Abstract
Background: Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is considered standard of care for patients with multiple myeloma (MM). The majority of patients with MM are diagnosed over the age of 65 and 37% are over the age of 75 (Van de Donk and Sonneveld, 2014). As treatment outcomes and survival improve across age groups for patients with MM (Libby, et al. 2013), more elderly patients are potential candidates for ASCT. Elderly patients have been defined as greater than age 65 in many studies of ASCT, but as referral age for transplantation continues to increase, the ASCT outcomes of patients 75 years and older need to be elucidated.
Methods: Between January 2005 and December 2015, 24 patients age 75 or older received ASCT for MM. High-risk disease (HRD) was defined as t(14;16), t(14;20), del 17p, t(4;14) or 1q gain by FISH, del 13q, monosomy 13 or hypodiploidy by standard cytogenetics, or high risk signature gene expression profiling. Patients were mobilized for peripheral blood stem cell collection with either a cyclophosphamide-based mobilization chemotherapy regimen with GSCF (Cy-G), plerixafor and GCSF (Pler-G), or with GCSF alone. Conditioning regimens were melphalan based, with patients receiving either 140 mg/m2 (Mel 140) or 200 mg/m2 (Mel 200). Response criteria was based on the International Working Group Diagnostic Criteria for MM. Outcomes reported included disease response, progression free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and cause of death.
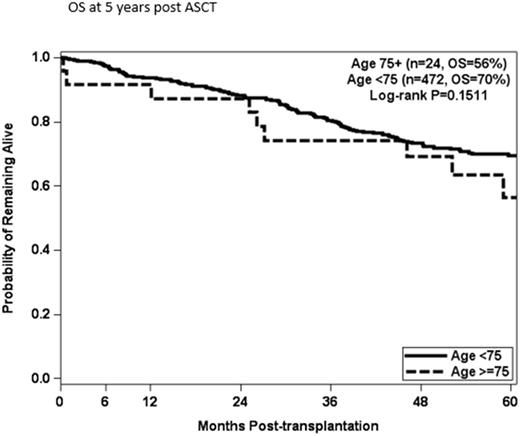
Results: The ages ranged from 75 to 84 years and 71% were male. HRD at diagnosis was reported for 8 patients (33%). Twenty patients (83%) were in a partial response (PR) or better at time of transplantation, with 1 patient in a complete response (CR), 10 patients (42%) in a very good partial response (VGPR), and 9 patients (37%) in a PR. No patient had progressive disease at the time of ASCT and 4 patients (17%) had stable disease (SD). Twelve patients (50%) received Cy-G for stem cell mobilization, 11 (49%) received Pler-G, and 1 patient received GCSF alone. Five patients received Mel 140 and 19 patients received Mel 200, 21% and 79% respectively. Best response post ASCT was CR in 10 patients (42%), VGPR in 5 patients (21%), PR in 4 patients (17%) and 2 patients (8%) had SD. There were 2 early deaths prior to day 100 post ASCT. One patient died of a subdural hematoma at day +11 and the other patient died of a staphylococcus aureus sepsis at day +25. PFS was 40% at 5 years and OS was 56% at 5 years. There was no difference in OS (p=0.1511) for patients age 75 and older at the time of transplantation compared to patients younger than age 75 (n=472).
Conclusions: ASCT for very elderly patients 75 years or older is feasible and can result in long-term survival. Elderly patients can tolerate chemotherapy for mobilization and doses of melphalan 200 mg/m2 for conditioning. Elderly patients with MM should not be denied ASCT based on age alone.
McKiernan: Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Siegel: Celgene, Takeda, Amgen Inc, Novartis and BMS: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Merck: Consultancy. Vesole: Takeda: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Skarbnik: Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Other: Ad board, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Speakers Bureau. Biran: Celgene, Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau. Richter: BMS: Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Pecora: Caladrius Biosciences: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; COTA: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties. Goy: Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics / J&J: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.