Of the 11 EMR failure pts who achieved MMR, only 4 remained in MMR at 60 mths. Pts failing to achieve BCR-ABL≤ 1% at 6 mths had similarly poor outcomes, with MMR and MR4.5 being 52% and 13% respectively. In pts failing to achieve MMR by 12 months, MMR and MR4.5 by 60 mths were 93% and 33% respectively. Twenty pts switched to NIL for IM intolerance prior to 24 mths: 9/20 already in MMR, and 3/20 already in MR4.5 at time of switching. For the remaining pts, MMR and MR4.5 were achieved by 100% and 88% after switching.
The TIDEL-II strategy of combining IM and NIL compares favourably with other upfront treatment strategies, with MR4.5 of 59% by 60 mths. IM dose escalation to 800mg OD for target failure was not well tolerated: only 18% of pts who dose escalated maintained this dose at 60 mths. However, this did not appear to be detrimental to overall outcomes, which were similar in the 2 cohorts. Pts switching to NIL for IM intolerance, and for failing to achieve MMR by 12 months after meeting prior goals, had high rates of MMR, superior to those who failed their 3 and 6 mth targets. Early identification of pts at high risk of EMR failure who might benefit from more intensive or experimental therapies may be necessary to further improve outcomes.
Yeung:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Ariad: Research Funding. White:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Branford:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Qiagen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Otsuka: Research Funding; Ariad: Research Funding; Bristol Myers-Squibb: Honoraria; Cepheid: Consultancy. Butcher:Janssen: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Gottlieb:Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding; Indee: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Arthur:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ross:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria. Tam:Novartis: Honoraria. Mills:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Meeting attendance sponsorship. Hughes:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Australasian Leukaemia and Lymphoma Group (ALLG): Other: Chair of the CML/MPN Disease Group; Ariad: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract