Abstract
Introduction:
After an allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT), analysis of donor chimerism (DC) is routinely used to monitor engraftment. In patients with myeloid malignancies, loss of a complete donor chimerism (CC) may indicate graft failure, but more often imminent leukemic relapse. Especially in patients without a valid marker for minimal residual disease (MRD), chimerism analysis may prompt reduction of immunosuppression or therapeutic interventions such as donor lymphocyte infusions (DLI) or hypomethylating agents (HMA). We retrospectively analyzed DC data and outcomes of 255 consecutive patients (pts) transplanted for an acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) at our center. Aims of our study were to evaluate the impact of (i) a falling DC, (ii) the first chimerism-guided intervention, and (iii) the application of DLI on survival and incidence of acute and chronic (a/c) GvHD.
Patients and Methods:
255 pts that received a first SCT between 2005 and 2016 were monitored regularly (approx. every two weeks from day +14 to +100, then monthly) for DC using a validated, CE-labeled multiplex-STR PCR at a single laboratory (AgenDix GmbH, Dresden, Germany). CC was defined as ≥99% and mixed chimerism (MC) as <99% donor cells. Overall survival (OS), GVHD-free, relapse-free survival (GFRS) and the cumulative incidence (CI) of GVHD was analyzed for the whole cohort, OS and CI GVHD were analyzed for pts with MC and pts that received DLI with a prophylactic/preemptive (pDLI) vs. therapeutic (tDLI) indication.
245 pts (median age 53 years (range 19-73), 136 male) with AML (n=222) or MDS (n=23) achieved a CC within 60 days post SCT and were eligible for our analysis, 10 pts were excluded due to refractory disease (n=9) or early death (n=1). 101 out of 222 AML pts (45%) had intermediate (int)-2 or adverse cytogenetics according to ELN guidelines, and 10 out of 23 MDS pts (43%) had IPSS int-2 or high risk. 121 pts (49%) were transplanted in first complete remission (CR), 107 (44%) with active disease. For SCT, 96 pts (39%) had received myeloablative (MAC) and 149 (61%) reduced intensity conditioning regimens (RIC). Donors were HLA-matched siblings (MRD, n= 60) or unrelated donors (MUD, n=149), mismatched related (MMRD, n= 1) or unrelated donors (MMUD, n=27), or haploidentical family members (n=8).
Results:
A MC was detected in 95 pts (39%) at a median of 104 (range, 28-1764) days post SCT, of whom 18 pts (32%) had aGVHD G2-4. Pts with MC had received RIC significantly more often compared to pts with continued CC (69% vs 55%, p=0.046), the two groups did not differ regarding high risk cytogenetics/IPSS and remission status at SCT.
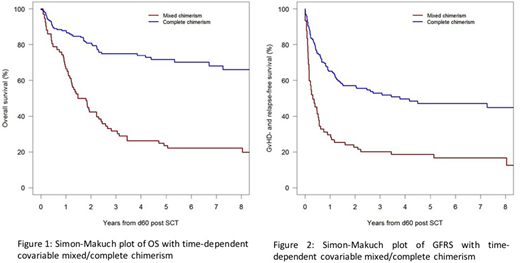
MC prompted reduction of immunosuppressive therapy (IST, n=35), DLI (n=7), HMA (n=16), DLI+HMA (n=7), chemotherapy and/or 2ndSCT (n=7), small molecules (n=10) or best supportive care (BSC, n=13) as deemed appropriate by the treating physician. Median OS and GFRS were significantly better for pts with CC (OS not reached; GFRS 46 months (mths)) compared to pts with MC (OS 15.7 mths; Hazard ratio (HR) 0.25, 95%-CI 0.17-0.37, p<0.001, GFRS 3.7 mths; HR 0.39, 95%-CI 0.26-0.58, p<0.001, figures 1,2). 3-year survival was 75% for the CC group vs 31.7% for the MC group. For the 95 pts with MC, median OS was 27.4 and 35.8 mths following IST reduction or DLI+HMA, respectively, and 12, 8.8, 5.1 and 1.2 mths for pts treated with chemo/2ndHSCT, HMA, small molecules or BSC. Treatment of MC induced aGVHD G2-4 in only 2 additional pts (G3-4: n=1). CI of cGVHD requiring systemic IST was 27% at 1-year for all pts with MC compared to 13.9% for pts in the CC group.
In the whole cohort, 46 pts (19%) received a median of 2 DLIs (median dose 0.5x106CD3+cells/kg). PDLIs were administered to 33 pts (72%) and tDLIs to 13 pts with relapsed disease (28%). The pDLI group had a 3-year survival of 82.9% and did not reach median OS, compared to 24.6% 3-year survival and 22 mths median OS in the tDLI group. Median GRFS was 91.4 vs 6.6 mths for the pDLI and tDLI group, respectively. No pt developed aGVHD G2-4 after DLI administration, 1 pt (8%) in the tDLI and 4 pts (12%) in the pDLI group developed cGVHD requiring systemic IST.
Conclusion
Occurrence of MC seems predictive of an inferior outcome, but early intervention such as careful reduction of IST if feasible or administration of DLI with or without HMA may effectively prolong OS and GRFS. Administration of pDLI after discontinuation of IST starting with low doses is safe and results in low rates of cGvHD.
Lang:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Research Funding. Toenges:Bayer: Research Funding. Schetelig:Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Serve:Bayer: Research Funding. Thiede:AgenDix: Other: Ownership; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding. Bug:Astellas Pharma: Other: Travel Grant; Novartis Pharma: Honoraria, Research Funding; Neovii: Other: Travel Grant; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Travel Grant; Janssen: Other: Travel Grant; Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.